
Imaging Microscope Objectives

- Infinity-Corrected Microscope Objectives for UV, Visible, and NIR
- Designed for Use with Air Between Objective and Sample or Cover Glass
- Magnifications Ranging from 1X to 100X
- Super Apochromat, Plan Achromat, Plan Apochromat VIS+, Plan Apochromat, and Plan Fluorite Designs
RMS4X
4X Plan Achromat
for Visible Wavelengths
TL1X-SAP
1X Super Apochromat
for 420 to 700 nm
N60X-PF
60X Plan Fluorite
for UV to NIR Wavelengths
MY10X-803
10X Plan Apochromat
for 480 to 1800 nm
LMUL-50X-UVB
50X Plan Achromat
for 240 to 360 nm
OVERVIEW
| Objective Lens Selection Guide |
|---|
| Objectives |
| Thorlabs Microscopy Objectives for Life Sciences Imaging Microscopy Objectives Microscopy Objectives, Oil Immersion Physiology Objectives, Water Dipping or Immersion Phase Contrast Objectives Long Working Distance Objectives Reflective Microscopy Objectives UV Focusing Objectives VIS and NIR Focusing Objectives |
| Scan Lenses and Tube Lenses |
| Scan Lenses F-Theta Scan Lenses Infinity-Corrected Tube Lenses |

Did You Know?
Multiple optical elements, including the microscope objective, tube lens, and eyepieces, together define the magnification of a system. See the Magnification & FOV tab to learn more.

Click for Details
Figure 1.1 Example of a Dry Objective Design
(See Objective Tutorial Tab for More Information About Microscope Objective Types)
Thorlabs offers imaging objectives made in house, as well as objectives from Olympus, Nikon, and Mitutoyo. Super apochromat, plan achromat, plan apochromat VIS+, plan apochromat, and plan fluorite (also called plan semi-apochromat or plan fluor) designs are available. For details about the differences between these types of objectives, please see the Objective Tutorial tab.
When choosing a microscope objective, it is important to keep in mind that objectives are often designed to integrate with a particular manufacturer's microscopes. Before interchanging objectives, be sure to check the design tube lens focal length and the threading type of the objectives. A full list of specifications for each objective can be found in the Specs tab. Please note that the performance of each objective may vary from the engraved specifications when integrated with components and systems from different manufacturers. See the Magnification and FOV tab for more information.
Our selection of imaging objectives can be used in applications from microscopy to fiber coupling and includes options optimized for use at wavelengths from the UV to the NIR. For information on recommended applications for specific objectives, see below.
Objectives featured on this page with RMS, M25 x 0.75, or M32 x 0.75 threading are compatible with our microscope nosepiece modules for DIY Cerna® Systems. Our W26 x 0.706-threaded objectives are also compatible with the nosepiece modules when used with our RMSW26S, M25W26S, and M32W26S microscope objective thread adapters. Parfocal lengths can be matched by using parfocal length extenders with compatible internal threads. The Olympus microscope objectives can be mounted directly to our fiber launch systems, or mounted into our 30 mm cage system using the CP42(/M) RMS-threaded cage plate, which is also post mountable. They can also be mounted to any of our multi-axis platforms or translation stages using an HCS013 RMS mount. Please note that the multi-axis platforms and translation stages need a 3 mm wide central keyway for the HCS013 RMS mount.
To use these objectives with a different thread standard, please see our microscope objective thread adapters.
| Quick Links | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Design Tube Lens Focal Length | Available Objective Classes |
||
| Thorlabs | 200 mm | Apochromatic | Achromatic, Microspot®UV Focusing | Plan Apochromatic VIS+ |
| Olympus | 180 mm | Plan Achromat | Plan Fluorite | |
| Nikon | 200 mm | Plan Fluorite | ||
| Mitutoyo | 200 mm | Plan Apochromat | ||
SPECS
| 1X - 7.5X Objective Specifications | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnificationa | 1Xb | 2X | 4X | 5X | 7.5X | ||||
| Manufacturer | Thorlabs | Olympus | Nikon | Mitutoyo | |||||
| Item # | TL1X-SAP | TL2X-SAP | TL4X-SAP | RMS4X | RMS4X-PF | N4X-PF | MY5X-802B | MY5X-822 | MY7X-807 |
| Objective Class | Super Apochromatc | Plan Achromat | Plan Fluorite | Plan Apochromat | |||||
| Numerical Aperture (NA) | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.21 | |
| Entrance Pupil Diameterd | 12 mm | 20 mm | 20 mm | 9.0 mm | 11.7 mm | 13 mm | 11.2 mm | ||
| Effective Focal Length (EFL) | 200 mm | 100 mm | 50 mm | 45 mm | 50 mm | 40 mm | 26.7 mm | ||
| Working Distance | 8.0 mm | 56.3 mm | 17.0 mm | 18.5 mm | 17 mm | 17.2 mm | 36.5 mm | 37.5 mm | 35.0 mm |
| Resolutione | 11.2 μm | 3.4 μm | 1.7 μm | 3.4 μm | 2.6 μm | 2.6 μm | 2.4 µm | 2.4 μm | 1.6 μm |
| Parfocal Length | 95.0 mm | 60.0 mm | 45.06 mm | 60 mm | 95 mm | ||||
| Design Tube Lens Focal Length | 200 mm | 180 mm | 200 mm | ||||||
| Coverglass Thickness | 0 - 5.0 mm | 0 - 0.17 mm | 0 mm | ||||||
| Diameter | 32.6 mm (Without Wave Plate) |
30.5 mm | 24.0 mm | 30.0 mm | 34.0 mm | ||||
| 34.5 mm (With Wave Plate) |
|||||||||
| Length | 85.5 mm (Without Wave Plate) |
43.5 mm | 46.4 mm | 30.9 mm | 32.4 mm | 46.6 mm | 63.5 mm | 62.5 mm | 65.0 mm |
| 90.6 mm (With Wave Plate) |
|||||||||
| Threading | M25 x 0.75 | RMS | M25 x 0.75 | W26 x 0.706 | |||||
| Threading Depth | 3.8 mm | 3.2 mm | 3.6 mm | 4.5 mm | 3.6 mm | 5.0 mm | |||
| Wavelength Range | 420 - 700 nm | 350 - 700 nm | Visible | Visible to NIR | UV to NIR | 436 - 656 nm | 480 - 1800 nm | 436 - 656 nm | |
| Antireflection Coating | Ravg < 0.5% (420 - 700 nm) |
Ravg < 0.5% (350 - 700 nm) |
Not Available | ||||||
| Field of View | Ø22 mm | Ø11 mm | Ø5.5 mm | Ø6.625 mm | Ø6.25 mm | Ø4.8 mm | Ø3.2 mm | ||
| Optical Field Number | 22 | 26.5 | 25 | 24 | |||||
| Coverslip Correction Collar | No | ||||||||
| 10X - 15X Objective Specifications | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnificationa | 10X | 15X | ||||||
| Manufacturer | Olympus | Nikon | Mitutoyo | Thorlabs | ||||
| Item # | RMS10X | RMS10X-PF | N10X-PF | MY10X-823 | MY10X-803 | LMUL-10X-UVB | TL10X-2P | TL15X-2P |
| Objective Class | Plan Achromat | Plan Fluorite | Plan Apochromat | Achromat | Super Apochromatb | Plan Apochromat VIS+b | ||
| Numerical Aperture (NA) | 0.25 | 0.3 | 0.26 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.70 | |
| Entrance Pupil Diameterc | 9.0 mm | 10.8 mm | 12 mm | 10.4 mm | 11.2 mm | 10.0 mm | 20.0 mm | 18.6 |
| Effective Focal Length (EFL) | 18 mm | 20 mm | 20 mm | 13.3 mm | ||||
| Working Distance | 10.6 mm | 10 mm | 16 mm | 31 mm | 34 mm | 20.0 mm | 7.77 mm | 2.6 mmd |
| Resolutione | 1.3 μm | 1.1 μm | 1.3 μm | 1.2 μm | 0.9 μm | 0.7 μm | 0.5 μm | |
| Parfocal Length | 45.06 mm | 60 mm | 95 mm | 95.0 mm | 75.0 mm | |||
| Design Tube Lens Focal Length | 180 mm | 200 mm | ||||||
| Cover Glass Thickness | 0 - 0.17 mm | 0.17 | 0 mm | 0 mm | 0 - 2.6 mm | 0 - 2.8 mm | ||
| Diameter | 24.0 mm | 30.0 mm | 34.0 mm | 34.0 mm | 40.6 mm | 38.1 mm | ||
| Length | 38.8 mm | 39.4 mm | 48.7 mm | 68.5 mm | 66.0 mm | 80.0 mm | 90.4 mm | 76.9 mm |
| Threading | RMS | M25 x 0.75 | W26 x 0.706 | W26 x 0.706 | M32 x 0.75 | |||
| Threading Depth | 4.5 mm | 5.0 mm | 5.0 mm | 3.2 mm | 4.5 mm | |||
| Wavelength Range | Visible | Visible to NIR | UV to NIR | 480 - 1800 nm | 436 - 656 nm | 240 - 360 nm | 400 - 1300 nm | |
| Antireflection Coating | Not Available | <1.5% per Surface (240 - 360 nm) |
Rabs < 3% (400 - 450 nm) Rabs < 2%(450 - 1300 nm) @ 0° - 25° AOI |
|||||
| Field of View | Ø2.2 mm | Ø2.65 mm | Ø2.5 mm | Ø2.4 mm | Ø2.2 mm | Ø1.5 mm | ||
| Optical Field Number | 22 | 26.5 | 25 | 24 | 22 | |||
| Coverslip Correction Collar | No | Yes | ||||||
| 20X - 28X Objective Specifications | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnificationa | 20X | 28X | |||||
| Manufacturer | Thorlabs | Olympus | Nikon | Mitutoyo | Thorlabs | ||
| Item # | LMUL-20X-UVB | RMS20X | RMS20X-PF | N20X-PF | MY20X-804 | MY20X-824 | TL28X-MP |
| Objective Class | Achromat | Plan Achromat | Plan Fluorite | Plan Apochromat | |||
| Numerical Aperture (NA) | 0.36 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.42 | 0.40 | 1.10 | |
| Entrance Pupil Diameterb | 7.2 mm | 9.0 mm | 10 mm | 8.4 mm | 8.0 mm | 15.6 mm | |
| Effective Focal Length (EFL) | 10 mm | 9 mm | 10 mm | 7.1 mm | |||
| Working Distance | 15.3 mm | 1.2 mm | 2.1 mm | 20.0 mm | 2.8 mmc | ||
| Resolutiond | 0.6 μm | 0.8 μm | 0.7 μm | 0.8 μm | 0.3 µm | ||
| Parfocal Length | 95.0 mm | 45.06 mm | 60 mm | 95 mm | 95.0 mm | ||
| Design Tube Lens Focal Length | 200 mm | 180 mm | 200 mm | ||||
| Cover Glass Thickness | 0 mm | 0.17 mm | 0 mm | 0 - 0.23 mm | |||
| Diameter | 34.0 mm | 24.0 mm | 26.0 mm | 28.0 mm | 34.0 mm | 43.6 mm | |
| Length | 84.7 mm | 48.5 mm | 47.3 mm | 63.5 mm | 80.0 mm | 97.6 mm | |
| Threading | W26 x 0.706 | RMS | M25 x 0.75 | W26 x 0.706 | M32 x 0.75 | ||
| Threading Depth | 5.0 mm | 4.8 mm | 4.5 mm | 5.0 mm | 5.4 mm | ||
| Wavelength Range | 240 - 360 nm | Visible | Visible to NIR | UV to NIR | 436 - 656 nm | 480 - 1800 nm | 400 - 1650 nme |
| Antireflection Coating | <1.5% per Surface (240 - 360 nm) |
Not Available | |||||
| Field of View | Ø1.2 mm | Ø1.1 mm | Ø1.325 mm | Proprietary | Ø1.2 mm | Ø0.79 mm | |
| Optical Field Number | 24 | 22 | 26.5 | Proprietary | 24 | 22 | |
| Coverslip Correction Collar | No | Yes | |||||
| 40X - 50X Objective Specifications | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnificationa | 40X | 50X | |||||
| Manufacturer | Olympus | Nikon | Thorlabs | Mitutoyo | |||
| Item # | RMS40X | RMS40X-PF | N40X-PF | LMUL-50X-UVB | HPA50XAB | MY50X-805 | MY50X-825 |
| Objective Class | Plan Achromat | Plan Fluorite | Achromat | Plan Apochromat VIS+b | Plan Apochromat | ||
| Numerical Aperture (NA) | 0.65 | 0.75 | 0.42 | 0.75 | 0.55 | 0.42 | |
| Entrance Pupil Diameterc | 5.8 mm | 6.8 mm | 7.5 mm | 3.4 mm | 6.0 mm | 4.4 mm | 3.4 mm |
| Effective Focal Length (EFL) | 4.5 mm | 5.0 mm | 4 mm | 4.0 mm | |||
| Working Distance | 0.6 mm | 0.51 mm | 0.66 mm | 12.0 mm | 5.0 mm | 13.0 mm | 17.0 mm |
| Resolutiond | 0.5 μm | 0.4 μm | 0.5 μm | 0.4 μm | 0.6 μm | 0.8 μm | |
| Parfocal Length | 45.06 mm | 60 mm | 95.0 mm | 95 mm | |||
| Design Tube Lens Focal Length | 180 mm | 200 mm | |||||
| Cover Glass Thickness | 0.17 mm | 0 mm | |||||
| Diameter | 24.0 mm | 26.0 mm | 30.0 mm | 34.0 mm | |||
| Length | 48.8 mm | 48.9 mm | 59.1 mm | 88.0 mm | 95.0 mm | 87.0 mm | 82.4 mm |
| Threading | RMS | M25 x 0.75 | W26 x 0.706 | ||||
| Threading Depth | 4.5 mm | 5.1 mm | 5.0 mm | ||||
| Wavelength Range | Visible | Visible to NIR | UV to NIR | 240 - 360 nm | 400 - 1100 nme | 436 - 656 nm | 480 - 1800 nm |
| Antireflection Coating | Not Available | <1.5% per Surface (240 - 360 nm) |
Ravg<1.0% (400 - 1100 nm) |
Not Available | |||
| Field of View | Ø0.55 mm | Ø0.663 mm | Ø0.625 mm | Ø0.48 mm | |||
| Optical Field Number | 22 | 26.5 | 25 | 24 | |||
| Coverslip Correction Collar | No | ||||||
| 60X - 100X Objective Specifications | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnificationa | 60X | 100X | |
| Manufacturer | Olympus | Nikon | Mitutoyo |
| Item # | RMS60X-PFC | N60X-PF | MY100X-806 |
| Objective Class | Plan Fluorite | Plan Apochromat | |
| Numerical Aperture (NA) | 0.9 | 0.85 | 0.70 |
| Entrance Pupil Diameterb | 5.4 mm | 5.7 mm | 2.8 mm |
| Effective Focal Length (EFL) | 3.0 mm | 3.3 mm | 2.0 mm |
| Working Distance | 0.2 mm | 0.31 - 0.4 mm | 6.0 mm |
| Resolutionc | 0.4 μm | 0.5 μm | |
| Parfocal Length | 45.06 mm | 60 mm | 95 mm |
| Design Tube Lens Focal Length | 180 mm | 200 mm | 200 mm |
| Cover Glass Thickness | 0.11 - 0.23 mm | 0 mm | |
| Diameter | 31.0 mm | 31.4 mm | 34.0 mm |
| Length | 49.4 mm | 65.0 mm | 94.0 mm |
| Threading | RMS | M25 x 0.75 | W26 x 0.706 |
| Threading Depth | 4.7 mm | 5.0 mm | |
| Wavelength Range | Visible to NIR | UV to NIR | 436 - 656 nm |
| Antireflection Coating | Not Available | ||
| Field of View | Ø0.44 mm | Ø0.42 mm | Ø0.24 mm |
| Optical Field Number | 26.5 | 25 | 24 |
| Coverslip Correction Collar | Yes | No | |
OBJECTIVE TUTORIAL
| Table 89A Chromatic Aberration Correction per ISO Standard 19012-2 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Objective Class | Common Abbreviations | Axial Focal Shift Tolerancesa |
| Achromat | ACH, ACHRO, ACHROMAT | |δC' - δF'| ≤ 2 x δob |
| Semiapochromat (or Fluorite) |
SEMIAPO, FL, FLU | |δC' - δF'| ≤ 2 x δob |δF' - δe| ≤ 2.5 x δob |δC' - δe| ≤ 2.5 x δob |
| Apochromat | APO | |δC' - δF'| ≤ 2 x δob |δF' - δe| ≤ δob |δC' - δe| ≤ δob |
| Super Apochromat | SAPO | See Footnote b |
| Improved Visible Apochromat | VIS+ | See Footnotes b and c |
Parts of a Microscope Objective
Click on each label for more details.
Figure 89C This microscope objective serves only as an example. The features noted above with an asterisk may not be present on all objectives; they may be added, relocated, or removed from objectives based on the part's needs and intended application space.
Objective Tutorial
This tutorial describes features and markings of objectives and what they tell users about an objective's performance.
Objective Class and Aberration Correction
Objectives are commonly divided by their class. An objective's class creates a shorthand for users to know how the objective is corrected for imaging aberrations. There are two types of aberration corrections that are specified by objective class: field curvature and chromatic aberration.
Field curvature (or Petzval curvature) describes the case where an objective's plane of focus is a curved spherical surface. This aberration makes widefield imaging or laser scanning difficult, as the corners of an image will fall out of focus when focusing on the center. If an objective's class begins with "Plan", it will be corrected to have a flat plane of focus.
Images can also exhibit chromatic aberrations, where colors originating from one point are not focused to a single point. To strike a balance between an objective's performance and the complexity of its design, some objectives are corrected for these aberrations at a finite number of target wavelengths.
Five objective classes are shown in Table 89A; only three common objective classes are defined under the International Organization for Standards ISO 19012-2: Microscopes -- Designation of Microscope Objectives -- Chromatic Correction. Due to the need for better performance, we have added two additional classes that are not defined in the ISO classes.
Immersion Methods
Click on each image for more details.
Figure 89B Objectives can be divided by what medium they are designed to image through. Dry objectives are used in air; whereas dipping and immersion objectives are designed to operate with a fluid between the objective and the front element of the sample.
| Glossary of Terms | |
|---|---|
| Back Focal Length and Infinity Correction | The back focal length defines the location of the intermediate image plane. Most modern objectives will have this plane at infinity, known as infinity correction, and will signify this with an infinity symbol (∞). Infinity-corrected objectives are designed to be used with a tube lens between the objective and eyepiece. Along with increasing intercompatibility between microscope systems, having this infinity-corrected space between the objective and tube lens allows for additional modules (like beamsplitters, filters, or parfocal length extenders) to be placed in the beam path. Note that older objectives and some specialty objectives may have been designed with finite back focal lengths. In their inception, finite back focal length objectives were meant to interface directly with the objective's eyepiece. |
| Entrance Pupil Diameter (EP) | The entrance pupil diameter (EP), sometimes referred to as the entrance aperture diameter, corresponds to the appropriate beam diameter one should use to allow the objective to function properly. EP = 2 × NA × Effective Focal Length |
| Field Number (FN) and Field of View (FOV) |
The field number corresponds to the diameter of the field of view in object space (in millimeters) multiplied by the objective's magnification. Field Number = Field of View Diameter × Magnification |
| Magnification (M) | The magnification (M) of an objective is the lens tube focal length (L) divided by the objective's effective focal length (F). Effective focal length is sometimes abbreviated EFL: M = L / EFL . The total magnification of the system is the magnification of the objective multiplied by the magnification of the eyepiece or camera tube. The specified magnification on the microscope objective housing is accurate as long as the objective is used with a compatible tube lens focal length. Objectives will have a colored ring around their body to signify their magnification. This is fairly consistent across manufacturers; see the Parts of a Microscope Objective section for more details. |
| Numerical Aperture (NA) | Numerical aperture, a measure of the acceptance angle of an objective, is a dimensionless quantity. It is commonly expressed as: NA = ni × sinθa where θa is the maximum 1/2 acceptance angle of the objective, and ni is the index of refraction of the immersion medium. This medium is typically air, but may also be water, oil, or other substances. |
| Working Distance (WD) |
The working distance, often abbreviated WD, is the distance between the front element of the objective and the top of the specimen (in the case of objectives that are intended to be used without a cover glass) or top of the cover glass, depending on the design of the objective. The cover glass thickness specification engraved on the objective designates whether a cover glass should be used. |
MAGNIFICATION & FOV
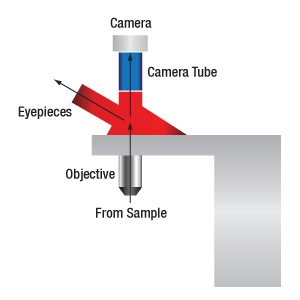
Figure 73A When viewing an image with a camera, the system magnification is the product of the objective and camera tube magnifications. When viewing an image with trinoculars, the system magnification is the product of the objective and eyepiece magnifications.
| Table 73B Focal Lengths by Manufacturer | |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Tube Lens Focal Length |
| Leica | f = 200 mm |
| Mitutoyo | f = 200 mm |
| Nikon | f = 200 mm |
| Olympus | f = 180 mm |
| Thorlabs | f = 200 mm |
| Zeiss | f = 165 mm |
Magnification and Sample Area Calculations
Magnification
The magnification of a system is the multiplicative product of the magnification of each optical element in the system. Optical elements that produce magnification include objectives, camera tubes, and trinocular eyepieces, as shown in Figure 73A. It is important to note that the magnification quoted in these products' specifications is usually only valid when all optical elements are made by the same manufacturer. If this is not the case, then the magnification of the system can still be calculated, but an effective objective magnification should be calculated first, as described below.
To adapt the examples shown here to your own microscope, please use our Magnification and FOV Calculator, which is available for download by clicking on the Magnification and FOV Calculator button. Note the calculator is an Excel spreadsheet that uses macros. In order to use the calculator, macros must be enabled. To enable macros, click the "Enable Content" button in the yellow message bar upon opening the file.
Example 1: Camera Magnification
When imaging a sample with a camera, the image is magnified by the objective and the camera tube. If using a 20X Nikon objective and a 0.75X Nikon camera tube, then the image at the camera has 20X × 0.75X = 15X magnification.
Example 2: Trinocular Magnification
When imaging a sample through trinoculars, the image is magnified by the objective and the eyepieces in the trinoculars. If using a 20X Nikon objective and Nikon trinoculars with 10X eyepieces, then the image at the eyepieces has 20X × 10X = 200X magnification. Note that the image at the eyepieces does not pass through the camera tube, as shown by Figure 73A.
Using an Objective with a Microscope from a Different Manufacturer
Magnification is not a fundamental value: it is a derived value, calculated by assuming a specific tube lens focal length. Each microscope manufacturer has adopted a different focal length for their tube lens, as shown by Table 73B. Hence, when combining optical elements from different manufacturers, it is necessary to calculate an effective magnification for the objective, which is then used to calculate the magnification of the system.
The effective magnification of an objective is given by Equation 1:

Here, the Design Magnification is the magnification printed on the objective, fTube Lens in Microscope is the focal length of the tube lens in the microscope you are using, and fDesign Tube Lens of Objective is the tube lens focal length that the objective manufacturer used to calculate the Design Magnification. These focal lengths are given by Table 73B.
Note that Leica, Mitutoyo, Nikon, and Thorlabs use the same tube lens focal length; if combining elements from any of these manufacturers, no conversion is needed. Once the effective objective magnification is calculated, the magnification of the system can be calculated as before.
Example 3: Trinocular Magnification (Different Manufacturers)
When imaging a sample through trinoculars, the image is magnified by the objective and the eyepieces in the trinoculars. This example will use a 20X Olympus objective and Nikon trinoculars with 10X eyepieces.
Following Equation 1 and Table 73B, we calculate the effective magnification of an Olympus objective in a Nikon microscope:
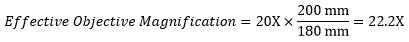
The effective magnification of the Olympus objective is 22.2X and the trinoculars have 10X eyepieces, so the image at the eyepieces has 22.2X × 10X = 222X magnification.
 Figure 73C Sample Area When Imaged on a Camera
Figure 73C Sample Area When Imaged on a CameraSample Area When Imaged on a Camera
When imaging a sample with a camera, the dimensions of the sample area are determined by the dimensions of the camera sensor and the system magnification, as shown by Equation 2.

The camera sensor dimensions can be obtained from the manufacturer, while the system magnification is the multiplicative product of the objective magnification and the camera tube magnification (see Example 1). If needed, the objective magnification can be adjusted as shown in Example 3.
As the magnification increases, the resolution improves, but the field of view also decreases. The dependence of the field of view on magnification is shown in Figure 73C.
Example 4: Sample Area
The dimensions of the camera sensor in Thorlabs' previous-generation 1501M-USB Scientific Camera are 8.98 mm × 6.71 mm. If this camera is used with the Nikon objective and trinoculars from Example 1, which have a system magnification of 15X, then the image area is:
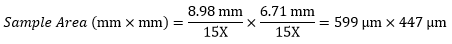
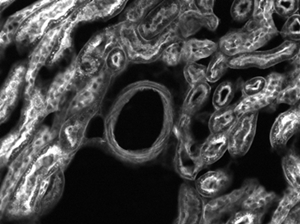
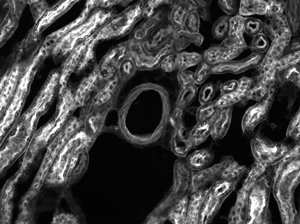
Sample Area Examples
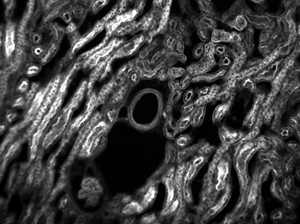
Figures 73D through 73F, images of a mouse kidney, were all acquired using the same objective and the same camera. However, the camera tubes used were different. Figures 73D through 73F demonstrate that decreasing the camera tube magnification enlarges the field of view at the expense of the size of the details in the image.
RESOLUTION
Resolution Tutorial
An important parameter in many imaging applications is the resolution of the objective. This tutorial describes the different conventions used to define an objective's resolution. Thorlabs provides the theoretical Rayleigh resolution for all of the imaging objectives offered on our site; the other conventions are presented for informational purposes.
Resolution
The resolution of an objective refers to its ability to distinguish closely-spaced features of an object. This is often theoretically quantified by considering an object that consists of two point sources and asking at what minimum separation can these two point sources be resolved. When a point source is imaged, rather than appearing as a singular bright point, it will appear as a broadened intensity profile due to the effects of diffraction. This profile, known as an Airy disk, consists of an intense central peak with surrounding rings of much lesser intensity. The image produced by two point sources in proximity to one another will therefore consist of two overlapping Airy disk profiles, and the resolution of the objective is therefore determined by the minimum spacing at which the two profiles can be uniquely identified. There is no fundamental criterion for establishing what exactly it means for the two profiles to be resolved and, as such, there are a few criteria that are observed in practice. In microscopic imaging applications, the two most commonly used criteria are the Rayleigh and Abbe criteria. A third criterion, more common in astronomical applications, is the Sparrow criterion.
Rayleigh Criterion
The Rayleigh criterion states that two overlapping Airy disk profiles are resolved when the first intensity minimum of one profile coincides with the intensity maximum of the other profile [1]. It can be shown that the first intensity minimum occurs at a radius of 1.22λf/D from the central maximum, where λ is the wavelength of the light, f is the focal length of the objective, and D is the entrance pupil diameter. Thus, in terms of the numerical aperture (NA = 0.5*D/f), the Rayleigh resolution is:
rR = 0.61λ/NA
An idealized image of two Airy disks separated by a distance equal to the Rayleigh resolution is shown in Figure 109A; the illumination source has been assumed to be incoherent. A corresponding horizontal line cut across the intensity maxima is plotted in Figure 109B. The vertical dashed lines in the intensity profile show that the maximum of each individual Airy disk overlaps with the neighboring minimum. Between the two maxima, there is a local minimum which appears in the image as a gray region between the two white peaks.
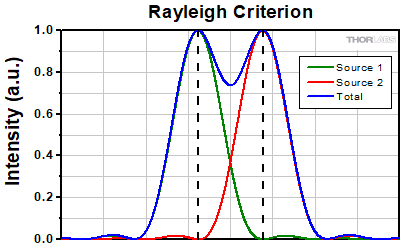 Click to Enlarge
Click to EnlargeFigure 109B The vertical dashed lines show how the maximum of each intensity profile overlaps with the first minimum of the other.
 Figure 109A Two point sources are considered resolved when separated by the Rayleigh resolution. The gray region between the two white peaks is clearly visible.
Figure 109A Two point sources are considered resolved when separated by the Rayleigh resolution. The gray region between the two white peaks is clearly visible.Thorlabs provides the theoretical Rayleigh resolution for all of the imaging objectives offered on our site in their individual product presentations.
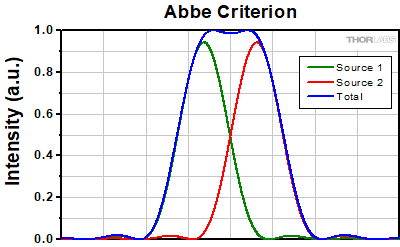
Abbe Criterion
The Abbe theory describes image formation as a double process of diffraction [2]. Within this framework, if two features separated by a distance d are to be resolved, at a minimum both the zeroth and first orders of diffraction must be able to pass through the objective's aperture. Since the first order of diffraction appears at the angle: sin(θ1) = λ/d, the minimum object separation, or equivalently the resolution of the objective, is given by d = λ/n*sin(α), where α is the angular semi-aperture of the objective and a factor of n has been inserted to account for the refractive index of the imaging medium. This result overestimates the actual limit by a factor of 2 because both first orders of diffraction are assumed to be accepted by the objective, when in fact only one of the first orders must pass through along with the zeroth order. Dividing the above result by a factor of 2 and using the definition of the numerical aperture (NA = n*sin(α)) gives the famous Abbe resolution limit:
rA = 0.5λ/NA
In Figure 109C, two Airy disks are shown separated by the Abbe resolution limit. Compared to the Rayleigh limit, the decrease in intensity at the origin is much harder to discern. The horizontal line cut in Figure 109D shows that the intensity decreases by only ≈2%.
 Click to Enlarge
Click to EnlargeFigure 109D The line cut shows the small intensity dip between the two maxima.
 Figure 109C Two point sources separated by the Abbe resolution limit. Though observable, the contrast between the maxima and central minimum is much weaker compared to the Rayleigh limit.
Figure 109C Two point sources separated by the Abbe resolution limit. Though observable, the contrast between the maxima and central minimum is much weaker compared to the Rayleigh limit.Sparrow Criterion
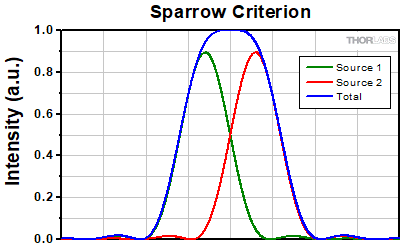
For point source separations corresponding to the Rayleigh and Abbe resolution criteria, the combined intensity profile has a local minimum located at the origin between the two maxima. In a sense, this feature is what allows the two point sources to be resolved. That is to say, if the sources' separation is further decreased beyond the Abbe resolution limit, the two individual maxima will merge into one central maximum and resolving the two individual contributions will no longer be possible. The Sparrow criterion posits that the resolution limit is reached when the crossover from a central minimum to a central maximum occurs.
At the Sparrow resolution limit, the center of the combined intensity profile is flat, which implies that the derivative with respect to position is zero at the origin. However, this first derivative at the origin is always zero, given that it is either a local minimum or maximum of the combined intensity profile (strictly speaking, this is only the case if the sources have equal intensities). Consider then, that because the Sparrow resolution limit occurs when the origin's intensity changes from a local minimum to a maximum, that the second derivative must be changing sign from positive to negative. The Sparrow criterion is thus a condition that is imposed upon the second derivative, namely that the resolution limit occurs when the second derivative is zero [3]. Applying this condition to the combined intensity profile of two Airy disks leads to the Sparrow resolution:
rS = 0.47λ/NA
Figure 109E shows two Airy disks separated by the Sparrow resolution limit. As described above, the intensity is constant in the region between the two peaks and there is no intensity dip at the origin. In the line cut in Figure 109F, the constant intensity near the origin is confirmed.
 Click to Enlarge
Click to EnlargeFigure 109F At the Sparrow resolution limit, the combined intensity is a constant near the origin. The scale here has been normalized to 1.
 Figure 109E Two Airy disk profiles separated by the Sparrow resolution limit. Note that, unlike the Rayleigh or Abbe limits, there is no decrease in intensity at the origin.
Figure 109E Two Airy disk profiles separated by the Sparrow resolution limit. Note that, unlike the Rayleigh or Abbe limits, there is no decrease in intensity at the origin.References
[1] Eugene Hecht, "Optics," 4th Ed., Addison-Wesley (2002)
[2] S.G. Lipson, H. Lipson, and D.S. Tannhauser, "Optical Physics," 3rd Ed., Cambridge University Press (1995)
[3] C.M. Sparrow, "On Spectroscopic Resolving Power," Astrophys. J. 44, 76-87 (1916)
Thorlabs Apochromatic Objectives for Life Science

| Table G1.2 Protective Accessories | |
|---|---|
| Objective | Objective Case |
| TL1X-SAP | Lid: OC2M25 Canister: OC24 |
| TL2X-SAP | Lid: OC2M25 Canister: OC22 |
| TL4X-SAP | |
| TL10X-2P | Lid: OC2M32 Canister: OC24a |
| TL15X-2P | |

Click to Enlarge
Figure G1.1 The TL1X-SAP objective includes a removable wave plate that is attached via magnets to the end of the objective barrel. White markings on the end of the barrel and a black dot on the wave plate serve as reference points when rotating the wave plate.
- Infinity-Corrected Apochromatic Design Corrects Chromatic Aberrations Across the Visible or NIR Spectrum
- Ideal for Imaging or Focusing Laser Light or Multiphoton Imaging
- M25 x 0.75 or M32 x 0.75 Threading
- Designed for a Tube Lens Focal Length of 200 mm
- Click Here for Full Presentation
Thorlabs offers super apochromatic microscope objectives with 1X, 2X, 4X, or 10X magnification, and plan apochromatic 15X or 28X objectives with improved visible or NIR performance, respectively. The objectives are designed to provide axial color correction over a wide field of view with no vignetting over the entire field. For more details on these objectives, please click the info icons (![]() ) in Table G1.4 or see the full presentation.
) in Table G1.4 or see the full presentation.
TL10X-2P Super Apochromatic Microscope Objective
Our 1X telecentric objective is ideal for machine vision applications and features a removable magnetic waveplate that minimizes back reflections when used with an epi-illuminated system, thus enabling an increase in contrast; see Figure G1.1. Our 2X and 4X objectives pair low magnification with NAs of 0.10 and 0.20, respectively, making them ideal for widefield imaging. Lastly, our 10X, 15X, and 28X objectives are designed for multiphoton imaging applications and provide excellent transmission out to 1300 nm, and out to 1650 nm for Item # TL28X-MP. These multiphoton objectives have correction collars that allow adjustment for spherical aberrations introduced by imaging through aqueous solutions or thick cover glasses. The TL15X-2P objective additionally features a locking mechanism to fix the correction collar in place for improved repeatability. The TL28X-MP objective is designed for water immersion or water dipping. Since the lens at its tip is concave, water should be injected into the tip of the objective using a pipette or syringe to avoid forming an air bubble.
All objectives are shipped in an objective case comprised of a lid and container; please see Table G1.2 for compatible replacement cases for each objective. Each objective housing is engraved with the item #, magnification, NA, wavelength range, and working distance (the 15X and 28X objectives display the tube lens focal length instead of working distance). The housings are each designed for a tube lens of focal length 200 mm. The TL1X-SAP, TL2X-SAP and TL4X-SAP objectives have M25 x 0.75 external threading, while the TL10X-2P, TL15X-2P, and TL28X-MP objectives have M32 x 0.75 external threading. To use the objectives with a different thread standard, please see our microscope objective thread adapters.
Part Number | Description | Price | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
TL1X-SAP | 1X Super Apochromatic Microscope Objective, 0.03 NA, 8.0 mm WD | $2,463.84 | Today |
TL2X-SAP | 2X Super Apochromatic Microscope Objective, 0.1 NA, 56.3 mm WD | $1,518.42 | Today |
TL4X-SAP | 4X Super Apochromatic Microscope Objective, 0.2 NA, 17.0 mm WD | $2,469.57 | Today |
TL10X-2P | Customer Inspired! 10X Super Apochromatic Microscope Objective, 0.50 NA, 7.77 mm WD | $9,219.33 | Today |
TL15X-2P | 15X Plan Apochromat VIS+ Microscope Objective, 0.70 NA, 2.6 mm WD | $11,209.27 | Today |
TL28X-MP | NEW! 28X Plan Apochromat NIR Microscope Objective, 1.10 NA, 2.8 mm WD | $19,900.00 | Today |
Thorlabs Achromatic, Microspot® UV Focusing Objective

- AR Coated for 240 - 360 nm
- Ideal for Laser Focusing and UV Imaging Applications
- Diffraction-Limited Performance
- Designed for a Tube Lens Focal Length of 200 mm
- 10X, 20X, or 50X Magnification
Thorlabs MicroSpot objectives provide long working distances while keeping axial focal shift low. Their optical design is chromatically optimized in the UV wavelength range. Diffraction-limited performance is guaranteed over the entire clear aperture. These objectives are ideal for laser cutting, surgical laser focusing, and spectrometry applications. They can also be used for scanning and micro-imaging applications like brightfield imaging under narrowband, UV laser illumination. Each objective is shipped in an objective case comprised of an OC2M26 lid and an OC24 canister.
Each objective is engraved with its class, magnification, numerical aperture, wavelength range, a zero (noting that it is to be used to image a sample without a cover glass), and optical field number. For an explanation of the defining properties of these objectives, please see the Objective Tutorial tab.
Thorlabs can provide these objectives with custom AR coatings on request by contacting Tech Support; options include broadband NUV (325 nm - 500 nm), dual band (266 and 532 nm), and laser line (248 nm, 266 nm, 355 nm, or 532 nm). We also offer additional MicroSpot objectives for laser-focusing applications in the UV as well as visible and near-IR wavelengths.
| Item # | Wavelength Range |
Ma | WD | EFL | NA | EPb | Resolutionc | Typical Transmission |
OFN | PFL | Cover Glass Thickness |
AR Coating Reflectanced |
Pulsed Damage Threshold |
Objective Threading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMUL-10X-UVB | 240 - 360 nm | 10X | 20.0 mm | 20 mm | 0.25 | 10.0 mm | 0.9 µm | Raw Data |
24 | 95.0 mm | 0 mm | (240 - 360 nm) |
5.0 J/cm2 (355 nm, 10 ns, 20 Hz, Ø0.342 mm) |
W26 x 0.706e; 5 mm Depth |
| LMUL-20X-UVB | 20X | 15.3 mm | 10 mm | 0.36 | 7.2 mm | 0.6 µm | Raw Data |
|||||||
| LMUL-50X-UVB | 50X | 12.0 mm | 4 mm | 0.42 | 3.4 mm | 0.5 µm | Raw Data |
Part Number | Description | Price | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
LMUL-10X-UVB | Long Working Distance MicroSpot Focusing Objective, 10X, 240 - 360 nm, NA = 0.25 | $10,405.39 | Today |
LMUL-20X-UVB | Customer Inspired! Long Working Distance MicroSpot Focusing Objective, 20X, 240 - 360 nm, NA = 0.36 | $14,945.11 | Today |
LMUL-50X-UVB | Long Working Distance MicroSpot Focusing Objective, 50X, 240 - 360 nm, NA = 0.42 | $15,159.52 | Today |
Thorlabs High-Resolution Plan Apochromatic VIS+ Objective

- AR-Coated for 400 - 1100 nm
- Axial Color Corrected for 436 - 850 nm
- Ideal for Laser Focusing; Brightfield, Darkfield, and Fluorescence Microscopy; and Two-Photon Imaging
- Designed for a Tube Lens Focal Length of 200 mm
- 50X Magnification
Thorlabs offers a High-Resolution Plan Apochromatic Improved Visible (APO VIS+) Microscope Objective for 400 to 1100 nm which provides axial color correction over a wide field of view with no vignetting over the entire field. Compared to common apochromatic microscope objectives, which are typically axial color corrected from the 436 nm (g-line) to 656 nm (C-line), our PLAN APO VIS+ objective has an extended corrected wavelength range from 436 nm (g-line) to 850 nm. The objective is designed for use with a tube lens focal length of 200 mm and has optical elements that are AR-coated for improved transmission between 400 nm and 1100 nm. For more details on these objectives, please click the info icon (![]() ) below. Our 50X objective has a high numerical aperture (NA) of 0.75, making it ideal for applications requiring high-resolution such as laser focusing; brightfield, darkfield, and fluorescence microscopy; and two-photon imaging. Thorlabs offers the objective case (Item #s OC2M26 and OC24) separately as a replacement if the case shipped with each of these objectives is lost or broken.
) below. Our 50X objective has a high numerical aperture (NA) of 0.75, making it ideal for applications requiring high-resolution such as laser focusing; brightfield, darkfield, and fluorescence microscopy; and two-photon imaging. Thorlabs offers the objective case (Item #s OC2M26 and OC24) separately as a replacement if the case shipped with each of these objectives is lost or broken.
This objective is engraved with its class, magnification, numerical aperture, a zero (noting that it is to be used to image a sample without a cover glass), and optical field number. For an explanation of the defining properties of this objective, please see the Objective Tutorial tab.
Part Number | Description | Price | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
HPA50XAB | Customer Inspired! 50X High-Resolution Plan Apochromat VIS+ Objective, 400 - 1100 nm, 0.75 NA, 5.0 mm WD | $8,457.26 | Today |
Olympus Plan Achromat Objectives

- Infinity-Corrected Plan Achromat Design
- Ideal for Imaging or Focusing Laser Light
- RMS (0.800"-36) Threading
- Designed for a Tube Lens Focal Length of 180 mm
- 45.06 mm Parfocal Length
These infinity-corrected, imaging microscope objectives for visible wavelengths provide 4X, 10X, 20X, or 40X magnification. With their high numerical apertures (NA) and large magnifications, they are suitable for focusing or collimating laser light. These Olympus objectives are ideal for imaging applications due to their diffraction-limited performance across the entire visible spectrum. Alternatively, they can be used to focus light to a diffraction-limited spot, enabling efficient coupling of monochromatic or broadband light into a waveguide or fiber. Each of these objectives is suitable for use in brightfield microscopy, while the RMS10X, RMS20X, and RMS40X also offer excellent performance in darkfield imaging.
Their designation as plan achromats indicates that they are flat field and aberration corrected at two different wavelengths in the visible spectrum, leading to better spherical and chromatic corrections and superb field flatness. These achromatic objectives have an ultra-wide antireflection coating and standard RMS threading. To use these objectives with a different thread standard, please see our microscope objective thread adapters.
| Item # | Wavelength Range | Ma | WD | EFL | NA | EPb | Resolutionc | OFN | PFL | Cover Glass Thickness |
Performance Graphs |
AR Coating Reflectance |
Pulsed Damage Threshold |
Objective Threading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMS4X | Visible | 4X | 18.5 mm | 45 mm | 0.10 | 9 mm | 3.4 µm | 22 | 45.06 mm | 0 - 0.17 mm | Not Available |
Not Available |
- | RMS; 4.5 mm Depth |
| RMS10X | 10X | 10.6 mm | 18 mm | 0.25 | 9 mm | 1.3 µm | ||||||||
| RMS20X | 20X | 1.2 mm | 9 mm | 0.4 | 7.2 mm | 0.8 µm | 0.17 mm | RMS; 4.8 mm Depth |
||||||
| RMS40X | 40X | 0.6 mm | 4.5 mm | 0.65 | 5.9 mm | 0.5 µm | 0.17 mm | RMS; 4.5 mm Depth |
Part Number | Description | Price | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
RMS4X | 4X Olympus Plan Achromat Objective, 0.10 NA, 18.5 mm WD | $175.04 | In Stock Overseas |
RMS10X | 10X Olympus Plan Achromat Objective, 0.25 NA, 10.6 mm WD | $449.12 | Today |
RMS20X | 20X Olympus Plan Achromat Objective, 0.4 NA, 1.2 mm WD | $554.20 | Today |
RMS40X | 40X Olympus Plan Achromat Objective, 0.65 NA, 0.6 mm WD | $823.64 | Today |
Olympus Plan Fluorite Objectives

- Infinity-Corrected Plan Fluorite Design
- Ideal for Imaging or Focusing Laser Light
- RMS (0.800"-36) Threading
- Designed for a Tube Lens Focal Length of 180 mm
- 45.06 mm Parfocal Length
These infinity-corrected, imaging microscope objectives for visible to NIR wavelengths provide 4X, 10X, 20X, 40X, or 60X magnification. Plan Fluorite objectives, also called a plan semi-apochromat, are corrected for four wavelengths. These are well suited for color photomicrography. The RMS60X-PFC features variable coverslip correction; it has a rotating correction collar that changes the distance between the objective elements, allowing the coverslip correction to be adjusted from 0.11 mm to 0.23 mm.
All of these objectives are excellent for brightfield microscopy, while the RMS10X-PF, RMS20X-PF, RMS40-PF, and RMS60X-PFC objectives are also excellent for DIC microscopy. These objectives use standard RMS threading. To use these objectives with a different thread standard, please see our microscope objective thread adapters.
| Item # | Wavelength Range | Ma | WD | EFL | NA | EPb | Resolutionc | OFN | PFL | Cover Glass Thickness |
Performance Graphs |
AR Coating Reflectance |
Pulsed Damage Threshold |
Objective Threading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMS4X-PF | Visible to NIR | 4X | 17 mm | 45 mm | 0.13 | 11.7 mm | 2.6 µm | 26.5 | 45.06 mm | 0 - 0.17 mm | Not Available |
Not Available |
- | RMS; 4.5 mm Depth |
| RMS10X-PF | 10X | 10 mm | 18 mm | 0.3 | 10.8 mm | 1.1 µm | 0 - 0.17 mm | |||||||
| RMS20X-PF | 20X | 2.1 mm | 9 mm | 0.5 | 9 mm | 0.7 µm | 0.17 mm | |||||||
| RMS40X-PF | 40X | 0.51 mm | 4.5 mm | 0.75 | 6.8 mm | 0.4 µm | 0.17 mm | |||||||
| RMS60X-PFC | 60X | 0.2 mm | 3 mm | 0.9 | 5.4 mm | 0.4 µm | 0.11 - 0.23 mmd | RMS; 4.7 mm Depth |
Part Number | Description | Price | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
RMS4X-PF | 4X Olympus Plan Fluorite Objective, 0.13 NA, 17 mm WD | $738.91 | Today |
RMS10X-PF | 10X Olympus Plan Fluorite Objective, 0.3 NA, 10 mm WD | $1,320.22 | Today |
RMS20X-PF | 20X Olympus Plan Fluorite Objective, 0.5 NA, 2.1 mm WD | $1,567.66 | Today |
RMS40X-PF | 40X Olympus Plan Fluorite Objective, 0.75 NA, 0.51 mm WD | $1,715.10 | Today |
RMS60X-PFC | 60X Olympus Plan Fluorite Objective with Correction Collar, 0.9 NA, 0.2 mm WD | $4,619.94 | Today |
Nikon Plan Fluorite Objectives

- Infinity-Corrected Plan Fluorite Design
- Ideal for Imaging or Focusing Laser Light
- M25 x 0.75 Threading
- Designed for a Tube Lens Focal Length of 200 mm
- 60 mm Parfocal Length
The Nikon Plan Fluorite Objectives provide 4X, 10X, 20X, 40X, or 60X magnification. They are designed to have high transmission in the UV to NIR wavelength range and to produce flat images across the field of view. These multi-purpose objectives can be utilized for brightfield microscopy, fluorescence microscopy, and polarization-sensitive observations. The N10X-PF, N20X-PF, N40X-PF, and N60X-PF objectives are also good for both darkfield and DIC microscopy.
Each objective is designed for use with a tube lens focal length of 200 mm and is compatible with our DIY Cerna® Systems. They use M25 x 0.75 threading; to use these objectives with a different thread standard, please see our microscope objective thread adapters.
These objectives are designed for use from -18 °C (0 °F) to 60 °C (140 °F) and are not recommended for use at extreme temperatures.
| Item # | Wavelength Range | Ma | WD | EFL | NA | EPb | Resolutionc | OFN | PFL | Cover Glass Thickness |
Performance Graphs | AR Coating Reflectance |
Pulsed Damage Threshold | Objective Threading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N4X-PF | UV to NIR | 4X | 17.2 mm | 50 mm | 0.13 | 13 mm | 2.6 µm | Not Available | 60 mm | 0 - 0.17 mm | Not Available |
Not Available |
- | M25 x 0.75; 3.6 mm Depth |
| N10X-PF | 10X | 16 mm | 20 mm | 0.3 | 12 mm | 1.1 µm | 25 | 0.17 mm | M25 x 0.75; 5 mm Depth |
|||||
| N20X-PF | 20X | 2.1 mm | 10 mm | 0.50 | 10 mm | 0.7 µm | Not Available | 0.17 mm | ||||||
| N40X-PF | 40X | 0.66 mm | 5 mm | 0.75 | 7.5 mm | 0.4 µm | 25 | 0.17 mm | M25 x 0.75; 5.1 mm Depth |
|||||
| N60X-PF | 60X | 0.31 - 0.4 mm | 3.3 mm | 0.85 | 5.7 mm | 0.4 µm | 25 | 0.11 - 0.23 mmd | M25 x 0.75; 5 mm Depth |
Part Number | Description | Price | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
N4X-PF | 4X Nikon Plan Fluorite Imaging Objective, 0.13 NA, 17.2 mm WD | $686.39 | Today |
N10X-PF | 10X Nikon Plan Fluorite Imaging Objective, 0.3 NA, 16 mm WD | $1,247.26 | Today |
N20X-PF | 20X Nikon Plan Fluorite Imaging Objective, 0.50 NA, 2.1 mm WD | $1,382.29 | In Stock Overseas |
N40X-PF | 40X Nikon Plan Fluorite Imaging Objective, 0.75 NA, 0.66 mm WD | $2,369.19 | In Stock Overseas |
N60X-PF | 60X Nikon Plan Fluorite Imaging Objective with Correction Collar, 0.85 NA, 0.31 - 0.4 mm WD | $3,648.23 | Today |
Mitutoyo Plan Apochromat Objectives

- Long Working Distance
- Infinity-Corrected Plan Apochromat Design
- W26 x 0.706 Threading
- Designed for a Tube Lens Focal Length of 200 mm
- 95 mm Parfocal Length
Thorlabs offers Mitutoyo Plan Apochromat Objectives with 5X, 7.5X, 10X, 20X, 50X, or 100X magnification. They feature a flat field of focus and chromatic correction over their operating ranges: either 436 nm to 656 nm or 480 nm to 1800 nm. The long working distance provides a wide space between the lens surface and the object, making them ideal for machine vision applications. Each objective is engraved with its class, magnification, numerical aperture, a zero (noting that it is to be used to image a sample without a cover glass), and the tube lens focal length for which the specified magnification is valid. For an explanation of the defining properties of these objectives, please see the Objective Tutorial tab. If the case shipped with each of these objectives is lost or broken, Thorlabs offers an objective case (Item #s OC2M26 and OC24) that can be used as a replacement.
The objectives have external W26 x 0.706 threads; to use these objectives with a different thread standard, please see our microscope objective thread adapters. These objectives do not feature adjustment to correct for cover glass thickness and should be used without a cover slip.
Part Number | Description | Price | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
MY5X-802B | 5X Mitutoyo Plan Apochromat Objective, 436 - 656 nm, 0.14 NA, 36.5 mm WD | $883.40 | In Stock Overseas |
MY7X-807 | Customer Inspired! 7.5X Mitutoyo Plan Apochromat Objective, 436 - 656 nm, 0.21 NA, 35 mm WD | $1,621.22 | Today |
MY10X-803 | Customer Inspired! 10X Mitutoyo Plan Apochromat Objective, 436 - 656 nm, 0.28 NA, 34 mm WD | $1,109.65 | Today |
MY20X-804 | Customer Inspired! 20X Mitutoyo Plan Apochromat Objective, 436 - 656 nm, 0.42 NA, 20 mm WD | $2,613.33 | Today |
MY50X-805 | Customer Inspired! 50X Mitutoyo Plan Apochromat Objective, 436 - 656 nm, 0.55 NA, 13 mm WD | $3,254.52 | Today |
MY100X-806 | Customer Inspired! 100X Mitutoyo Plan Apochromat Objective, 436 - 656 nm, 0.70 NA, 6 mm WD | $4,406.82 | Today |
MY5X-822 | 5X Mitutoyo Plan Apochromat Objective, 480 - 1800 nm, 0.14 NA, 37.5 mm WD | $1,947.88 | Today |
MY10X-823 | 10X Mitutoyo Plan Apochromat Objective, 480 - 1800 nm, 0.26 NA, 30.5 mm WD | $2,226.14 | Today |
MY20X-824 | 20X Mitutoyo Plan Apochromat Objective, 480 - 1800 nm, 0.40 NA, 20.0 mm WD | $4,004.64 | Today |
MY50X-825 | 50X Mitutoyo Plan Apochromat Objective, 480 - 1800 nm, 0.42 NA, 17.0 mm WD | $4,924.13 | Today |






 Click to Enlarge
Click to Enlarge