UV Fused Silica Plano-Convex Cylindrical Lenses

- Used to Focus Light in One Dimension
- Focal Lengths Available: 8 mm to 500 mm
- Available Uncoated or with One of Four AR Coatings
LJ4359-C
LJ4878-B
LJ4426
LJ4748-A
LJ4918-UV

Please Wait
| Common Specifications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Material | UV Grade Fused Silicaa | |
| Wavelength Range | Uncoated: 185 nm - 2.1 μm -UV Coated: 245 - 400 nm -A Coated 350 - 700 nm -B Coated: 650 - 1050 nm -C Coated: 1050 - 1700 nm |
|
| Design Wavelength | 546 nm | |
| Broadband AR Coating Reflectanceb | Ravg < 0.5% | |
| Length/Height Tolerance | +0.00/-0.10 mm (Uncoated and -UV Coated) +0.0/-0.1 mm (-A, -B, and C-Coated) |
|
| Center Thickness Tolerance | ±0.10 mm (Uncoated and -UV Coated) ±0.1 mm (-A, -B, and -C Coated) |
|
| Focal Length Tolerance | ±1% | |
| Surface Quality | 60-40 Scratch-Dig | |
| Centration | f ≤ 50 mm: ≤5 arcmin f > 50 mm: ≤3 arcmin |
|
| Surface Flatness (Plano Side) |
Height | <λ/2 |
| Length | <λ/2 | |
| Cylindrical Surface Powerc (Convex Side) |
Height | <3λ/2 |
| Length | <3λ/2 | |
| Irregularity (Peak to Valley) |
Height (Plano, Curved) | λ/4, λ |
| Length (Plano, Curved) | λ/4, λ/cm | |
| Clear Aperture | >90% of Surface Dimensions | |
| Plano-Convex Cylindrical Lens Selection Guide | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate | N-BK7 | UV Fused Silica | N-BK7 (Round) |
UV Fused Silica (Round) |
| AR Coating Range |
Uncoated 350 - 700 nm 650 - 1050 nm 1050 - 1700 nm |
Uncoated 245 - 400 nm 350 - 700 nm 650 - 1050 nm 1050 - 1700 nm |
Uncoated 350 - 700 nm 650 - 1050 nm 1050 - 1700 nm |
Uncoated 350 - 700 nm 650 - 1050 nm 1050 - 1700 nm |
| Click on the red Document icon next to the item numbers below to access the Zemax file download. Our entire Zemax Catalog is also available. |
Features
- Made of UV Grade Fused Silica
- Available Uncoated or with a Broadband AR Coating
- 185 nm - 2.1 µm (Uncoated)
- 245 - 400 nm (UV Coated
- 350 - 700 nm (A Coated)
- 650 - 1050 nm (B Coated)
- 1050 - 1700 nm (C Coated)
- Collimate & Circularize the Output of a Laser Diode
- Focal Lengths from 8 mm to 500 mm Available
Applications
- Anamorphic Beam Shaping
- Collimate and Circularize the Output of a Laser Diode
- Couple Light into a Slit
- 1D Image Compression
Thorlabs offers both uncoated and AR-coated plano-convex cylindrical lenses. The UV-, A-, B-, and C-coated lenses have an antireflection coating for the 245 - 400 nm, 350 - 700 nm, 650 - 1050 nm, or 1050 - 1700 nm ranges on both surfaces, respectively. UV-grade fused silica offers high transmission in the deep UV and exhibits virtually no laser-induced fluorescence (as measured at 193 nm), making it an ideal choice for applications from the UV to the near IR. These positive cylindrical lenses are ideal for applications requiring magnification in one dimension. While spherical lenses act symmetrically in two dimensions on an incident ray, cylindrical lenses act in the same manner but only in one dimension. A typical application is to use a pair of cylindrical lenses to provide anamorphic shaping of a beam. A pair of positive cylindrical lenses can be used to collimate and circularize the output of a laser diode. Another application possibility would be to use a single lens to focus a diverging beam on to a detector array. To minimize the introduction of spherical aberration, a collimated light source should be incident on the curved surface when focusing into a line, and a line source should be incident on the plano surface to form a collimated line.
For cage system and lens tube compatibility, please see our Mounted Plano-Convex Round Cylindrical lenses. These lenses are typically easier to integrate into our standard optomechanics.
UV Fused Silica Plano-Convex Cylindrical Lenses
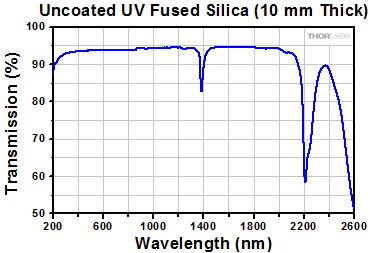
Click to Enlarge
Click Here for Raw Data
Above is the transmission curve for a 10 mm thick uncoated sample of UV fused silica when the incident light is normal to the surface. Please note that this is the measured transmission, including surface reflections.
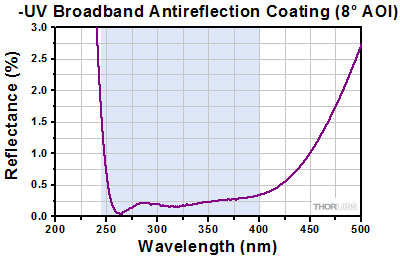
Click to Enlarge
Click Here for Raw Data
The blue shaded region indicates the specified 245 - 400 nm wavelength range for optimum performance.
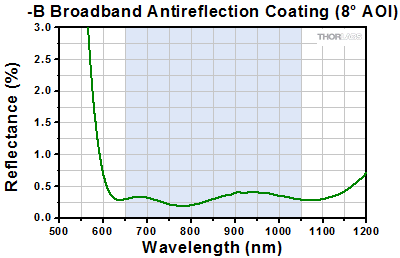
Click to Enlarge
Click Here for Raw Data
The blue shaded region indicates the specified 650 - 1050 nm wavelength range for optimum performance.
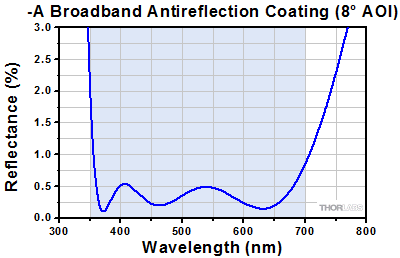
Click to Enlarge
Click Here for Raw Data
The blue shaded region indicates the specified 350 - 700 nm wavelength range for optimum performance.
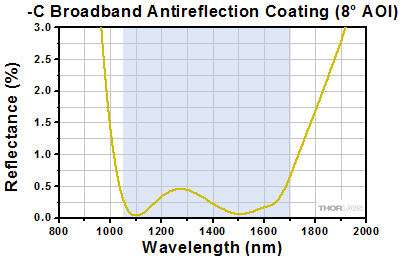
Click to Enlarge
Click Here for Raw Data
The blue shaded region indicates the specified 1050 - 1700 nm wavelength range for optimum performance.
| Damage Threshold Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Coating Designation (Item # Suffix) |
Damage Threshold |
| -UV | 5 J/cm2 (355 nm, 10 ns, 10 Hz, Ø0.350 mm) |
| -A | 7.5 J/cm2 (532 nm, 10 ns, 10 Hz, Ø0.491 mm) |
| -B | 0.246 J/cm2 (800 nm, 99 fs, 1 kHz, Ø0.166 mm) 7.5 J/cm2 (810 nm, 10 ns, 10 Hz, Ø0.133 mm) |
| -C | 7.5 J/cm2 (1542 nm, 10 ns, 10 Hz, Ø0.123 mm) |
Damage Threshold Data for Thorlabs' UV, A-, B-, and C-Coated UV Fused Silica Lenses
The specifications to the right are measured data for Thorlabs' UV, A-, B-, and C-coated UV fused silica lenses. Damage threshold specifications are constant for all UV fused silica lenses with a given coating type, regardless of the size or the focal length of the lens.
Laser Induced Damage Threshold Tutorial
The following is a general overview of how laser induced damage thresholds are measured and how the values may be utilized in determining the appropriateness of an optic for a given application. When choosing optics, it is important to understand the Laser Induced Damage Threshold (LIDT) of the optics being used. The LIDT for an optic greatly depends on the type of laser you are using. Continuous wave (CW) lasers typically cause damage from thermal effects (absorption either in the coating or in the substrate). Pulsed lasers, on the other hand, often strip electrons from the lattice structure of an optic before causing thermal damage. Note that the guideline presented here assumes room temperature operation and optics in new condition (i.e., within scratch-dig spec, surface free of contamination, etc.). Because dust or other particles on the surface of an optic can cause damage at lower thresholds, we recommend keeping surfaces clean and free of debris. For more information on cleaning optics, please see our Optics Cleaning tutorial.
Testing Method
Thorlabs' LIDT testing is done in compliance with ISO/DIS 11254 and ISO 21254 specifications.
First, a low-power/energy beam is directed to the optic under test. The optic is exposed in 10 locations to this laser beam for 30 seconds (CW) or for a number of pulses (pulse repetition frequency specified). After exposure, the optic is examined by a microscope (~100X magnification) for any visible damage. The number of locations that are damaged at a particular power/energy level is recorded. Next, the power/energy is either increased or decreased and the optic is exposed at 10 new locations. This process is repeated until damage is observed. The damage threshold is then assigned to be the highest power/energy that the optic can withstand without causing damage. A histogram such as that below represents the testing of one BB1-E02 mirror.

The photograph above is a protected aluminum-coated mirror after LIDT testing. In this particular test, it handled 0.43 J/cm2 (1064 nm, 10 ns pulse, 10 Hz, Ø1.000 mm) before damage.
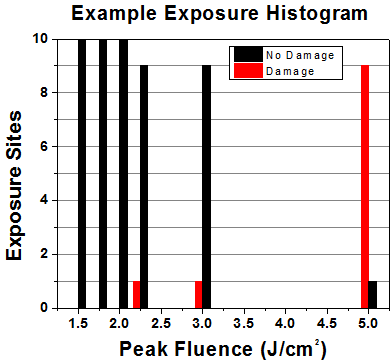
| Example Test Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fluence | # of Tested Locations | Locations with Damage | Locations Without Damage |
| 1.50 J/cm2 | 10 | 0 | 10 |
| 1.75 J/cm2 | 10 | 0 | 10 |
| 2.00 J/cm2 | 10 | 0 | 10 |
| 2.25 J/cm2 | 10 | 1 | 9 |
| 3.00 J/cm2 | 10 | 1 | 9 |
| 5.00 J/cm2 | 10 | 9 | 1 |
According to the test, the damage threshold of the mirror was 2.00 J/cm2 (532 nm, 10 ns pulse, 10 Hz, Ø0.803 mm). Please keep in mind that these tests are performed on clean optics, as dirt and contamination can significantly lower the damage threshold of a component. While the test results are only representative of one coating run, Thorlabs specifies damage threshold values that account for coating variances.
Continuous Wave and Long-Pulse Lasers
When an optic is damaged by a continuous wave (CW) laser, it is usually due to the melting of the surface as a result of absorbing the laser's energy or damage to the optical coating (antireflection) [1]. Pulsed lasers with pulse lengths longer than 1 µs can be treated as CW lasers for LIDT discussions.
When pulse lengths are between 1 ns and 1 µs, laser-induced damage can occur either because of absorption or a dielectric breakdown (therefore, a user must check both CW and pulsed LIDT). Absorption is either due to an intrinsic property of the optic or due to surface irregularities; thus LIDT values are only valid for optics meeting or exceeding the surface quality specifications given by a manufacturer. While many optics can handle high power CW lasers, cemented (e.g., achromatic doublets) or highly absorptive (e.g., ND filters) optics tend to have lower CW damage thresholds. These lower thresholds are due to absorption or scattering in the cement or metal coating.

LIDT in linear power density vs. pulse length and spot size. For long pulses to CW, linear power density becomes a constant with spot size. This graph was obtained from [1].
Pulsed lasers with high pulse repetition frequencies (PRF) may behave similarly to CW beams. Unfortunately, this is highly dependent on factors such as absorption and thermal diffusivity, so there is no reliable method for determining when a high PRF laser will damage an optic due to thermal effects. For beams with a high PRF both the average and peak powers must be compared to the equivalent CW power. Additionally, for highly transparent materials, there is little to no drop in the LIDT with increasing PRF.
In order to use the specified CW damage threshold of an optic, it is necessary to know the following:
- Wavelength of your laser
- Beam diameter of your beam (1/e2)
- Approximate intensity profile of your beam (e.g., Gaussian)
- Linear power density of your beam (total power divided by 1/e2 beam diameter)
Thorlabs expresses LIDT for CW lasers as a linear power density measured in W/cm. In this regime, the LIDT given as a linear power density can be applied to any beam diameter; one does not need to compute an adjusted LIDT to adjust for changes in spot size, as demonstrated by the graph to the right. Average linear power density can be calculated using the equation below.
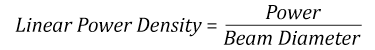
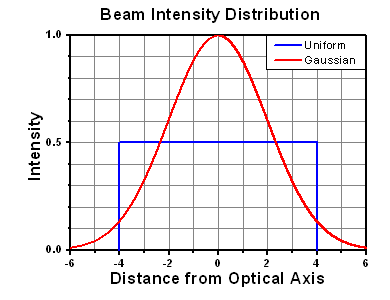
The calculation above assumes a uniform beam intensity profile. You must now consider hotspots in the beam or other non-uniform intensity profiles and roughly calculate a maximum power density. For reference, a Gaussian beam typically has a maximum power density that is twice that of the uniform beam (see lower right).
Now compare the maximum power density to that which is specified as the LIDT for the optic. If the optic was tested at a wavelength other than your operating wavelength, the damage threshold must be scaled appropriately. A good rule of thumb is that the damage threshold has a linear relationship with wavelength such that as you move to shorter wavelengths, the damage threshold decreases (i.e., a LIDT of 10 W/cm at 1310 nm scales to 5 W/cm at 655 nm):

While this rule of thumb provides a general trend, it is not a quantitative analysis of LIDT vs wavelength. In CW applications, for instance, damage scales more strongly with absorption in the coating and substrate, which does not necessarily scale well with wavelength. While the above procedure provides a good rule of thumb for LIDT values, please contact Tech Support if your wavelength is different from the specified LIDT wavelength. If your power density is less than the adjusted LIDT of the optic, then the optic should work for your application.
Please note that we have a buffer built in between the specified damage thresholds online and the tests which we have done, which accommodates variation between batches. Upon request, we can provide individual test information and a testing certificate. The damage analysis will be carried out on a similar optic (customer's optic will not be damaged). Testing may result in additional costs or lead times. Contact Tech Support for more information.
Pulsed Lasers
As previously stated, pulsed lasers typically induce a different type of damage to the optic than CW lasers. Pulsed lasers often do not heat the optic enough to damage it; instead, pulsed lasers produce strong electric fields capable of inducing dielectric breakdown in the material. Unfortunately, it can be very difficult to compare the LIDT specification of an optic to your laser. There are multiple regimes in which a pulsed laser can damage an optic and this is based on the laser's pulse length. The highlighted columns in the table below outline the relevant pulse lengths for our specified LIDT values.
Pulses shorter than 10-9 s cannot be compared to our specified LIDT values with much reliability. In this ultra-short-pulse regime various mechanics, such as multiphoton-avalanche ionization, take over as the predominate damage mechanism [2]. In contrast, pulses between 10-7 s and 10-4 s may cause damage to an optic either because of dielectric breakdown or thermal effects. This means that both CW and pulsed damage thresholds must be compared to the laser beam to determine whether the optic is suitable for your application.
| Pulse Duration | t < 10-9 s | 10-9 < t < 10-7 s | 10-7 < t < 10-4 s | t > 10-4 s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Damage Mechanism | Avalanche Ionization | Dielectric Breakdown | Dielectric Breakdown or Thermal | Thermal |
| Relevant Damage Specification | No Comparison (See Above) | Pulsed | Pulsed and CW | CW |
When comparing an LIDT specified for a pulsed laser to your laser, it is essential to know the following:
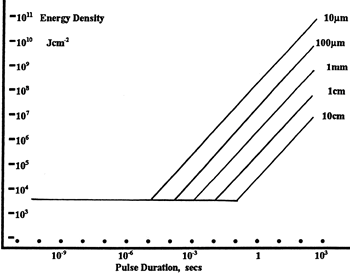
LIDT in energy density vs. pulse length and spot size. For short pulses, energy density becomes a constant with spot size. This graph was obtained from [1].
- Wavelength of your laser
- Energy density of your beam (total energy divided by 1/e2 area)
- Pulse length of your laser
- Pulse repetition frequency (prf) of your laser
- Beam diameter of your laser (1/e2 )
- Approximate intensity profile of your beam (e.g., Gaussian)
The energy density of your beam should be calculated in terms of J/cm2. The graph to the right shows why expressing the LIDT as an energy density provides the best metric for short pulse sources. In this regime, the LIDT given as an energy density can be applied to any beam diameter; one does not need to compute an adjusted LIDT to adjust for changes in spot size. This calculation assumes a uniform beam intensity profile. You must now adjust this energy density to account for hotspots or other nonuniform intensity profiles and roughly calculate a maximum energy density. For reference a Gaussian beam typically has a maximum energy density that is twice that of the 1/e2 beam.
Now compare the maximum energy density to that which is specified as the LIDT for the optic. If the optic was tested at a wavelength other than your operating wavelength, the damage threshold must be scaled appropriately [3]. A good rule of thumb is that the damage threshold has an inverse square root relationship with wavelength such that as you move to shorter wavelengths, the damage threshold decreases (i.e., a LIDT of 1 J/cm2 at 1064 nm scales to 0.7 J/cm2 at 532 nm):
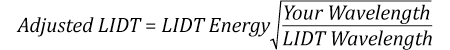
You now have a wavelength-adjusted energy density, which you will use in the following step.
Beam diameter is also important to know when comparing damage thresholds. While the LIDT, when expressed in units of J/cm², scales independently of spot size; large beam sizes are more likely to illuminate a larger number of defects which can lead to greater variances in the LIDT [4]. For data presented here, a <1 mm beam size was used to measure the LIDT. For beams sizes greater than 5 mm, the LIDT (J/cm2) will not scale independently of beam diameter due to the larger size beam exposing more defects.
The pulse length must now be compensated for. The longer the pulse duration, the more energy the optic can handle. For pulse widths between 1 - 100 ns, an approximation is as follows:
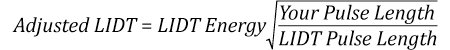
Use this formula to calculate the Adjusted LIDT for an optic based on your pulse length. If your maximum energy density is less than this adjusted LIDT maximum energy density, then the optic should be suitable for your application. Keep in mind that this calculation is only used for pulses between 10-9 s and 10-7 s. For pulses between 10-7 s and 10-4 s, the CW LIDT must also be checked before deeming the optic appropriate for your application.
Please note that we have a buffer built in between the specified damage thresholds online and the tests which we have done, which accommodates variation between batches. Upon request, we can provide individual test information and a testing certificate. Contact Tech Support for more information.
[1] R. M. Wood, Optics and Laser Tech. 29, 517 (1998).
[2] Roger M. Wood, Laser-Induced Damage of Optical Materials (Institute of Physics Publishing, Philadelphia, PA, 2003).
[3] C. W. Carr et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 127402 (2003).
[4] N. Bloembergen, Appl. Opt. 12, 661 (1973).
In order to illustrate the process of determining whether a given laser system will damage an optic, a number of example calculations of laser induced damage threshold are given below. For assistance with performing similar calculations, we provide a spreadsheet calculator that can be downloaded by clicking the button to the right. To use the calculator, enter the specified LIDT value of the optic under consideration and the relevant parameters of your laser system in the green boxes. The spreadsheet will then calculate a linear power density for CW and pulsed systems, as well as an energy density value for pulsed systems. These values are used to calculate adjusted, scaled LIDT values for the optics based on accepted scaling laws. This calculator assumes a Gaussian beam profile, so a correction factor must be introduced for other beam shapes (uniform, etc.). The LIDT scaling laws are determined from empirical relationships; their accuracy is not guaranteed. Remember that absorption by optics or coatings can significantly reduce LIDT in some spectral regions. These LIDT values are not valid for ultrashort pulses less than one nanosecond in duration.

A Gaussian beam profile has about twice the maximum intensity of a uniform beam profile.
CW Laser Example
Suppose that a CW laser system at 1319 nm produces a 0.5 W Gaussian beam that has a 1/e2 diameter of 10 mm. A naive calculation of the average linear power density of this beam would yield a value of 0.5 W/cm, given by the total power divided by the beam diameter:
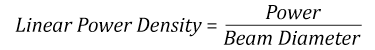
However, the maximum power density of a Gaussian beam is about twice the maximum power density of a uniform beam, as shown in the graph to the right. Therefore, a more accurate determination of the maximum linear power density of the system is 1 W/cm.
An AC127-030-C achromatic doublet lens has a specified CW LIDT of 350 W/cm, as tested at 1550 nm. CW damage threshold values typically scale directly with the wavelength of the laser source, so this yields an adjusted LIDT value:

The adjusted LIDT value of 350 W/cm x (1319 nm / 1550 nm) = 298 W/cm is significantly higher than the calculated maximum linear power density of the laser system, so it would be safe to use this doublet lens for this application.
Pulsed Nanosecond Laser Example: Scaling for Different Pulse Durations
Suppose that a pulsed Nd:YAG laser system is frequency tripled to produce a 10 Hz output, consisting of 2 ns output pulses at 355 nm, each with 1 J of energy, in a Gaussian beam with a 1.9 cm beam diameter (1/e2). The average energy density of each pulse is found by dividing the pulse energy by the beam area:
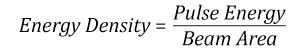
As described above, the maximum energy density of a Gaussian beam is about twice the average energy density. So, the maximum energy density of this beam is ~0.7 J/cm2.
The energy density of the beam can be compared to the LIDT values of 1 J/cm2 and 3.5 J/cm2 for a BB1-E01 broadband dielectric mirror and an NB1-K08 Nd:YAG laser line mirror, respectively. Both of these LIDT values, while measured at 355 nm, were determined with a 10 ns pulsed laser at 10 Hz. Therefore, an adjustment must be applied for the shorter pulse duration of the system under consideration. As described on the previous tab, LIDT values in the nanosecond pulse regime scale with the square root of the laser pulse duration:
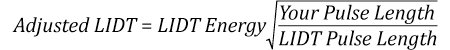
This adjustment factor results in LIDT values of 0.45 J/cm2 for the BB1-E01 broadband mirror and 1.6 J/cm2 for the Nd:YAG laser line mirror, which are to be compared with the 0.7 J/cm2 maximum energy density of the beam. While the broadband mirror would likely be damaged by the laser, the more specialized laser line mirror is appropriate for use with this system.
Pulsed Nanosecond Laser Example: Scaling for Different Wavelengths
Suppose that a pulsed laser system emits 10 ns pulses at 2.5 Hz, each with 100 mJ of energy at 1064 nm in a 16 mm diameter beam (1/e2) that must be attenuated with a neutral density filter. For a Gaussian output, these specifications result in a maximum energy density of 0.1 J/cm2. The damage threshold of an NDUV10A Ø25 mm, OD 1.0, reflective neutral density filter is 0.05 J/cm2 for 10 ns pulses at 355 nm, while the damage threshold of the similar NE10A absorptive filter is 10 J/cm2 for 10 ns pulses at 532 nm. As described on the previous tab, the LIDT value of an optic scales with the square root of the wavelength in the nanosecond pulse regime:
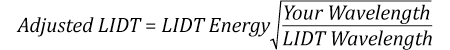
This scaling gives adjusted LIDT values of 0.08 J/cm2 for the reflective filter and 14 J/cm2 for the absorptive filter. In this case, the absorptive filter is the best choice in order to avoid optical damage.
Pulsed Microsecond Laser Example
Consider a laser system that produces 1 µs pulses, each containing 150 µJ of energy at a repetition rate of 50 kHz, resulting in a relatively high duty cycle of 5%. This system falls somewhere between the regimes of CW and pulsed laser induced damage, and could potentially damage an optic by mechanisms associated with either regime. As a result, both CW and pulsed LIDT values must be compared to the properties of the laser system to ensure safe operation.
If this relatively long-pulse laser emits a Gaussian 12.7 mm diameter beam (1/e2) at 980 nm, then the resulting output has a linear power density of 5.9 W/cm and an energy density of 1.2 x 10-4 J/cm2 per pulse. This can be compared to the LIDT values for a WPQ10E-980 polymer zero-order quarter-wave plate, which are 5 W/cm for CW radiation at 810 nm and 5 J/cm2 for a 10 ns pulse at 810 nm. As before, the CW LIDT of the optic scales linearly with the laser wavelength, resulting in an adjusted CW value of 6 W/cm at 980 nm. On the other hand, the pulsed LIDT scales with the square root of the laser wavelength and the square root of the pulse duration, resulting in an adjusted value of 55 J/cm2 for a 1 µs pulse at 980 nm. The pulsed LIDT of the optic is significantly greater than the energy density of the laser pulse, so individual pulses will not damage the wave plate. However, the large average linear power density of the laser system may cause thermal damage to the optic, much like a high-power CW beam.
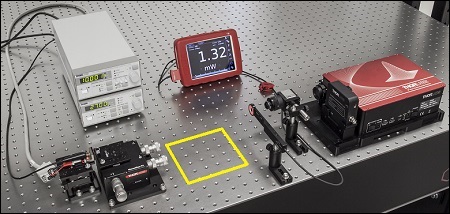
Click to Enlarge
Figure 1: The beam circularization systems were placed in the area of the experimental setup highlighted by the yellow rectangle.

Click to Enlarge
Figure 4: Spatial Filter System

Click to Enlarge
Figure 3: Anamorphic Prism Pair System

Click to Enlarge
Figure 2: Cylindrical Lens Pair System
Comparison of Circularization Techniques for Elliptical Beams
Edge-emitting laser diodes emit elliptical beams as a consequence of the rectangular cross sections of their emission apertures. The component of the beam corresponding to the narrower dimension of the aperture has a greater divergence angle than the orthogonal beam component. As one component diverges more rapidly than the other, the beam shape is elliptical rather than circular.
Elliptical beam shapes can be undesirable, as the spot size of the focused beam is larger than if the beam were circular, and as larger spot sizes have lower irradiances (power per area). Techniques for circularizing an elliptical beam include those based on a pair of cylindrical lenses, an anamorphic prism pair, or a spatial filter. This work investigated all three approaches. The characteristics of the circularized beams were evaluated by performing M2 measurements, wavefront measurements, and measuring the transmitted power.
While it was demonstrated that each circularization technique improves the circularity of the elliptical input beam, each technique was shown to provide a different balance of circularization, beam quality, and transmitted power. The results of this work, which are documented in this Lab Fact, indicate that an application's specific requirements will determine which is the best circularization technique to choose.
Experimental Design and Setup
The experimental setup is shown in Figure 1. The elliptically-shaped, collimated beam of a temperature-stabilized 670 nm laser diode was input to each of our circularization systems shown in Figures 2 through 4. Collimation results in a low-divergence beam, but it does not affect the beam shape. Each system was based on one of the following:
- LJ1874L2-A and LJ1638L1-A Plano-Convex Convex Cylindrical Lenses (Figure 2)
- PS873-A Unmounted Anamorphic Prism Pair (Figure 3)
- Previous Generation KT310 Spatial Filter System with P5S Ø5 µm Pinhole (Figure 4)
The beam circularization systems, shown to the right, were placed, one at a time, in the vacant spot in the setup highlighted by the yellow rectangle. With this arrangement, it was possible to use the same experimental conditions when evaluating each circularization technique, which allowed the performance of each to be directly compared with the others. This experimental constraint required the use of fixturing that was not optimally compact, as well as the use of an unmounted anamorphic prism pair, instead of a more convenient mounted and pre-aligned anamorphic prism pair.
The characteristics of the beams output by the different circularization systems were evaluated by making measurements using a power meter, a wavefront sensor, and an M2 system. In the image of the experimental setup, all of these systems are shown on the right side of the table for illustrative purposes; they were used one at a time. The power meter was used to determine how much the beam circularization system attenuated the intensity of the input laser beam. The wavefront sensor provided a way to measure the aberrations of the output beam. The M2 system measurement describes the resemblance of the output beam to a Gaussian beam. Ideally, the circularization systems would not attenuate or aberrate the laser beam, and they would output a perfectly Gaussian beam.
Edge-emitting laser diodes also emit astigmatic beams, and it can be desirable to force the displaced focal points of the orthogonal beam components to overlap. Of the three circularization techniques investigated in this work, only the cylindrical lens pair can also compensate for astigmatism. The displacement between the focal spots of the orthogonal beam components were measured for each circularization technique. In the case of the cylindrical lens pair, their configuration was tuned to minimize the astigmatism in the laser beam. The astigmatism was reported as a normalized quantity.
Experimental Results
The experimental results are summarized in the following table, in which the green cells identify the best result in each category. Each circularization approach has its benefits. The best circularization technique for an application is determined by the system’s requirements for beam quality, transmitted optical power, and setup constraints.
Spatial filtering significantly improved the circularity and quality of the beam, but the beam had low transmitted power. The cylindrical lens pair provided a well-circularized beam and balanced circularization and beam quality with transmitted power. In addition, the cylindrical lens pair compensated for much of the beam's astigmatism. The circularity of the beam provided by the anamorphic prism pair compared well to that of the cylindrical lens pair. The beam output from the prisms had better M2 values and less wavefront error than the cylindrical lenses, but the transmitted power was lower.
| Method | Beam Intensity Profile | Circularitya | M2 Values | RMS Wavefront | Transmitted Power | Normalized Astigmatismb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collimated Source Output (No Circularization Technique) |
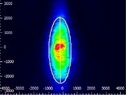 Click to Enlarge Scale in Microns |
0.36 | Y Axis: 1.63 |
0.17 | Not Applicable | 0.67 |
| Cylindrical Lens Pair | 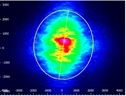 Click to Enlarge Scale in Microns |
0.84 | X Axis: 1.90 Y Axis: 1.93 |
0.30 | 91% | 0.06 |
| Anamorphic Prism Pair |
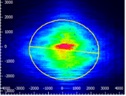 Click to Enlarge Scale in Microns |
0.82 | X Axis: 1.60 Y Axis: 1.46 |
0.16 | 80% | 1.25 |
| Spatial Filter | 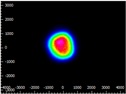 Click to Enlarge Scale in Microns |
0.93 | X Axis: 1.05 Y Axis: 1.10 |
0.10 | 34% | 0.36 |
Components used in each circularization system were chosen to allow the same experimental setup be used for all experiments. This had the desired effect of allowing the results of all circularization techniques to be directly compared; however, optimizing the setup for a circularization technique could have improved its performance. The mounts used for the collimating lens and the anamorphic prism pair enabled easy manipulation and integration into this experimental system. It is possible that using smaller mounts would improve results by allowing the members of each pair to be more precisely positioned with respect to one another. In addition, using made-to-order cylindrical lenses with customized focal lengths may have improved the results of the cylindrical lens pair circularization system. All results may have been affected by the use of the beam profiler software algorithm to determine the beam radii used in the circularity calculation.
Additional Information
Some information describing selection and configuration procedures for several components used in this experimental work can be accessed by clicking the following hyperlinks:
| Posted Comments: | |
David Angeley
(posted 2020-02-07 09:47:08.26) This is a question with regards to cylindrical lenses, part # LJ4862 & LJ4395.
We will use these as an anamorphic telescope. We want to mount these lenses and reference the side in order to set the rotation or clocking of these optics. Ideally we want to rely on machining tolerances instead of putting in a rotation adjustment.
Can you provide a tolerance on how well the cylindrical axis references one or all of the sides (maybe one side is the best reference). I see this called out as axial twist with other vendors, Do you have a tolerance on axial twist for these items.
Thank You,
Dave nbayconich
(posted 2020-02-10 02:34:02.0) Thank you for contacting Thorlabs. We specify centration error for our cylindrical lenses which also includes axial twist. For LJ4862 the centration will be < 3arcmin and for LJ4395 <5 arcmin. tor
(posted 2010-11-19 08:39:48.0) A reply from Tor at Thorlabs: We are happy to provide customized optics. If you would like to know whether we can meet your specific needs, please send your request to techsupport@thorlabs.com. user
(posted 2010-11-18 17:43:20.0) We actually need to focus horizontally, not vertically, so we could really use a lens with H=45mm and the other curvature. We can turn LJ4147-UV on its side, but this gives us less coverage. |
 Products Home
Products Home
















 Plano-Convex, UV Fused Silica
Plano-Convex, UV Fused Silica