Fixed Focus Collimation Packages: SMA905 Connectors

- Mates with SMA905 Connectors
- Simplifies Collimation of Output from Single Mode Fiber
- Collimated Beam Diameters Ranging from 0.64 mm to 4.0 mm
- Models Aligned at 13 Key Wavelengths from 405 nm to 4.55 µm
Back
Front
F220SMA-A
543 nm, Focal Length: 10.92 mm
Fixed Focus Collimators Contain
One Factory-Aligned Aspheric Lens
F240SMA-A Collimator Mounted in an
AD12F SM1-Threaded Collimator Adapter

Please Wait
Features
- Fiber Collimators with SMA905 Connectors for Single Mode Patch Cables
- Aligned at Wavelengths from 405 nm to 4.55 µm (See Table to the Right)
- Collimated Beam Diameters from 0.64 mm to 4.0 mm Depending on Wavelength
- Each Collimation Package is Factory Aligned
- Simplifies Fiber-Coupled Detection Systems
- Non-Magnetic Stainless Steel Housing
- Custom Options, Including Custom Alignment Wavelengths, Available by Contacting Tech Support
These fiber collimation packages are pre-aligned to collimate light from an SMA905-terminated fiber with diffraction-limited performance. Because these fiber collimators have no movable parts, they are compact and easy to integrate into an existing setup. Due to chromatic aberration, the effective focal length (EFL) of the aspheric lens is wavelength dependent. The design wavelength indicates the wavelength of ideal beam divergence (see the Divergence Plots and Calculations tabs for more information). Collimation packages at select design wavelengths are available with different collimated beam diameters. Select a wavelength from the quick links table to the right for details.

Click to Enlarge
A fiber collimator and mounted asphere focus light exiting a patch cable using the AD1109F adapter.
The aspheric lens is factory aligned for collimation at the design wavelength when connected to its specified single mode fiber patch cable. In addition, the aspheric lens has an AR coating on both sides that minimizes surface reflections. For some applications they may also be used at other wavelengths within the AR coating range; please refer to the theoretical divergence plot for each collimator to determine if it is appropriate for your application. The operating temperature range for these collimators is -40 °C to 93 °C. Please note that these collimation packages are not vacuum compatible. Collimation packages with custom alignment wavelengths, operating temperature ranges, or vacuum compatibility are available by contacting Tech Support.
These fiber collimators are intended for use with single mode patch cables but can also be used with small-core, low-NA, multimode fiber optic patch cables. For improved performance, we recommend using these collimators with our AR-coated multimode patch cables. These cables feature an antireflective coating on one fiber end for increased transmission and improved return loss at the fiber-to-free-space interface. Please note performance specifications are guaranteed only when used with single mode fiber.
To mount these fiber collimation packages, we recommend using our collimator mounting adapters, including our kinematic collimator mounting adapters that provide pitch and yaw adjustment. In addition to Ø1/2" and Ø1" unthreaded versions, options are available with external SM05 (0.535"-40), RMS (0.800"-36), or SM1 (1.035"-40) threading. The collimation packages with external M12 x 0.5 threading can be mounted directly into our cage plate CP1M12(/M) to be integrated into our 30 mm cage systems.
Mid-IR Collimators
For our collimators with an alignment wavelength of 3.45 µm and 4.55 µm, we manufacture fluoride fiber patch cables. Although these collimators are factory aligned for a specific wavelength, they have low divergence angles over a broad range of wavelengths. Therefore, they may be used at other wavelengths within the AR coating range. Please refer to the theoretical divergence plot for each collimator to determine if it is appropriate for your application.
Alternatives
We also offer a line of adjustable collimation packages called FiberPorts that are well suited for a wide range of wavelengths. These are ideal solutions for adjustable, compact fiber couplers. For other collimation and coupling options, please see our Collimator Guide tab or contact Tech Support.
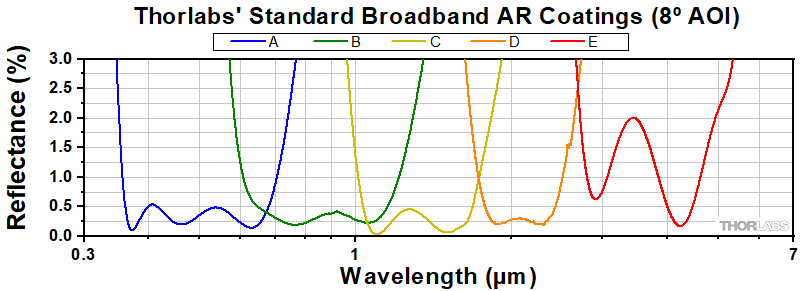
| Coating Information | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coating Designation | 405 | Aa | Ba | 1064 | C | D | E |
| Coating Range |
395 - 415 nm | 350 - 700 nm or 400 - 600 nm |
600 - 1050 nm or 650 - 1050 nm |
1050 - 1075 nm | 1050 - 1620 nm or 1050 - 1700 nm |
1.8 - 3.0 µm | 3 - 5 µm |
| Reflectance | Ravg<0.25% @ 405 nm | Ravg < 0.5% within Coating Range |
Ravg < 0.5% within Coating Range |
<0.25% @ 1064 nm | Ravg < 0.5% within Coating Range |
Ravg < 1.0% within Coating Range |
Ravg < 1.0% within Coating Range |
| θ | Divergence Angle |
| D | Mode-Field Diameter (MFD) |
| f | Focal Length of Collimator |
The divergence angle (in Degrees) ,
,
where D and f must be in the same units.
Divergence Angle Comparison
The divergence angle can be estimated using the formula shown to the right, given that the light emerging from the fiber has a Gaussian intensity profile. This formula works well for single mode fibers but will underestimate the divergence angle for multimode fibers where the light emerging from the fiber has a non-Gaussian intensity profile.
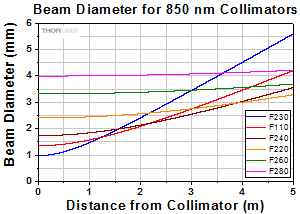
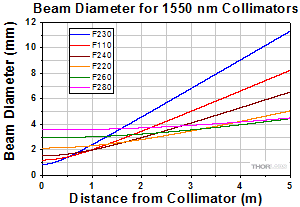
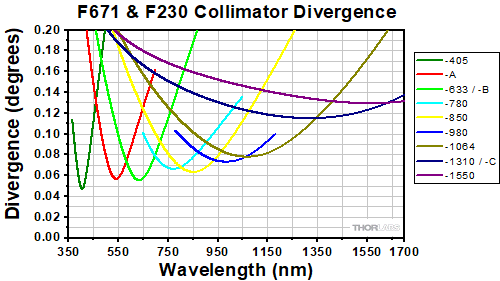
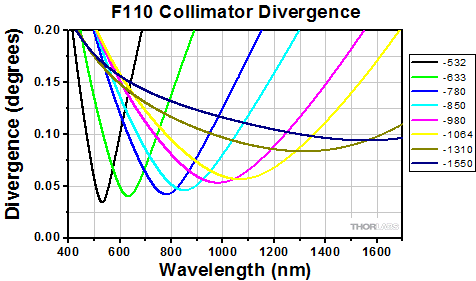
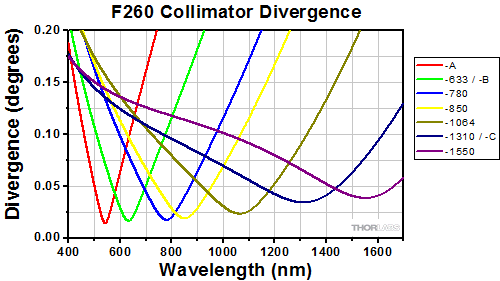
Simulations of the theoretical divergence when using one of our standard collimators at wavelengths other than the design wavelength are shown in the graphs below. For example, if you need to collimate 700 nm light from a fiber into a ~1.5 mm diameter beam, the F240SMA-780 collimator (represented by the '-780' line in the F240 graph below) can be used but will provide a higher divergence than at its design wavelength of 780 nm. Individual theoretical divergence plots and raw data are also available below for each collimator. Please contact Tech Support to request a collimator aligned at a custom wavelength.
Theoretical Approximation of the Divergence Angle
The beam diameter as a function of propagation distance was simulated for each of our collimators at the design wavelength, assuming input from the design fiber and a Gaussian intensity profile. The design wavelength and fiber are specified in the caption for each graph.
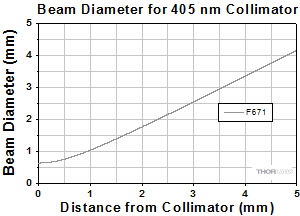
Click to Enlarge
At 405 nm with S405-XP Fiber
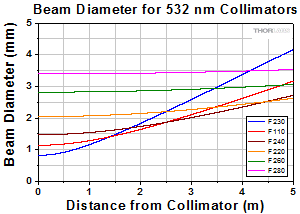
Click to Enlarge
At 532 nm with 460HP Fiber
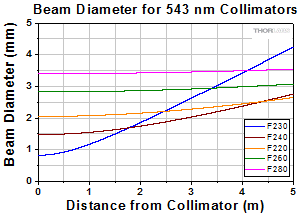
Click to Enlarge
At 543 nm with 460HP Fiber
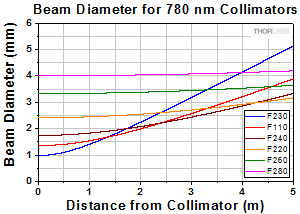
Click to Enlarge
At 780 nm with 780HP Fiber
Click to Enlarge
At 850 nm with 780HP Fiber
Click to Enlarge
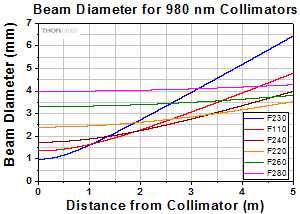
At 980 nm with SM980-5.8-125 Fiber
Click to Enlarge
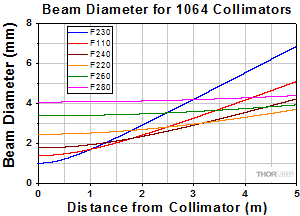
At 1064 nm with SM980-5.8-125 Fiber
Click to Enlarge
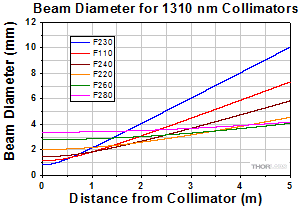
At 1310 nm with SMF-28-J9 Fiber
Click to Enlarge
At 1550 nm with SMF-28-J9 Fiber
Click to Enlarge
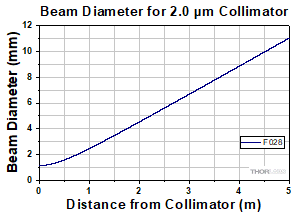
At 2000 nm with SM2000 Fiber
Click to Enlarge
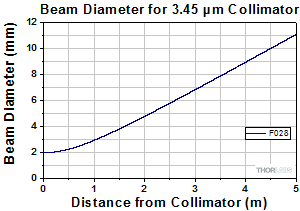
At 3.45 µm with ZrF4 Fiber
Click to Enlarge
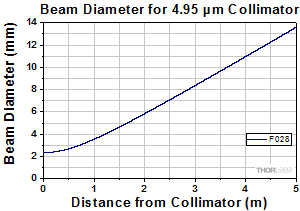
At 4.55 µm with InF3 Fiber
Theoretical Approximation of the Divergence Angle
The full-angle beam divergence listed in the specifications tables is the theoretically-calculated value associated with the fiber collimator. This divergence angle is easy to approximate theoretically using the formula below as long as the light emerging from the fiber has a Gaussian intensity profile. Consequently, the formula works well for single mode fibers, but it will underestimate the divergence angle for multimode (MM) fibers since the light emerging from a multimode fiber has a non-Gaussian intensity profile.
The Full Divergence Angle (in degrees) is given by
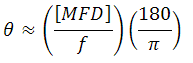
where MFD is the mode field diameter and f is the focal length of the collimator. (Note: MFD and f must have the same units in this equation).
Example:
When the F220FC-A collimator (f ≈ 11.0 mm; not exact since the design wavelength is 543 nm) is used to collimate 515 nm light emerging from a 460HP fiber (MFD = 3.5 µm), the divergence angle is approximately given by
θ ≈ (0.0035 mm / 11.0 mm) x (180 / pi) = 0.018°.
When the beam divergence angle was measured for the F220FC-A collimator, a 460HP fiber was used with 543 nm light. The result was a divergence angle of 0.018°.
Theoretical Approximation of the Output Beam Diameter
The output beam diameter can be approximated from
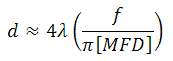
where λ is the wavelength of light being used, MFD is the mode field diameter, and f is the focal length of the collimator. (Note: MFD and f must have the same units in this equation).
Example:
When the F240FC-1550 collimator (f = 8.18 mm) is used with the P1-SMF28E-FC-1 patch cable (MFD = 10.4 µm) and 1550 nm light, the output beam diameter is
d ≈ (4)(0.00155 mm)[8.18 mm / (pi · 0.0104 mm)] = 1.55 mm.
Theoretical Approximation of the Maximum Waist Distance
The maximum waist distance, which is the furthest distance from the lens the waist can be located in order to maintain collimation, may be approximated by
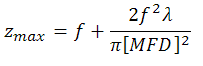
where f is the focal length of the collimator, λ is the wavelength of light used, and MFD is the mode field diameter. (Note: MFD and f must have the same units in this equation).
Example:
When the F220FC-532 collimator (f = 10.9 mm) is used with the P1-460B-FC-1 patch cable (MFD ≈ 4.0 µm; calculated approximate value) and 532 nm light, then the maximum waist distance is approximately
zmax ≈ 10.9 mm + [2 · (10.9 mm)2 · 0.000532 mm] / [pi · (0.004 mm)2] = 2526 mm.
Insights into Best Lab Practices
Scroll down to read about some practices we follow when setting up lab equipment.
- Align Fiber Collimators to Create Free Space Between Fibers
- Fiber Collimators: Tip for Mounting with Adapters
Click here for more insights into lab practices and equipment.
Align Fiber Collimators to Create Free Space Between Fibers
Two collimators, inserted into a fiber optic setup, provide free-space access to the beam. The first collimator accepts the highly diverging light from the first fiber and outputs a free-space beam, which propagates with an approximately constant diameter to the second collimator. The second collimator accepts the free-space beam and couples that light into the second fiber. Some collimation packages, including the pair used in this demonstration, are designed for use with optical fibers and mate directly to fiber connectors.
Ideally, 100% of the light emitted by the first fiber would be coupled into the second fiber, but some light will always be lost due to reflections, scattering, absorption, and misalignment. Misalignment, typically the largest source of loss, can be minimized using the alignment and stabilization techniques described in this video.
In this demonstration, the first fiber is single mode. The optical power incident on the second collimator, as well as the power output by the second fiber, are measured. When the second fiber is multimode with a 50 µm diameter core, alignment resulted in 91% of the power incident on the second collimator being measured at the fiber output. This value was 86% when the second fiber is single mode. Some differences in collimator designs, and their effects on the characteristics of the collimated beams, are also discussed.
If you would like more information about tips, tricks, and other methods we often use in the lab, we recommend our other Video Insights. In addition, our webinars provide practical and theoretical introductions to our different products.
| Products Featured During Demonstration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber-Coupled Laser | Kinematic Mounts | Fiber Adapter Cap (for Power Sensor) |
Single Mode Patch Cable (FC/PC) | Fiber Cable Storage Reels |
| Triplet Fiber Optic Collimators | Power Sensor | Power Meter | Hybrid Single Mode Patch Cable | 2" Posts |
| Adapter (Mount-to-Collimator) |
SM1 Thread Adapter (for Power Sensor) |
Fiber Connector Cleaner | Step-Index Multimode Patch Cable | Ø1/2" Post Holders |
Date of Last Edit: April 21, 2021
Fiber Collimators: Tip for Mounting with Adapters
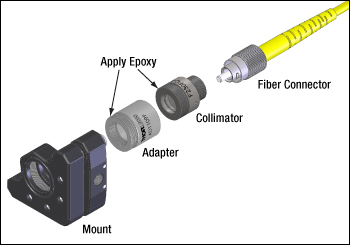
Click to Enlarge
Figure 1: The components shown above are joined using threaded interfaces. Since unscrewing the fiber connector could unintentionally loosen connections between the other components, Thorlabs suggests applying epoxy to the other two interfaces to immobilize them.
Fiber collimators are often used to introduce light into an optical setup from a fiber coupled source. Thorlabs offers a variety of fiber collimator packages, some only provide a smooth barrel (like the triplet collimators) and others have a metric thread at the end of the barrel (like the asphere collimators).
For both packages, Thorlabs typically suggests the use of an adapter with a nylon tipped set screw that holds the barrel against a two line contact.
Adapters for the external thread are available (AD1109F) that allow the user to thread the fiber collimator into a mount.
However, the use of these adapters results in a stack up of threaded interfaces (threaded fiber connector, threaded collimator, and threaded adapter). As a result, it is possible that unscrewing the fiber connector could inadvertently loosen another thread interface and create an unknown source of instability in the setup.
For this reason, Thorlabs suggests epoxying the threaded fiber collimators into the threaded mounts if that mounting mechanism is preferred.
Figure 1 indicates the assembly order and places to apply the epoxy.
Date of Last Edit: Dec. 4, 2019
| Posted Comments: | |
Alex Klekx
(posted 2024-03-04 17:58:49.003) Hello, I've purchased F110SMA-633 and it meets the specification on the output diameter nicely. However, I would like to further decrease the beam size after that collimator, say, 4-5 times. What would be the best solution for that?
Thank you in advance,
Alex cdolbashian
(posted 2024-03-11 03:36:32.0) Thank you for reaching out to us with this inquiry Alex. You can use something like a beam expander, in reverse, although the divergence of your collimated beam will increase by approximately the same factor in which our beam is reduced. I have contacted you directly to discuss this in further detail. Guillaume Clément
(posted 2023-08-17 08:15:25.467) Hello,
What is the material of the lens in the F220SMA please ?
I would need it for simulation purposes.
Thanks in advance,
Best,
Guillaume jdelia
(posted 2023-08-17 02:28:56.0) Thank you for contacting Thorlabs. The lens used in the F220SMA-532 is made out of D-ZK3 glass. user
(posted 2023-01-06 15:24:30.447) I'm using the F220SMA-1550 collimator for a 1470 nm laser with 75 W.
The values from the Full-Angle Divergence diagram and the Beam Diameter Plots seemed sufficient for my application.
Now I have the following problem:
The beam diameter of my laser deviates greatly from the beam diameter plots. The beam is not being collimated at all, has a very high divergence and after about 20 cm the beam diameter is 15 mm and more.
Since I did not find any information about the damage threshold in the datasheet, I have the suspicion that the collimator is not suitable for the powers at 1470 nm and could be defective now. Do you have any information about the damage threshold of the collimator? cdolbashian
(posted 2023-01-10 03:14:10.0) Good afternoon and thank you for the feedback! I have contacted you directly to discuss your application and potential issues! user
(posted 2021-05-13 04:10:26.32) I'd like to collimate the output of a 105 micron NA 0.22 fiber with 200 W of power at 976 nm to between 2 and 4 mm. I'm looking at F220SMA-980. First, what can I expect for a beam diameter when collimating with my fiber? Second, is it likely that this collimator can handle this power level? YLohia
(posted 2021-08-27 02:20:08.0) Thank you for contacting Thorlabs. The collimated beam diameter right at the exit of the collimator can be estimated as d = 2 * f * tan(NA of fiber) = 4.99 mm. Assuming that the signal is CW, 200 W at this wavelength will be fine for the collimator. Furkan Fatih KÖKER
(posted 2021-03-16 16:27:09.043) Hi I have a 60W 808 nm fibre with SMA905 connector that I want to roughly collimate. the fiber NA is 0.22 which collimator would you recommend? Do you have any damage threshold information about collimator products? YLohia
(posted 2021-03-16 11:54:14.0) Thank you for contacting Thorlabs. Unfortunately, we don't have formal damage threshold test data for these collimators on-hand, but based on data from similar parts we do not expect 60W CW @ 808 nm to damage these collimators (please note that this is not a formal spec). Given that the power levels are quite high, please ensure that the surface of the lens is clean and free of dust/debris prior to operation. Any of the FxxxSMA-780 parts should be suitable for your application. The F240SMA-780 may perform particularly well for you, depending on your application. Clayton Chang
(posted 2020-11-25 21:29:14.647) F220SMA-980, can this be used with a 980nm 50W diode laser? YLohia
(posted 2020-12-08 03:25:54.0) Thank you for contacting Thorlabs. Unfortunately, we don't have damage threshold test data for this specific collimator on-hand, but based on data from similar parts we do not expect 50W CW @ 980 nm to damage this part (please note that this is not a formal spec). Jeremy Chang
(posted 2020-11-25 01:59:28.06) I have a multimode fiber laser, it is a CW laser. Now I need a collimator to make the beam size below 2mm, and Laser power is 200W. Which series should I pick ? YLohia
(posted 2020-12-29 03:22:24.0) Hello Jeremy, what wavelength will you be operating these at and what NA and the type of a connector does the fiber output of your laser have? I had reached out to you directly at the time of your original post. If you still need assistance picking out a suitable collimator, please email techsupport@thorlabs.com. Jeremy Chang
(posted 2020-11-25 01:57:07.06) I have a multimode fiber CW laser which is 200W. I need a collimator. I wonder which series should I pick ? Abdul Rahman Johari
(posted 2020-10-27 22:57:35.063) Hello,
I have a request for this item. Can you make custom for external threading to M10?
Thank you. YLohia
(posted 2020-10-28 09:35:07.0) Hello, custom versions of these collimators can be requested by contacting techsupport@thorlabs.com or by clicking the "Request Quote" button above. We will discuss the possibility of offering this customization directly. Aleksandr Novikov
(posted 2020-01-30 08:46:13.407) Hello!
Is it possible to know the transmission of the collimator F280SMA-C on the wavelength about 3000 nm? YLohia
(posted 2020-02-18 08:12:23.0) Hallo, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. I have reached out to you directly regarding this. Brenden Villars
(posted 2019-11-27 12:17:01.857) Any information you may have on the power handling of these modules would be greatly appreciated. Apologies if I've missed it somewhere on this page or on the datasheets. nbayconich
(posted 2019-12-02 04:38:42.0) At the moment we have not yet formally tested these optics for pulsed or CW damage thresholds. I will reach out to you to discuss the specifications of your laser source to see if it will be suitable with these products. paul.taylor
(posted 2018-09-18 12:59:47.073) Hi
I have a 30W 808 nm fibre with SMA905 connector that I want to roughly collimate. the fiber NA is 0.22
which collimator would you recommend? YLohia
(posted 2018-09-18 09:02:21.0) Hello, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. Based on our discussion via email, for a ~2mm diameter beam, the PAF2S-7B or F240SMA-850 would be good options to look into. axb1179
(posted 2018-05-24 15:11:40.373) Hi, is it possible to obtain the transmission graph for the lens that is used in the F240SMA-780 collimator. YLohia
(posted 2018-05-24 10:32:12.0) Hello, the 352240-B lens is used in the F240SMA-780 collimator. The transmission plot can be obtained by clicking the blue "info" icon next to the part number on this (https://www.thorlabs.com/newgrouppage9.cfm?objectgroup_id=3811&pn=352240-B) page. michael.moeller
(posted 2018-03-17 14:51:12.853) Dear Sir oder Madam,
is it possible to realign this collimator in order to image the fiber end face at an adjustable distance? llamb
(posted 2018-03-31 10:19:21.0) Hello, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. This may be feasible as a custom-aligned collimator, though aspheric lenses are often not ideal for imaging. Objective lenses or GRIN lenses would be better suited to image a fiber end face. We will reach out to you directly to discuss a possible customization. thomas.dalby
(posted 2017-08-02 16:00:02.807) Hello, are you able to provide the reflectance data for AR coating C down to 600nm? Thanks nbayconich
(posted 2017-08-10 10:16:15.0) Thank you for contacting Thorlabs. I will reach out to you directly with extended reflectivity data for our -C coating. selwinhageraats
(posted 2016-02-22 09:09:11.747) Dear Sir or Madam,
We are looking for a collimator capable of collimating broadband light exiting an SMA fiber. The wavelengths we intend to cover lie between 200 and 800 nm approximately. Transmission above 50% for the whole wavelength range would be highly preferable. Would any of the fixed focus collimators offered by Thorlabs meet this requirement? Also, are the front and backside of the collimator both SMA-compatible? That is, could it function as a connector between a male and female SMA thread? We intend to use the collimator as a connection between an optical fiber and the input of an echelle spectrometer.
Thanks in advance. besembeson
(posted 2016-03-04 01:33:13.0) Response from Bweh at Thorlabs USA: These can be used but the performance (degree of collimation and throughput) will vary over the wavelength range. These are manufactured with the lens position optimized for minimum divergence at a single wavelength. They are also AR coated to have excellent throughput over different wavelength ranges as indicated. The fiber input end has SMA connector while the output end has either M11x0.5 or M12x0.5 thread and we provide various adapters to connect to other components. mhope
(posted 2015-10-27 15:13:45.06) What is the CW power handling capability of these? We have an 808nM beam exiting from an armored SMA MM fiber. The beam power will be ~1.5W, the core diameter is 125um. besembeson
(posted 2015-10-29 11:43:14.0) Response from Bweh at Thorlabs USA: This could be suitable, depending on the numerical aperture of your fiber. I will follow-up with you. feut.alexis
(posted 2015-05-13 10:12:57.823) Dear Thorlabs, I am using your F240SMA-B collimator into an optical system, and to optimize my system thanks to an optical software (opticstudio by Zemax), i need more information about the collimator.
Can you give me all technical information about the lens into the collimator ? And the real distance from the fiber to the lens in the collimator ?( I use a M37L02 fiber connector, d=550um, NA=0.22 )
Thanking you by advance. jlow
(posted 2015-08-25 11:43:50.0) Response from Jeremy at Thorlabs: The Zemax file for the F240SMA-B is located on the webpage for the item, http://www.thorlabs.com/thorproduct.cfm?partnumber=F240SMA-B, on the right hand side. zitka12
(posted 2015-02-17 22:47:40.82) Hello, what is divergence of F671SMA-405 for waveleght 280 nm. Or how its working on this wave lenght? besembeson
(posted 2015-02-18 08:02:49.0) Response from Bweh at Thorlabs USA: The lens used in the F671SMA-405 is made from ECO-550 which has very poor transmission at 280nm so we would not recommend this for that wavelength. I will share the transmission graph with you by email and look into alternatives for your application. tcohen
(posted 2012-06-27 15:04:00.0) Response from Tim at Thorlabs: The short answer is no, I would not recommend this part for 40W. There are a few things we need to look at in order to determine the power handling capability. First let’s look at the collimating lens. We see from the table that the lens in the F220SMA-780 is AR coated D-K59. These collimators also utilize epoxy. A conservative estimate we have for these lenses is approximately ~100W/cm^2. Let’s say your power is 40W and your beam diameter is 1mm. We then see that the power density is 40W/.05cm*.05cm*pi or 5093W/cm^2 (1mm BD). Now let us turn our attention to the fiber and the connector. A rough estimate for standard fiber is 10-15mW/um^2 and a typical threshold for our standard connectors is 2W. Whether you are collimating or coupling will also alter the damage threshold. If you use a wavelength of 808nm, you can expect to see ~10um chromatic focal length shift from a 780nm collimator. If focal shifts are present, coupling efficiency will be reduced and therefore so will the damage threshold. We do have high power fiber cables with SMA connectors rated to 50W: http://www.thorlabs.de/NewGroupPage9.cfm?ObjectGroup_ID=4393. To summarize our three parameters: standard connectors would not be suitable. Most standard fiber would not be suitable as well. High power connectors and fiber would be needed for this application, and even with this, we can see that the third item of interest, the collimator itself, is still a limiting factor. I will contact you to discuss other ways to collimate your source. vgvg1
(posted 2012-06-26 13:43:23.0) Hello. How much power can handle these collimators? Can it handle 40W 808nm? tcohen
(posted 2012-05-08 10:12:00.0) Response from Tim at Thorlabs: Thank you for your recommendation. The Adjustable U-Benches offer a stable and compact solution for fiber to fiber coupling. Depending on the requirements of the free space beam, this can be the ideal product for a SMF to SMF application. If there is ever a question of which product is best for your setup, please contact us at techsupport@thorlabs.com where an Applications Engineer will be able to assist you. user
(posted 2012-05-07 17:57:30.0) For SM fiber to fiber coupling a U-Bench is the way to go. See the FiberPorts premounted to a U-Bench, FBP-B-FC here:
http://www.thorlabs.com/NewGroupPage9.cfm?ObjectGroup_ID=3160 tcohen
(posted 2012-05-04 17:21:00.0) Response from Tim at Thorlabs: Thank you for your feedback. Some of the things to consider will be the desired travel distance, beam width, whether translation between the fiber/optic will be needed for optimization, etc. You can find descriptions of our collimation packages on the "Selection Guide" tab which may help you determine which would be preferable to you. I will contact you directly to discuss the options that may suit your application. scottie730318
(posted 2012-05-04 14:08:28.0) Dear Thorlabs, I want to use the "Fiber Optic Collimation/Coupling Packages" to collimate and refocus the beam out and into the Hi-1060 SMF fiber,respectively. And the wavelength varies from 1040nm to 1070nm . I need very high coupling efficiency. Could you recommend the collimate/focusing meet my need? Thanks. tcohen
(posted 2012-05-04 12:26:00.0) Response from Tim at Thorlabs: Thank you for your feedback! The F220XXX-780 and F240XXX-780 use the same lenses as found in the F220XXX-B and F240XXX-B respectively and it seems that the raw data was mistakenly linked to them. The chromatic focal length shift for the lens will be the same. However, they should be zeroed at the design wavelength for clarity. Thank you for pointing this out! user
(posted 2012-05-03 21:35:13.0) I should have mentioned the part numbers I was referring to: F240SMA-780, F220SMA-780. tcohen
(posted 2012-04-30 15:44:00.0) Response from Tim at Thorlabs: These collimators have centration better than 0.0015" (this excludes the fiber tolerances of the ferrule/core). aljasem
(posted 2012-04-26 05:25:58.0) Does Thorlabs -or somone else- have data about coaxiality of the collimators (SMA and FC)? tcohen
(posted 2012-03-21 14:46:00.0) Response from Tim at Thorlabs: Thank you for your feedback. If you are using a fiber coupled laser which you are collimating, please make sure that the NA of the lens is equal or greater than the NA of the fiber to reduce loss. The lens has an AR coating and is produced from D-K59 glass which at the design wavelength will have >99% transmission. However, if you are planning to use this to couple into fiber, you will have some coupling efficiency which will reduce your power. I have contacted you to discuss this further. afontova
(posted 2012-03-16 03:40:33.0) Dear Sir/Madamm
Recently I bought 3 SMA's collimator (F220SMA-780) in order to measure the power applied by a laser.
I would appretiate if you could send me information about the atenuation introduced by the collimater.
Kind Regards
Andreu tcohen
(posted 2012-03-08 13:07:00.0) Response from Tim at Thorlabs: Thank you for your feedback. Using the F240FC-780 outside of the design wavelength will cause a slight focal length shift. This will alter your coupling efficiency. However, for your application it seems that the F240FC-780 will meet your needs. Please note that it is still recommended to keep your focused spot size and NA of the collimator equal to or smaller than the MFD and NA of the fiber respectively. ZWJIORO
(posted 2012-03-08 07:30:46.0) Dear Thorlabs, I want to use the F240FC-780 to couple a collimated ellipse laser beam to a fiber to test the wavelength. And the wavelength varies from 770nm to 790nm . I do not need very high coupling efficiency. Could the F240FC-780 meet my need? Thanks. bdada
(posted 2012-01-31 23:39:00.0) Response from Buki at Thorlabs:
Thank you for using our feedback forum. You are correct that for maximum coupling, the focus spot size should be exactly the same as the MFD of the SM fiber. However, in reality, this is not always a possibility because the selection of the focal length is not continuous. One would then have to choose the closest focal length lens available.
We have contacted you to continue this discussion. niels.martinsen
(posted 2011-12-30 14:55:17.0) Hi!
In the "Overview" it is stated that:
“To obtain a high coupling efficiency, the NA of the patch cable needs to be greater than or equal to the NA of the collimator, and the diameter of the focused beam needs to be smaller than the MFD/core of the fiber. […].”
I understand that the beam width cannot exceed the fiber diameter, but why is the beam allowed to have a width less than the MFD of the fiber? Shouldn’t it ideally be equal to the MFD in order to maximize efficiency? jjurado
(posted 2011-06-17 13:38:00.0) Response from Javier at Thorlabs to acable: Hi Alex, we will update all the drawings with the OD call-outs shortly. acable
(posted 2011-06-16 18:39:56.0) Please add the OD to all the drawings, openned a couple and just found a callout for the thread, but nothing on the OD of the package. Thorlabs
(posted 2010-11-30 00:11:22.0) Response from Javier at Thorlabs to KO: We can provide adjustable SMA collimators as custom options. I will contact you directly to discuss the details. koakes
(posted 2010-11-26 13:26:19.0) Any reason that you dont supply adjustable collimators with SMA couplers as well as FC /APC?
I see that you have SMA fixed focus collimators.
Thanks
KO Greg
(posted 2010-04-05 15:42:44.0) A response from Greg at Thorlabs: This web page has been updated with accurate coating curves. We are checking on related products to ensure our curves are up to date on their web pages as well. Thank you again for pointing this out. Adam
(posted 2010-04-05 14:36:03.0) A response from Adam at Thorlabs: I understand your concern and we have checked with our optics division. The curves are incorrect and will be updated today. Thanks for bringing this to our attention. user
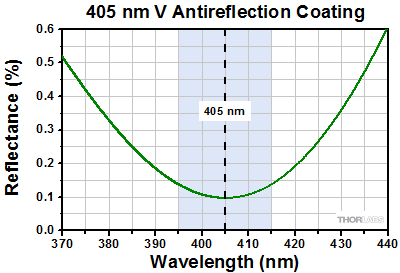
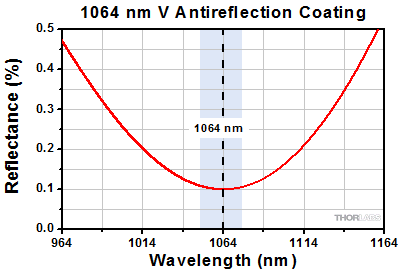
(posted 2010-04-04 16:18:41.0) Your AR coating curves are simply not believable, the broadband curves indicate something less than 0.05% on either end, and then the V-coat at 405 nm seems to go to zero. The one that looks believable is the 1064 nm coating with a roughly 0.08% with the center wavelength (minimum) being shifted slightly from the design wavelength. It would be helpful to have vertical scales that allowed the read to understand the residual reflectivity, and ideally the V-coats would have the same vertical scales.
Please review and confirm that your curves are updated and accurate. klee
(posted 2009-10-27 15:00:40.0) A response from Ken at Thorlabs to siegel: We have actually started engraving the part numbers on the barrels since 2007. Therefore, any new one that you purchase from now on will have part numbers on it. siegel
(posted 2009-10-27 14:36:23.0) Can you please include little labels that contain the part numbers that we can adhere to the barrels of the collimators when we receive them? Better yet, can you label them somehow (acid-etch, ink, whatever)? I have a drawer full of (unlabeled) collimators that I have no time to characterize. Had I known that they were not labeled, I would have labeled them the moment I opened the plastic pouches! But alas, its now too late for me. However maybe this message can save future generations from the same fate . . . Thanks. |
Fiber Collimator Selection Guide
Click on the collimator type or photo to view more information about each type of collimator.
| Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed FC, APC, or SMA Fiber Collimators |  |
These fiber collimation packages are pre-aligned to collimate light from an FC/PC-, FC/APC-, or SMA-terminated fiber. Each collimation package is factory aligned to provide diffraction-limited performance for wavelengths ranging from 405 nm to 4.55 µm. Although it is possible to use the collimator at detuned wavelengths, they will only perform optimally at the design wavelength due to chromatic aberration, which causes the effective focal length of the aspheric lens to have a wavelength dependence. |
| Air-Spaced Doublet, Large Beam Collimators |  |
For large beam diameters (Ø5.3 - Ø8.5 mm), Thorlabs offers FC/APC, FC/PC, and SMA air-spaced doublet collimators. These collimation packages are pre-aligned at the factory to collimate a laser beam propagating from the tip of an FC or SMA-terminated fiber and provide diffraction-limited performance at the design wavelength. |
| Triplet Collimators |  |
Thorlabs' High Quality Triplet Fiber Collimation packages use air-spaced triplet lenses that offer superior beam quality performance when compared to aspheric lens collimators. The benefits of the low-aberration triplet design include an M2 term closer to 1 (Gaussian), less divergence, and less wavefront error. |
| Achromatic Collimators for Multimode Fiber |  |
Thorlabs' High-NA Achromatic Collimators pair a meniscus lens with an achromatic doublet for high performance across the visible to near-infrared spectrum with low spherical aberration. Designed for use with high-NA multimode fiber, these collimators are ideal for Optogenetics and Fiber Photometry applications. |
| Reflective Collimators |  |
Thorlabs' metallic-coated Reflective Collimators are based on a 90° off-axis parabolic mirror. Mirrors, unlike lenses, have a focal length that remains constant over a broad wavelength range. Due to this intrinsic property, a parabolic mirror collimator does not need to be adjusted to accommodate various wavelengths of light, making them ideal for use with polychromatic light. Our fixed reflective collimators are recommended for collimating single and multimode fiber and coupling into multimode fiber. These collimators are available with UV-enhanced aluminum or protected silver reflective coatings and with FC/PC, FC/APC, or SMA connector compatibility. |
| Compact Reflective Collimators |  |
Thorlabs' Compact Reflective Collimators incorporate a 90° off-axis parabolic mirror with a protected silver coating. Because the focal length is independent of wavelength for an off-axis parabolic mirror, they are ideal for use with polychromatic light. Our fixed reflective collimators are recommended for collimating single and multimode fiber and coupling into multimode fiber. These collimators are directly compatible with our 16 mm cage system. They are available with FC/PC, FC/APC, or SMA connector inputs. |
| Adjustable Reflective Collimators |  |
Thorlabs' Adjustable Focus Reflective Collimators are based on a 90° off-axis parabolic (OAP) mirror with a protected silver coating. The adjustable fiber-to-OAP distance, combined with the OAP having a constant focal length across wavelengths, makes these collimators ideal for optimizing collimation or coupling of polychromatic light with single mode or multimode fiber. These adjustable collimators have a 15 mm reflected focal length and are available with FC/PC, FC/APC, or SMA connectors. |
| FiberPorts |  |
These compact, ultra-stable FiberPort micropositioners provide an easy-to-use, stable platform for coupling light into and out of FC/PC, FC/APC, or SMA terminated optical fibers. It can be used with single mode, multimode, or PM fibers and can be mounted onto a post, stage, platform, or laser. The built-in aspheric or achromatic lens is available with five different AR coatings and has five degrees of alignment adjustment (3 translational and 2 pitch). The compact size and long-term alignment stability make the FiberPort an ideal solution for fiber coupling, collimation, or incorporation into OEM systems. |
| Adjustable Fiber Collimators |  |
These collimators are designed to connect onto the end of an FC/PC, FC/APC, or SMA connector and contain an AR-coated aspheric lens. The distance between the aspheric lens and the tip of the fiber can be adjusted to compensate for focal length changes or to recollimate the beam at the wavelength and distance of interest. |
| Achromatic Fiber Collimators with Adjustable Focus |  |
Thorlabs' Achromatic Fiber Collimators with Adjustable Focus are designed with an effective focal length (EFL) of 20 mm, 40 mm, or 80 mm, have optical elements broadband AR coated for one of three wavelength ranges, and are available with FC/PC, FC/APC, or SMA905 connectors. A four-element, air-spaced lens design produces superior beam quality (M2 close to 1) and less wavefront error when compared to aspheric lens collimators. These collimators can be used for free-space coupling into a fiber, collimation of output from a fiber, or in pairs for collimator-to-collimator coupling over long distances, which allows the beam to be manipulated prior to entering the second collimator. |
| Zoom Fiber Collimators |  |
These collimators provide a variable focal length between 6 and 18 mm, while maintaining the collimation of the beam. As a result, the size of the beam can be changed without altering the collimation. This universal device saves time previously spent searching for the best suited fixed fiber collimator and has a very broad range of applications. They are offered with FC/PC, FC/APC, or SMA905 connectors with three different antireflection wavelength ranges to choose from. |
| Single Mode Pigtailed Collimators |  |
Our single mode pigtailed collimators come with one meter of fiber, consist of an AR-coated aspheric lens pre-aligned with respect to a fiber, and are collimated at one of eight wavelengths: 532 nm, 633 nm, 780 nm, 850 nm, 1030 nm, 1064 nm, 1310 nm, or 1550 nm. Although it is possible to use the collimator at any wavelength within the coating range, the coupling loss will increase as the wavelength is detuned from the design wavelength. |
| Polarization Maintaining Pigtailed Collimators |  |
Our polarization maintaining pigtailed collimators come with one meter of fiber, consist of an AR-coated aspheric lens pre-aligned with respect to a fiber, and are collimated at one of five wavelengths: 633 nm, 780 nm, 980 nm, 1064 nm, or 1550 nm. Custom wavelengths and connectors are available as well. A line is engraved along the outside of the housing that is parallel to the fast axis. As such, it can be used as a reference when polarized light is launched accordingly. Although it is possible to use the collimator at any wavelength within the coating range, the coupling loss will increase as the wavelength is detuned from the design wavelength. |
| GRIN Fiber Collimators |  |
Thorlabs offers gradient index (GRIN) fiber collimators that are aligned at a variety of wavelengths from 630 to 1550 nm and have either FC terminated, APC terminated, or unterminated fibers. Our GRIN collimators feature a Ø1.8 mm clear aperture, are AR-coated to ensure low back reflection into the fiber, and are coupled to standard single mode or graded-index multimode fibers. |
| GRIN Lenses |  |
These graded-index (GRIN) lenses are AR coated for applications at 630, 830, 1060, 1300, or 1560 nm that require light to propagate through one fiber, then through a free-space optical system, and finally back into another fiber. They are also useful for coupling light from laser diodes into fibers, coupling the output of a fiber into a detector, or collimating laser light. Our GRIN lenses are designed to be used with our Pigtailed Glass Ferrules and GRIN/Ferrule sleeves. |

| Item # | Alignment Wavelengtha |
Lens AR Coating | Waist Diameterb | Waist Distancec | Full Angle Divergenced | Theoretical Divergence |
NA | Focal Lengthe | Housing Outer Diameterf |
External Threadingf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F671SMA-405 | 405 nm | 395 - 415 nm (405) Ravg < 0.25% |
0.64 mm | 3.56 mm | 0.05° +0.01 / -0.00° | Raw Data |
0.60 | 4.02 mm | 11 mm | M11 x 0.5 |

| Item # | Alignment Wavelengtha |
Lens AR Coating | Waist Diameterb | Waist Distancec | Full-Angle Divergence | Theoretical Divergence |
NA | Focal Lengthd | Housing Outer Diameter |
External Threading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F110SMA-532 | 532 nm | 350 - 700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
1.14 mm | 5.85 mm | 0.03 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.38 | 6.09 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F240SMA-532 | 532 nm | 350 - 700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
1.48 mm | 6.96 mm | 0.03 +0.01 / -0.00°f | Raw Data |
0.51 | 7.86 mm | 12 mmh | M12 x 0.5h |
| F220SMA-532 | 532 nm | 350 - 700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
2.1 mm | 10.72 mm | 0.02 +0.01 / -0.00°f | Raw Data |
0.25 | 10.90 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |

| Item # | Alignment Wavelengtha |
Lens AR Coating | Waist Diameterb | Waist Distancec | Full-Angle Divergenced | Theoretical Divergence |
NA | Focal Lengthe | Housing Outer Diameter |
External Threading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F230SMA-A | 543 nm | 350 - 700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
0.80 mm | 4.02 mm | 0.05 +0.01 / -0.00° | Raw Data |
0.57 | 4.34 mm | 11 mmf | M11 x 0.5f |
| F240SMA-A | 543 nm | 350 - 700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
1.50 mm | 6.97 mm | 0.027 +0.01 / -0.00° | Raw Data |
0.51 | 7.86 mm | 12 mmg | M12 x 0.5g |
| F220SMA-A | 543 nm | 350 - 700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
2.06 mm | 10.74 mm | 0.019 +0.01 / -0.00° | Raw Data |
0.25 | 10.92 mm | 11 mmf | M11 x 0.5f |
| F260SMA-A | 543 nm | 350 - 700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
2.80 mm | 14.85 mm | 0.014 +0.01 / -0.00° | Raw Data |
0.17 | 15.01 mm | 11 mmf | M11 x 0.5f |
| F280SMA-A | 543 nm | 350 - 700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
3.30 mm | 17.40 mm | 0.012 +0.01 / -0.00° | Raw Data |
0.15 | 18.07 mm | 11 mmf | M11 x 0.5f |

| Item # | Alignment Wavelengtha |
Lens AR Coating | Waist Diameterb | Waist Distancec | Full-Angle Divergence | Theoretical Divergence |
NA | Focal Lengthd | Housing Outer Diameter |
External Threading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F230SMA-B | 633 nm | 650 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5%e |
0.80 mm | 4.07 mm | 0.056 +0.01 / -0.00°f | Raw Data |
0.56 | 4.43 mm | 11 mmh | M11 x 0.5h |
| F110SMA-633 | 633 nm | 350 - 700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
1.16 mm | 5.93 mm | 0.04 +0.01 / -0.00°g | Raw Data |
0.38 | 6.17 mm | 11 mmh | M11 x 0.5h |
| F240SMA-B | 633 nm | 600 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
1.49 mm | 6.96 mm | 0.031 +0.01 / -0.00°f | Raw Data |
0.50 | 7.94 mm | 12 mmi | M12 x 0.5i |
| F220SMA-B | 633 nm | 650 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5%e |
2.10 mm | 10.83 mm | 0.022 +0.01 / -0.00°f | Raw Data |
0.25 | 10.99 mm | 11 mmh | M11 x 0.5h |
| F260SMA-B | 633 nm | 600 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
2.88 mm | 14.87 mm | 0.016 +0.01 / -0.00°f | Raw Data |
0.16 | 15.15 mm | 11 mmh | M11 x 0.5h |
| F280SMA-B | 633 nm | 600 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
3.40 mm | 17.52 mm | 0.015 +0.01 / -0.00°f | Raw Data |
0.15 | 18.24 mm | 11 mmh | M11 x 0.5h |

| Item # | Alignment Wavelengtha |
Lens AR Coating | Waist Diameterb | Waist Distancec | Full-Angle Divergence | Theoretical Divergence |
NA | Focal Lengthd | Housing Outer Diameter |
External Threading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F230SMA-780 | 780 nm | 650 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
0.98 mm | 4.12 mm | 0.06 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.55 | 4.51 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F110SMA-780 | 780 nm | 650 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
1.36 mm | 6.00 mm | 0.04 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.37 | 6.24 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F240SMA-780 | 780 nm | 600 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
1.50 mm | 7.09 mm | 0.036 +0.01 / -0.00°f | Raw Data |
0.50 | 8.00 mm | 12 mmh | M12 x 0.5h |
| F220SMA-780 | 780 nm | 600 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
2.10 mm | 10.91 mm | 0.026 +0.01 / -0.00°f | Raw Data |
0.26 | 11.07 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F260SMA-780 | 780 nm | 650 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
3.33 mm | 15.11 mm | 0.026 +0.010 / -0.000°e | Raw Data |
0.16 | 15.29 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F280SMA-780 | 780 nm | 650 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
4.00 mm | 17.68 mm | 0.01 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.15 | 18.40 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |

| Item # | Alignment Wavelengtha |
Lens AR Coating | Waist Diameterb | Waist Distancec | Full-Angle Divergence | Theoretical Divergence |
NA | Focal Lengthd | Housing Outer Diameter |
External Threading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F230SMA-850 | 850 nm | 650 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
0.98 mm | 4.13 mm | 0.06 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.49 | 4.53 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F110SMA-850 | 850 nm | 650 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
1.36 mm | 6.02 mm | 0.05 +0.01 / -0.00°f | Raw Data |
0.37 | 6.26 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F240SMA-850 | 850 nm | 650 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
1.74 mm | 7.11 mm | 0.04 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.50 | 8.02 mm | 12 mmh | M12 x 0.5h |
| F220SMA-850 | 850 nm | 650 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
2.41 mm | 10.94 mm | 0.03 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.25 | 11.12 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F260SMA-850 | 850 nm | 650 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
3.32 mm | 15.15 mm | 0.02 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.16 | 15.33 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F280SMA-850 | 850 nm | 650 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
3.99 mm | 17.73 mm | 0.02 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.15 | 18.45 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |

| Item # | Alignment Wavelengtha |
Lens AR Coating | Waist Diameterb | Waist Distancec | Full-Angle Divergence | Theoretical Divergence |
NA | Focal Lengthd | Housing Outer Diameter |
External Threading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F110SMA-980 | 980 nm | 650 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
1.35 mm | 6.05 mm | 0.05 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.37 | 6.29 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F240SMA-980 | 980 nm | 600 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
1.7 mm | 7.15 mm | 0.04 +0.01 / -0.00°f | Raw Data |
0.50 | 8.06 mm | 12 mmh | M12 x 0.5h |
| F220SMA-980 | 980 nm | 600 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
2.4 mm | 10.99 mm | 0.03 +0.01 / -0.00°f | Raw Data |
0.25 | 11.16 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F280SMA-980 | 980 nm | 600 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
4.0 mm | 17.81 mm | 0.02 +0.01 / -0.00°f | Raw Data |
0.15 | 18.53 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |

| Item # | Alignment Wavelengtha |
Lens AR Coating | Waist Diameterb | Waist Distancec | Full-Angle Divergence | Theoretical Divergence |
NA | Focal Lengthd | Housing Outer Diameterg |
External Threadingg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F110SMA-1064 | 1064 nm | 1050 - 1700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
1.38 mm | 6.07 mm | 0.06 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.37 | 6.31 mm | 11 mm | M11 x 0.5 |
| F220SMA-1064 | 1064 nm | 1050 - 1075 nm R < 0.25% |
2.40 mm | 11.02 mm | 0.032 +0.01 / -0.00°f | Raw Data |
0.25 | 11.17 mm | 11 mm | M11 x 0.5 |
| F260SMA-1064 | 1064 nm | 650 - 1050 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
3.37 mm | 15.25 mm | 0.02 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.16 | 15.43 mm | 11 mm | M11 x 0.5 |

| Item # | Alignment Wavelengtha |
Lens AR Coating | Waist Diameterb | Waist Distancec | Full-Angle Divergence | Theoretical Divergence |
NA | Focal Lengthd | Housing Outer Diameter |
External Threading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F230SMA-C | 1310 nm | 1050 - 1620 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
0.80 mm | 4.20 mm | 0.114 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.53 | 4.64 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F110SMA-1310 | 1310 nm | 1050 - 1700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
1.15 mm | 6.10 mm | 0.08 +0.01 / -0.00°f | Raw Data |
0.37 | 6.35 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F240SMA-C | 1310 nm | 1050 - 1620 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
1.47 mm | 7.21 mm | 0.065 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.49 | 8.12 mm | 12 mmh | M12 x 0.5h |
| F220SMA-C | 1310 nm | 1050 - 1700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
2.04 mm | 11.08 mm | 0.047 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.24 | 11.26 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F260SMA-C | 1310 nm | 1050 - 1620 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
2.88 mm | 15.35 mm | 0.034 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.16 | 15.52 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F280SMA-C | 1310 nm | 1050 - 1700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
3.40 mm | 17.96 mm | 0.028 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.15 | 18.67 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |

| Item # | Alignment Wavelengtha |
Lens AR Coating | Waist Diameterb | Waist Distancec | Full-Angle Divergence | Theoretical Divergence |
NA | Focal Lengthd | Housing Outer Diameter |
External Threading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F230SMA-1550 | 1550 nm | 1050 - 1700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
0.90 mm | 4.21 mm | 0.128 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.53 | 4.67 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F110SMA-1550 | 1550 nm | 1050 - 1700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
1.21 mm | 6.13 mm | 0.09 +0.01 / -0.00°f | Raw Data |
0.37 | 6.37 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F240SMA-1550 | 1550 nm | 1050 - 1700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
1.55 mm | 7.26 mm | 0.073 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.49 | 8.17 mm | 12 mmh | M12 x 0.5h |
| F220SMA-1550 | 1550 nm | 1050 - 1700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
2.15 mm | 11.15 mm | 0.053 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.24 | 11.32 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F260SMA-1550 | 1550 nm | 1050 - 1620 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
3.00 mm | 15.44 mm | 0.038 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.16 | 15.58 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |
| F280SMA-1550 | 1550 nm | 1050 - 1700 nm Ravg < 0.5% |
3.60 mm | 18.07 mm | 0.032 +0.01 / -0.00°e | Raw Data |
0.15 | 18.75 mm | 11 mmg | M11 x 0.5g |

| Item # | Alignment Wavelengtha |
Lens AR Coating | Waist Diameterb | Waist Distancec | Full-Angle Divergenced | Theoretical Divergence |
NA | Focal Lengthe | Housing Outer Diameterf |
External Threadingf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F028SMA-2000 | 2 µm | 1.8 - 3.0 µm Ravg < 1.0% |
1.6 mm | 5.73 mm | 0.129° +0.01 / -0.00° | Raw Data |
0.56 | 5.91 mm | 11 mm | M11 x 0.5 |

Although this collimator is factory aligned for a specific wavelength, it has low divergence angles over a broad range of wavelengths. Therefore, it may be used at other wavelengths within the AR coating range. Please refer to the theoretical divergence plot for this collimator to determine if it is appropriate for your application.
| Item # | Alignment Wavelength |
Lens AR Coating | Waist Diametera | Waist Distanceb | Full-Angle Divergencec | Theoretical Divergence |
NA | Focal Lengthd | Housing Outer Diametere |
External Threadinge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F028SMA-3450 | 3.45 µm | 3 - 5 µm Ravg < 1.0% |
2.01 mm | 5.77 mm | 0.125 +0.01 / -0.00° | Raw Data |
0.56 | 5.94 mm | 11 mm | M11 x 0.5 |

Although this collimator is factory aligned for a specific wavelength, it has a low divergence angle over a broad range of wavelengths. Therefore, it may be used at other wavelengths within the AR coating range. Please refer to the theoretical divergence plot for this collimator to determine if it is appropriate for your application.
| Item # | Alignment Wavelength |
Lens AR Coating | Waist Diametera | Waist Distanceb | Full-Angle Divergencec | Theoretical Divergence |
NA | Focal Lengthd | Housing Outer Diametere |
External Threadinge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F028SMA-4950 | 4.55 µm | 3 - 5 µm Ravg < 1.0% |
2.16 mm | 5.79 mm | 0.15 +0.05 / -0° | Raw Data |
0.56 | 5.97 mm | 11 mm | M11 x 0.5 |
 Products Home
Products Home














 SMA905 Fixed Focus Collimation Packages
SMA905 Fixed Focus Collimation Packages