Complete Laser Diode (LD) Operation Starter Sets

- Bundles Include LD Controller, TEC Controller, LD Mount, Collimation Optic, and Accessories
- Ideal for Stable and Safe Operation of Standard Laser Diodes
Included Accessories
LTC56B
Ø5.6 mm LD Controller Kit
(Controller Cables Included)
SM1NT
C230TMD-B
(Coating Varies
with Item #)
BA2
S1TM09
SPW301
SPW909
WS02
2x
TR1.5
2x
PH1.5

Please Wait
| Key Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Specification | Value |
| LDC205C Laser Diode Current Controllera | |
| LD Current Control Range | 0 to ±500 mA |
| Compliance Voltage | >10 V |
| Photocurrent Control Range | 25 µA to 10 mA |
| Small Signal 3 dB Bandwidth | DC to 150 kHz |
| TED200C Temperature Controllera | |
| TEC Current Control Range | -2 A to +2 A |
| Compliance Voltage | >6 V |
| Maximum Output Power | 12 W |
| Thermistor Control Range | 10 Ω to 20 kΩ / 100 Ω to 200 kΩ (2 Ranges) |
| Supported IC Sensors | AD590, AD592, LM135, LM335 |
| LDM56(/M) Laser Diode Mount with Integrated TECb | |
| Supported Laser Diode Package/ Pin Configurations |
Ø5.6 mm TO Can, A, B, C, D, E, G, and H |
| Laser Current (Max) | 2 A |
| TEC Current | 5 A |
| TEC Heating/Cooling Capacity | 8 W (@ 25 ºC) |
| RF Modulation Frequency | 100 kHz to 600 MHz |
Included Items:
- LDC205C Benchtop LD Current Controller
- TED200C Benchtop Temperature Controller
- LDM56(/M) LD/TEC Mount for Ø5.6 mm TO-Can Laser Diodes
- AR-Coated Collimation Optic:
- LTC56A(/M): C230TMD-A for 350 - 700 nm
- LTC56B(/M): C230TMD-B for 600 - 1050 nm
- LTC56C(/M): C230TMD-C for 1050 - 1700 nm
- Connection Cables and Related Accessories (See Kit Contents Tab for Details)
 Click To Enlarge
Click To EnlargeFor setups needing additional working distance, our 30 mm cage system components can be mounted into the face plate.
Thorlabs' LTC56 Series Kits are complete laser diode (LD) current and temperature controller sets including a laser diode mount, collimating optic, and accessories. They include the LDC205C LD Current Controller, TED200C Temperature Controller, LDM56(/M) Laser Diode Mount, and other items necessary for the stable and safe operation of standard Ø5.6 mm laser diodes. These starter sets are offered at a discount over the cost of individual components.
The kit is offered in three versions depending of the anti-reflection coating of the collimation optic: LTC56A(/M) for 350 - 700 nm, LTC56B(/M) for 600 - 1050 nm, and LTC56C(/M) for 1050 - 1700 nm. For detailed information about the included components, please refer to the Kit Contents tab above. Each unit ships with two cables, one for the temperature controller (CAB420-15) and one for the laser diode controller (CAB400). Although all necessary cables are packaged with the purchase of the controllers and starter sets presented above, replacements can be purchased separately.
The LDMXY Flexure Adapter, sold separately below, attaches to the laser diode mount and enables precise positioning of a collimating aspheric lens. The two piece design also enables coarse repositioning of the attached 30 mm or 60 mm cage system that is independent of the laser diode and collimating optic. We also offer the LDM56DJ Mounting Flange for use with 532 nm DPSS lasers, available separately below.
These sets are available with imperial or metric mounting hardware. The LDC205C and TED200C controllers operate with a line voltage of 100, 115, or 230 VAC.
| Laser Diode Accessory Selection Guide | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Other Temperature Controlled Mounts |
Passive Mounts | Passive Mounts with Collimation Package |
Strain Relief Cables | Diode Sockets | Other Controllers |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Item # | LDC205C |
|---|---|
| Current Control (Constant Current Mode) | |
| Control Range | 0 to ±500 mA |
| Compliance Voltage | >10 V |
| Resolution | 10 µA |
| Accuracy | ±0.5 mA |
| Noise Without Ripple (10 Hz to 10 MHz, rms, typ.) |
< 3 µA |
| Ripple (50/60 Hz, rms, typ.) | < 2 µA |
| Transients (Typ.) | < 0.5 mA |
| Drift, 24 hours (typ., 0-10Hz, at constant ambient temperature) |
<10 µA |
| Temperature Coefficient | <50 ppm/ °C |
| Current Limit | |
| Setting Range | 0 to >500 mA |
| Resolution | 10 µA |
| Accuracy | ±1.5 mA |
| Power Control (Constant Power Mode) | |
| Photocurrent Control Range | 25 µA to 10 mA |
| Photocurrent Resolution | 1 µA |
| Photocurrent Accuracy | ±10 µA |
| Analog Modulation Input | |
| Input Resistance | 10 kΩ |
| Small Signal 3 dB Bandwidth, CC Mode |
DC to 150 kHz |
| Modulation Coefficient, CC Mode |
50 mA/V ±5% |
| Modulation Coefficient, CP Mode |
1 mA/V ±5% |
| Laser Current Monitor Output | |
| Load Resistance | >10 kΩ |
| Transmission Coefficient | 20 V/A ±5% |
| General Data | |
| Safety Features | Interlock, Laser Current Limit, Soft Start, Short Circuit when Laser Off, Open Circuit Detection, Over Temperature Protection |
| Display | LED, 5 Digits |
| Connector for Laser, Photodiode, Interlock & Laser On Signal |
9-pin D-Sub Jack |
| Connectors for Control Input / Output |
BNC |
| Chassis Ground Connector | 4 mm Banana Jack |
| Line Voltage / Frequency | 100 V, 115 V, 230 V +15% –10% each / 50 to 60 Hz |
| Maximum Power Consumption | 30 VA |
| Mains Supply Overvoltage | Category II (Cat II) |
| Operating Temperature | 0 to +40 °C |
| Storage Temperature | -40 to +70 °C |
| Relative Humidity | Max. 80% Up to 30 °C, Decreasing to 50% at 40 °C |
| Pollution Degree (Indoor Use Only) | 2 |
| Operation Altitude | <2000 m |
| Warm-up Time for Rated Accuracy | 10 min |
| Weight | <3.1 kg |
| Dimensions (W X H X D) without Operating Elements |
146 mm x 66 mm x 290 mm |
| Dimensions (W X H X D) with Operating Elements |
146 mm x 77 mm x 320 mm |
| Item # | TED200C |
|---|---|
| TEC Current Output | |
| Control Range | -2 A to +2 A |
| Compliance Voltage | >6 V |
| Maximum Output Power | 12 W |
| Measurement Resolution | 1 mA |
| Measurement Accuracy | ±10 mA |
| Noise and Ripple (typ.) | <1 mA |
| TEC Current Limit | |
| Setting Range | 0 to >2 A |
| Resolution | 1 mA |
| Setting Accuracy | ±20 mA |
| Thermistor Sensorsa | |
| Control Range | 10 Ω to 20 kΩ / 100 Ω to 200 kΩ (2 Ranges) |
| Resolution (20kΩ / 200 kΩ Range) |
1 Ω / 10 Ω |
| Accuracy (20 kΩ / 200 kΩ Range) |
±10 Ω / ±100 Ω |
| Temperature Stability, 24 hoursb (20 kΩ / 200 kΩ Range) |
<0.5 Ω / <5 Ω |
| IC Sensors | |
| Supported Sensors | AD590, AD592, LM135, LM335 |
| Control Range with AD590, LM135 |
-45 °C to +145 °C |
| Control Range with AD592 | -25 °C to +105 °C |
| Control Range with LM335 | -40 °C to +100 °C |
| Resolution | 0.01 °C |
| Accuracy | ±0.1 °C |
| Temperature Stability, 24 Hours | <0.002 °C |
| Temperature Control Input | |
| Input Resistance | 10 kΩ |
| Control Voltage | -10V to +10V |
| Transmission Coefficient Thermistor (20 kΩ / 200 kΩ Range) |
2 kΩ/V / 20 kΩ/V ±5% |
| Transmission Coefficient IC-Sensors |
20 °C/V ±5% |
| Temperature Control Output | |
| Load Resistance | >10 kΩ |
| Transmission Coefficient Thermistor (20 kΩ / 200 kΩ Range) |
500 mV/kΩ / 50 mV/kΩ ±5% |
| Transmission Coefficient IC-Sensors |
50 mV/ °C ±5% |
| General Data | |
| Safety Features | TEC Current Limit, Short Circuit when TEC Off, Missing Sensor Protection, Open Circuit Detection, Over Temperature Protection |
| Display | LED, 5 Digits |
| Connector for Sensor, TE Cooler, TEC On Signal |
15-pin D-sub Jack |
| Connectors for Control Input / Output |
BNC |
| Chassis Ground Connector | 4mm Banana Jack |
| Line Voltage / Frequency | 100 V, 115 V, 230 V +15% -10% each / 50 to 60Hz |
| Maximum Power Consumption |
60 VA |
| Mains Supply Overvoltage | Category II (Cat II) |
| Operating Temperature | 0 to +40 °C |
| Storage Temperature | -40 to +70 °C |
| Relative Humidity | Max. 80% Up to 30 °C, Decreasing to 50% at 40 °C |
| Pollution Degree (Indoor Use Only) | 2 |
| Operation Altitude | <2000 m |
| Warm-up Time for Rated Accuracy |
10 min |
| Weight | <3.1 kg |
| Dimensions (W x H x D) without Operating Elements |
146 mm x 66 mm x 290 mm |
| Dimensions (W x H x D) with Operating Elements |
146 mm x 77 mm x 320 mm |
| Item # | LDM56(/M) | |
|---|---|---|
| Laser Diode | ||
| Supported Laser Diode Package | Ø5.6 mm | |
| Supported Pin Configuration(s) | A, B, C, D, E, Ga, and H (Switch Selectable) |
|
| Accepted Pin Lead Diameter | 0.015" - 0.020" (0.38 mm - 0.51 mm) | |
| Accepted Pin Lead Length | Up to 0.6" (15.24 mm) | |
| Laser Current (Max) | 2 A | |
| RF Modulation Frequency (Bias-T) | 100 kHz to 600 MHz | |
| RF Input Impedance | 50 Ω | |
| RF Max Power | 200 mW | |
| Temperature Controller | ||
| TEC Current (Max)b | 5 Ac | |
| TEC Voltage (Max) | 4 V | |
| TEC Heating/Cooling Capacity | 8 W (25 ºC) | |
| Typical Temperature Range (LD Dependent) |
0 to 70 °C | |
| Temperature Sensor |
Thermistor | 10 kΩ ± 3% @ 25 °C, NTC, β = 3977 K ± 0.75% |
| Thermocouple | AD592AN (1 μA/°K) | |
| General Specifications | ||
| Laser Interface | DB9 Female | |
| TEC Interface | DB9 Male | |
| RF Modulation Connector | SMA | |
| Interlock Connector | 2.5 mm Phono Jack | |
| Indicator | Green LED - LD Enabled | |
| Mounting Holes |
Imperial Mounts | 1/4"-20 (9 Places) |
| Metric Mounts | M6 x 1.0 (9 Places) | |
| Cage Compatibility | 4-40 Taps (8 Places) for 30 mm and 60 mm Cage Systems |
|
| Operating Temperature | 10 to 40 °C | |
| Storage Temperature | 10 to 80 °C | |
| Dimensions (L x W x D) | 4.00" x 4.00" x 2.07" (101.6 mm × 101.6 mm × 52.6 mm) |
|
| Weight | 1.9 lbs (0.87 kg) | |
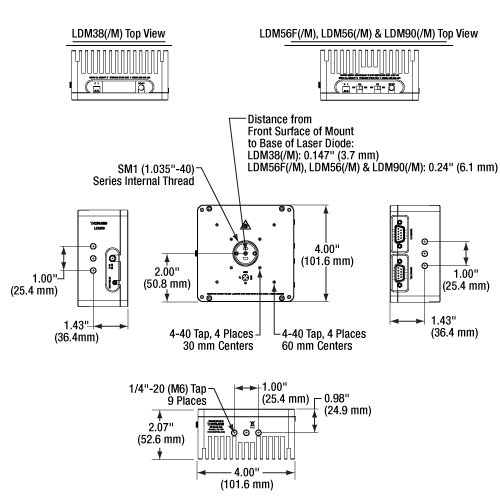
Click to Enlarge
LDM56(/M) Mounting Features Diagram
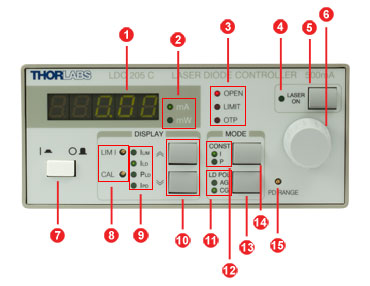
LDC205C Front Panel
| Callout | Connection | Callout | Connection |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5-Digit LED Display | 9 | Display Indicators |
| 2 | Display Units | 10 | Up/Down Display Select |
| 3 | Interlock Indicators | 11 | Diode Polarization Indicator |
| 4 | Laser Status Indicator | ||
| 5 | Laser Current On/Off Switch | 12 | Output Mode Indicator |
| 6 | Display Adjustment Knob | 13 | Diode Polarization Select |
| 7 | Supply Power Switch | 14 | Output Mode Select |
| 8 | Current Limit and Power Calibration Pots | 15 | Photodiode Current Range Pot |
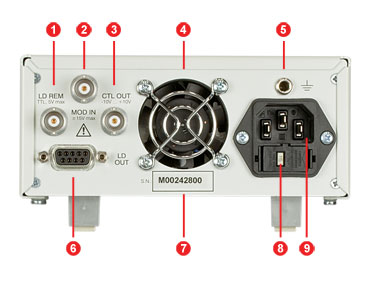
LDC205C Back Panel
| Callout | Connection | Callout | Connection |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TTL Input "LD REM" 0 to 5 V | 6 | Connector "LD OUT" for LD, PD, Interlock, & Status LED |
| 2 | Modulation Input / Analog Control Input "MOD IN", -10 to +10 V | 7 | Serial Number of the Unit |
| 3 | Analog Control Output "CTL OUT", -10 to +10 V |
8 | Indicator / Switch for Line Voltage (Included in Fuse Holder) |
| 4 | Cooling Fan | ||
| 5 | 4 mm Banana Jack for Chassis Ground | 9 | Power Connector and Fuse Holder |
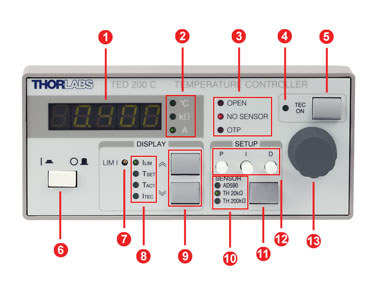
TED200C Front Panel
| Callout | Connection | Callout | Connection |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5-Digit LED Display | 8 | Display Indicators |
| 2 | Display Units | 9 | Up/Down Display Select |
| 3 | Interlock Indicators | 10 | Selected Sensor Inticators |
| 4 | TEC Status Indicator | 11 | Sensor Select Key |
| 5 | TEC Current On/Off Switch | 12 | Potentiometers for PID Gain Settings |
| 6 | Supply Power Switch | ||
| 7 | Potentiometer for Current Limit Setting | 13 | Display Adjustment Knob |
TED200C Back Panel
| Callout | Connection | Callout | Connection |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Analog Temperature Control Input "Tune In", -10 to 10 V | 5 | 15-pin D-sub Jack for the TEC Element and the Temperature Sensor "TE OUTPUT" |
| 2 | Analog Temperature Control Output "CTL Out", -10 to 10 V | 6 | Serial Number of the Unit |
| 3 | Cooling Fan | 7 | Indicator / Switch for Line Voltage (Included in Fuse Holder) |
| 4 | 4 mm Banana Jack for Chassis Ground | 8 | Power Connector and Fuse Holder |
LDC205C - Benchtop LD Current Controller
| Pin | Connection | Pin | Connection |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Interlock and Status LASER ON/OFF | 6 | Not Connected |
| 2 | Photodiode Cathode | 7 | Laser Diode Cathode (with Polarity Anode Grounded - AG) |
| 3 | Laser Diode Ground | 8 | Laser Diode Anode (with Polarity Cathode Grounded - CG) |
| 4 | Photodiode Anode | ||
| 5 | Ground for Pin 1 | 9 | Not Connected |
Laser Diode Connector
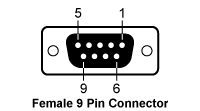
Laser Diode Remote

TTL Input (0 to +5 V)
Modulation Input

Analog Control Input
(-10 V to 10V)
Control Output

Analog Control Output
(0 to ±10 V)
Chassis Ground

TED200C - Benchtop Temperature Controller
| Pin | Connection | Pin | Connection |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Status LED (+) TEC ON/OFF | 9 | Not Connected |
| 2 | Not Connected | 10 | Transducer AD 590/592 (-), LM 135/335 (+) |
| 3 | Thermistor (-), Ground | 11 | Transducer AD 590/592 (+), LM 135/335 (+) |
| 4 | Thermistor (+) | ||
| 5 | TEC (+) | 12 | Not Connected |
| 6 | TEC (+) | 13 | TEC (-), Status-LED (-) |
| 7 | TEC (+) | 14 | TEC (-), Status-LED (-) |
| 8 | AGND LM 135/335 (-) | 15 | TEC (-), Status-LED (-) |
Temperature Sensor and Controller
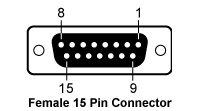
Analog Temperature Control Input

Analog Temperature Control Output
LDM56(/M) - Laser Diode Mount
LD Controller: D-Type Female
| Pin | Signal | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Interlock and Status Pin (LDC Specific) |
Laser Diode (LD) Status Indicator and Interlock Circuits input. |
| 2 | Photodiode Cathode | This pin is connected to the 9 o'clock pin on the laser socket when the photodiode (PD) polarity switch is set to anode ground (AG). It is attached to ground and the 12 o'clock and 6 o'clock pins on the laser socket when the PD polarity switch is set to cathode ground (CG). |
| 3 | Laser Ground (Case) | This pin is connected to the 12 o'clock and 6 o'clock pins on the laser socket and corresponds to the settings of the LD and PD polarity switches (i.e. If the LD and PD switches are set to AG then this pin grounds the anodes of the laser and photodiodes). |
| 4 | Photodiode Anode | This pin is connected to the 9 o'clock pin on the laser socket when the PD polarity switch is set to CG. It is attached to ground and the 12 o'clock and 6 o'clock pins on the laser socket when the PD polarity switch is set to AG. |
| 5 | Interlock and Status Return |
Status and interlock circuitry return. |
| 6 | Laser Diode Voltage (Cathode) |
This pin is connected to LD interface pin 7, through a 499 Ω resistor, when the LD polarity switch is set to AG. It is attached directly to LD interface pin 3 when the LD polarity switch is set to CG. |
| 7 | Laser Diode Cathode | This pin is connected to the 3 o'clock pin on the laser socket when the LD polarity switch is set to AG, and it floats otherwise. |
| 8 | Laser Diode Anode | This pin is connected to the 3 o'clock pin on the laser socket when the LD polarity switch is set to CG, and it floats otherwise. |
| 9 | Laser Diode Voltage (Anode) |
This pin is connected to LD interface pin 8, through a 499 Ω resistor, when the LD polarity switch is set to CG. It is attached directly to LD interface pin 3 when the LD polarity switch is set to AG. |
TEC Controller: D-Type Male
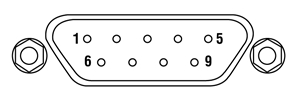
| Pin | Signal | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TEC Lockout (+) | This pin is connected to the anode of the photo-relay side of the TEC Lockout circuit. When using Thorlabs TEDs no external circuitry is required. To use these features with third-party controllers please refer to the Status and Interlock section of the mount's manual. |
| 2 | +Thermistor | The 10 kΩ at 25 °C NTC thermistor (provided for temperature feedback). |
| 3 | -Thermistor | The thermistor return pin. |
| 4 | +TEC | This pin is connected to the positive terminal of the TEC element. |
| 5 | -TEC and TEC Lockout (-) | This pin is connected to the negative terminal of the TEC element, and also is common to the cathode of the photo-relay of the TEC Lockout circuit - refer to the Status and Interlock section of the mount's manual. |
| 6 | N.C. | Not Used. |
| 7 | AD592(-) | The negative terminal of the AD592 temperature transducer. When using Thorlabs TEDs no external circuitry is required. To use this device with third party controllers it must be properly biased. Refer to Analog Devices AD592 Data for application information. |
| 8 | N.C. | Not Used. |
| 9 | AD592(+) | The positive terminal of the AD592 |
Optional Remote Interlock
2.5 mm Female Mono Phono Jack
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Type of Mating Connector | 2.5 mm Mono Phono Jack |
| Open Circuit Voltage | +5 VDC with Respect to System Ground (When Used in Conjunction with Thorlabs Drivers) |
| Short Circuit Current | 10 mA DC (Typ.) |
| Connector Polarity | Tip: Positive; Barrel: Ground |
| Interlock Switch Requirements | Must be N.O. dry contacts. Under no circumstances should any external voltages be applied to the Interlock input. |
RF Laser Modulation Input
SMA Female
RF input for modulation with an external source up to 600 MHz. This is a 50 Ω input that is AC-coupled directly to the laser through a Bias-T network.
| Photo (Click to Enlarge) |
Quantity | Item # in Imperial Kits |
Item # in Metric Kits |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
1 | LDC205C | Benchtop LD Current Controller, ±500 mA HV | |
 |
1 | TED200C | Benchtop Temperature Controller, ±2 A / 12 W | |
 |
1 | LDM56 | LDM56/M | TE-Cooled Mount for Ø5.6 mm Laser Diodes, 1/4"-20 (M6) Taps |
 |
1 | LTC56A(/M) Kit: C230TMD-A | Mounted Aspheric Lens, AR: 350 - 700 nm, f = 4.51 mm, NA = 0.55 | |
| LTC56B(/M) Kit: C230TMD-B | Mounted Aspheric Lens, AR: 650 - 1050 nm, f = 4.51 mm, NA = 0.55 | |||
| LTC56C(/M) Kit: C230TMD-C | Mounted Aspheric Lens, AR: 1050 - 1700 nm, f = 4.51 mm, NA = 0.55 | |||
 |
1 | S1TM09 | SM1 to M9 x 0.5 Lens Cell Adapter | |
 |
1 | SM1NT | SM1 (1.035"-40) Locking Ring | |
 |
2 | TR1.5 | TR40/M | Ø1/2" Optical Post, SS, 8-32 Setscrew, 1/4"-20 Tap, L = 1.5" (Ø12.7 mm Optical Post, SS, M4 Setscrew, M6 Tap, L = 40 mm) |
 |
2 | PH1.5 | PH40/M | Ø1/2" Post Holder, Spring-Loaded Hex-Locking Thumbscrew, L = 1.5" (Ø12.7 mm Post Holder, Spring-Loaded Hex-Locking Thumbscrew, L = 40 mm) |
 |
1 | BA2 | BA2/M | Mounting Base, 2" x 3" x 3/8" (50 mm x 75 mm x 10 mm) |
 |
1 | SPW909 | Spanner Wrench for SM1-Threaded Adapters, Length = 1" | |
 |
1 | SPW301 | Spanner Wrench for an M9 x 0.5 Optics Housing, Length = 1" | |
 |
1 | WS02 | Fabric Grounding Wrist Strap, Adjustable Circumference, 6 ft Coiled Cord | |
 |
2 Pieces | SS25E63Da | SS6M16Da | 1/4"-20 Stainless Steel Setscrew with Hex on Both Ends, 5/8" Long (M6 x 1.0 Stainless Steel Setscrew with Hex on Both Ends, 16 mm Long) |
PID Basics
The PID circuit is often utilized as a control loop feedback controller and is commonly used for many forms of servo circuits. The letters making up the acronym PID correspond to Proportional (P), Integral (I), and Derivative (D), which represents the three control settings of a PID circuit. The purpose of any servo circuit is to hold the system at a predetermined value (set point) for long periods of time. The PID circuit actively controls the system so as to hold it at the set point by generating an error signal that is essentially the difference between the set point and the current value. The three controls relate to the time-dependent error signal. At its simplest, this can be thought of as follows: Proportional is dependent upon the present error, Integral is dependent upon the accumulation of past error, and Derivative is the prediction of future error. The results of each of the controls are then fed into a weighted sum, which then adjusts the output of the circuit, u(t). This output is fed into a control device, its value is fed back into the circuit, and the process is allowed to actively stabilize the circuit’s output to reach and hold at the set point value. The block diagram below illustrates the action of a PID circuit. One or more of the controls can be utilized in any servo circuit depending on system demand and requirement (i.e., P, I, PI, PD, or PID).
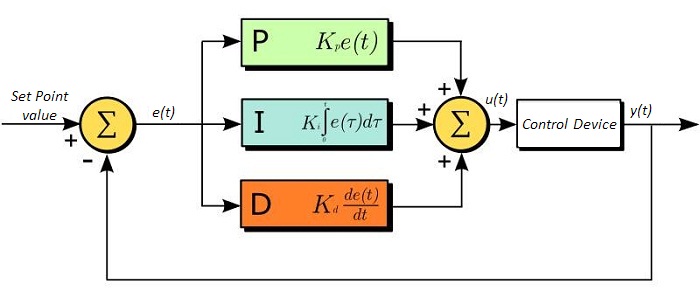
Through proper setting of the controls in a PID circuit, relatively quick response with minimal overshoot (passing the set point value) and ringing (oscillation about the set point value) can be achieved. Let’s take as an example a temperature servo, such as that for temperature stabilization of a laser diode. The PID circuit will ultimately servo the current to a Thermoelectric Cooler (TEC) (often times through control of the gate voltage on an FET). Under this example, the current is referred to as the Manipulated Variable (MV). A thermistor is used to monitor the temperature of the laser diode, and the voltage over the thermistor is used as the Process Variable (PV). The Set Point (SP) voltage is set to correspond to the desired temperature. The error signal, e(t), is then the difference between the SP and PV. A PID controller will generate the error signal and then change the MV to reach the desired result. For example, if e(t) states that the laser diode is too hot, the circuit will allow more current to flow through the TEC (proportional control). Since proportional control is proportional to e(t), it may not cool the laser diode quickly enough. In that event, the circuit will further increase the amount of current through the TEC (integral control) by looking at the previous errors and adjusting the output to reach the desired value. As the SP is reached (e(t) approaches zero), the circuit will decrease the current through the TEC in anticipation of reaching the SP (derivative control).
Please note that a PID circuit will not guarantee optimal control. Improper setting of the PID controls can cause the circuit to oscillate significantly and lead to instability in control. It is up to the user to properly adjust the PID gains to ensure proper performance.
PID Theory
The output of the PID control circuit, u(t), is given as
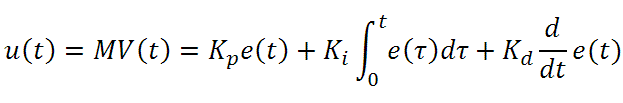
where
Kp= Proportional Gain
Ki = Integral Gain
Kd = Derivative Gain
e(t) = SP - PV(t)
From here we can define the control units through their mathematical definition and discuss each in a little more detail. Proportional control is proportional to the error signal; as such, it is a direct response to the error signal generated by the circuit:
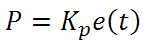
Larger proportional gain results in larger changes in response to the error, and thus affects the speed at which the controller can respond to changes in the system. While a high proportional gain can cause a circuit to respond swiftly, too high a value can cause oscillations about the SP value. Too low a value and the circuit cannot efficiently respond to changes in the system.
Integral control goes a step further than proportional gain, as it is proportional to not just the magnitude of the error signal but also the duration of the error.
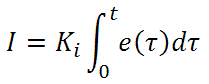
Integral control is highly effective at increasing the response time of a circuit along with eliminating the steady-state error associated with purely proportional control. In essence integral control sums over the previous error, which was not corrected, and then multiplies that error by Ki to produce the integral response. Thus, for even small sustained error, a large aggregated integral response can be realized. However, due to the fast response of integral control, high gain values can cause significant overshoot of the SP value and lead to oscillation and instability. Too low, and the circuit will be significantly slower in responding to changes in the system.
Derivative control attempts to reduce the overshoot and ringing potential from proportional and integral control. It determines how quickly the circuit is changing over time (by looking at the derivative of the error signal) and multiplies it by Kd to produce the derivative response.
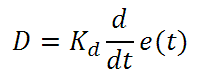
Unlike proportional and integral control, derivative control will slow the response of the circuit. In doing so, it is able to partially compensate for the overshoot as well as damp out any oscillations caused by integral and proportional control. High gain values cause the circuit to respond very slowly and can leave one susceptible to noise and high frequency oscillation (as the circuit becomes too slow to respond quickly). Too low and the circuit is prone to overshooting the SP value. However, in some cases overshooting the SP value by any significant amount must be avoided and thus a higher derivative gain (along with lower proportional gain) can be used. The chart below explains the effects of increasing the gain of any one of the parameters independently.
| Parameter Increased | Rise Time | Overshoot | Settling Time | Steady-State Error | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kp | Decrease | Increase | Small Change | Decrease | Degrade |
| Ki | Decrease | Increase | Increase | Decrease Significantly | Degrade |
| Kd | Minor Decrease | Minor Decrease | Minor Decrease | No Effect | Improve (for small Kd) |
Tuning
In general the gains of P, I, and D will need to be adjusted by the user in order to best servo the system. While there is not a static set of rules for what the values should be for any specific system, following the general procedures should help in tuning a circuit to match one’s system and environment. A PID circuit will typically overshoot the SP value slightly and then quickly damp out to reach the SP value.
Manual tuning of the gain settings is the simplest method for setting the PID controls. However, this procedure is done actively (the PID controller turned on and properly attached to the system) and requires some amount of experience to fully integrate. To tune your PID controller manually, first the integral and derivative gains are set to zero. Increase the proportional gain until you observe oscillation in the output. Your proportional gain should then be set to roughly half this value. After the proportional gain is set, increase the integral gain until any offset is corrected for on a time scale appropriate for your system. If you increase this gain too much, you will observe significant overshoot of the SP value and instability in the circuit. Once the integral gain is set, the derivative gain can then be increased. Derivative gain will reduce overshoot and damp the system quickly to the SP value. If you increase the derivative gain too much, you will see large overshoot (due to the circuit being too slow to respond). By playing with the gain settings, you can maximize the performance of your PID circuit, resulting in a circuit that quickly responds to changes in the system and effectively damps out oscillation about the SP value.
| Control Type | Kp | Ki | Kd |
|---|---|---|---|
| P | 0.50 Ku | - | - |
| PI | 0.45 Ku | 1.2 Kp/Pu | - |
| PID | 0.60 Ku | 2 Kp/Pu | KpPu/8 |
While manual tuning can be very effective at setting a PID circuit for your specific system, it does require some amount of experience and understanding of PID circuits and response. The Ziegler-Nichols method for PID tuning offers a bit more structured guide to setting PID values. Again, you’ll want to set the integral and derivative gain to zero. Increase the proportional gain until the circuit starts to oscillate. We will call this gain level Ku. The oscillation will have a period of Pu. Gains for various control circuits are then given to the right in the chart.
Note that when using the Ziegler-Nichols tuning method with some devices like the DSC1 digital servo controller, the integral and derivative terms must be normalized by the sample rate. To do this, the integral term determined from the table should be divided by the sample rate in Hertz and the derivative term should be multiplied by the sample rate in Hertz.
| Posted Comments: | |
George Brown
(posted 2024-04-02 14:17:23.26) I have a question about mating the S1TM09 lens cell adapter to the LDM56 Mount:
1, The depth of the cold plate of the LDM56 relative to the surface is 0.24 in.
2. The thickness of the flange securing the laser diode to the cold plate is 0.13 in.
3. This leaves 0.11 in. depth of SM1 threads.
4. The S1TM09 lens cell adapter, on the other hand, is 0.275 in. thick.
5. As a consequence, the S1TM09 adapter has only 0.11 in of threads available.
Could it be that the LD mounting flange is not intended to be used in conjunction with the S1TM09 lens cell adapter? Fedele Tagarelli
(posted 2022-11-24 13:14:01.097) The cables supplied with controllers for TEC and LD are very poor quality. The screws used to secure the DSUB connector to the LDM56 and the controlles wear out after first usage. I had to change the DSUB connectors of the supplied cables because they were not usable anymore. hchow
(posted 2022-11-24 09:49:18.0) Dear Mr. Tagarelli, thank you for your feedback. I am sorry to hear that the cables provided with this laser diode starter set are defective and did not meet your expectations. I sincerely apologize for any inconvenience you may have experienced due to this problem. Rest assured this issue will be taken care of. I will reach out to you personally to discuss possible solutions. Thank you. Mateusz Mrozowski
(posted 2020-08-25 08:01:13.84) Hello,
I was wondering if it would be possible to get LDM90 mount instead of LTC56B.
We are getting LD785-SEV300 diode and it requires bigger mount than one in the kit.
Kind regards,
Mateusz YLohia
(posted 2020-08-25 10:39:59.0) Hello Mateusz, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. Unfortunately, we currently do not offer the LTC56B kit with the LDM90 mount. You would have to add the components listed on the "Kit Contents" tab individually to your cart and swap out the LDM56 for the LDM90. That being said, we have noted your request and will look into adding such a kit to our catalog in the future. Nicolas Spegazzini
(posted 2020-07-07 23:58:53.487) Hello,
I'm name is Nicolas Spegazzini, professor and researcher in spectroscopy. At this moment I am in Argentina. I wonder if there is any possibility of being able to buy this laser kit (LTC56A / M) plus 532nm DPSS Lasers (DJ532-40).
Undergraduate Program Director
Professor, Departments of Chemistry and Pharmacy
School of Science
University of Belgrano
Villanueva 1324
C1426DQG Buenos Aires, Argentina YLohia
(posted 2020-07-08 10:22:42.0) Hello Nicolas, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. We can certainly quote you for these items. Our Sales Team will reach out to you directly. Jeonghun Lee
(posted 2020-03-19 09:39:31.19) Hi, do you think it is viable to make an external cavity diode laser (Littrow configuration) by using this in conjunction with a grating (which will be mounted on a separate nearby optical mount)? YLohia
(posted 2020-03-19 10:09:07.0) Hello, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. Unfortunately, TO-can laser diodes cannot be used to set up a Littrow ECL configuration because both facets of the diode chip must be accessible (please see schematic here : https://www.thorlabs.com/images/TabImages/Exlaser_Fig5.gif). A Littman configuration, however, is still possible with the proper gain chip. More information can be found on our tutorial here : https://www.thorlabs.com/tutorials.cfm?tabID=F7DFA931-5AFA-441B-8176-292D8735B143. We recommend using our SAF gain chips for this purpose: https://www.thorlabs.com/newgrouppage9.cfm?objectgroup_id=3913 ersen.beyatli
(posted 2017-09-18 13:25:39.743) This set is very useful for my applications is it possible to change the diode driver with LDC240C. If it is ok for you can you prepare a quotation for me?
thanks wskopalik
(posted 2017-09-19 03:02:35.0) This is a response from Wolfgang at Thorlabs. Thank you very much for your feedback.
We will be able to offer this configuration as a special item. I will contact you directly to provide a quotations. johncmetcalf
(posted 2017-06-05 11:50:33.953) https://www.thorlabs.com/newgrouppage9.cfm?objectgroup_id=2437
BNC diagram label for Temp Out is mislabeled. tcampbell
(posted 2017-06-06 02:57:47.0) Response from Tim at Thorlabs: Thank you for pointing out this error. We have corrected the second BNC female connector label to read "Analog Temperature Control Output." a_chehrghani
(posted 2016-06-28 01:41:22.24) Hello.
I have a complete laser diode set with LDC205C and TED200C controllers and TCLDM9 mount. I am ganna to handle a 660nm laser diode (L660P120). I set its pins according to catalog (C style configuration: it's ground pin inserted in 3 O'clock position), but when I want to drive the laser, the "open led" in LDC205C panel turn on. The LD and PD polarity was set to CG and AG respectively and the PD Polarity in LDC205C panel was set to CG.
Could you help me to resolve this error. user
(posted 2016-06-10 07:46:28.367) Hello, how necessary is the temperature controller? shallwig
(posted 2016-06-14 04:32:30.0) This is a response from Stefan at Thorlabs. Thank you very much for your inquiry. The need of active cooling with a temperature controller depends on the power consumption of the driven laser diode and how much electrical power gets converted into optical power and heat. To avoid damaging the laser diode and getting a stable laser output it is recommended to keep the temperature on a constant level.
As you left no contact information please contact me at europe@thorlabs.com for any further questions. sfzmousavi
(posted 2015-10-10 08:49:26.33) Hi
I need this package (LTC100-C) but instead of LDC205C, I need LDC220C (that is until 2A). Is this change possible for you? And if it is possible, how much this new package would cost?
I am looking forward to hearing back from you.
Regards jvigroux
(posted 2015-10-12 11:35:59.0) A response from Julien at Thorlabs: Thank you for your feedback. We will be able to offer this configuration as a special item, we will contact you directly to provide a quote. shallwig
(posted 2015-04-01 04:34:42.0) This is a response from Stefan at Thorlabs. Thank you very much for your inquiry. Together with the controllers you get the accessories mentioned on the homepage under “included items” and shown on the top image on the website: http://www.thorlabs.com/NewGroupPage9.cfm?ObjectGroup_ID=2437
The LTC100-B includes a collimation optic with AR coating for 600-1050nm. With this Kit you will be able to drive your laser diode and collimate the beam. I will contact you directly to check if there are any further optics or optomechanics necessary for your application. user
(posted 2015-03-31 12:44:26.627) Will this LTC100B come with a collimate tube or focus tube? What should I buy together with this product other than a laser diode? dingwuwen
(posted 2014-06-26 16:13:14.257) I'd like to know if I want to use the FPL1059T 1650 nm Fabry-Perot Laser Diode with the LTC100-C, which molded aspheric lenses should I chose?
I want to use the FPL1059T 1650 nm Fabry-Perot Laser Diode. Will the molded aspheric lenses in the LTC100-C work for the FPL1059T? Or which molded aspheric lenses should I chose? jlow
(posted 2014-08-01 01:36:04.0) Response from Jeremy at Thorlabs: The appropriate lens choice will depend on the output beam diameter you are looking for. The lens included in the current LTC100-C is the C230TMD-C, which can be used with the FPL1059T kedves
(posted 2014-04-07 15:56:09.99) Dear Thorlabs,
Is it possible to order a Complete Laser Diode Operation Starter Set with an LDC201CU or LDC202C current controller, instead of an LDC205C? Could you please send a quotation for these?
Thanks, cdaly
(posted 2014-04-08 07:17:02.0) Response from Chris at Thorlabs: Thank you for your inquiry. We have offered these kits with different controllers in the past. I will contact you directly to have a quote started for you. Future inquiries for custom versions can be sent to us directly at techsupport@thorlabs.com. bdada
(posted 2012-01-25 20:01:00.0) Response from Buki at Thorlabs:
Yes, cables for the controllers are included in the kit. Please contact TechSupport@thorlabs.com if you have further questions. user
(posted 2012-01-26 08:05:27.0) I can not find in the page but does cables come with the kit? sharrell
(posted 2012-01-23 11:21:00.0) An Additional Response from Sean at Thorlabs: We will soon add an LTC100 kit with an AR coated lens for 400 - 600 nm as a stock catalog item. For more details, please contact techsupport@thorlabs.com. bdada
(posted 2012-01-23 08:48:00.0) Response from Buki at Thorlabs:
We can provide you with a custom LTC100 kit with an AR coated lens for 400 - 600nm. We do not have your contact information, so please email TechSupport@thorlabs.com to get a quote. user
(posted 2012-01-19 14:04:16.0) Hi, is this Laser Diode Operation Starter Set compatible with short wavelenght laser diodes, for example, HL40023MG?
If so, then the accessories for 600-1050 nm or 1050-1550 nm are not needed, right?
Thanks, jvigroux
(posted 2012-01-10 09:38:00.0) A response from Julien at Thorlabs: Hello. Yes this is correct. If you would like to have more information about those laser diode drivers and their compatibility, please feel free to contact us a techsupport@thorlabs.com bslalit
(posted 2012-01-10 01:22:38.0) Hello, So I can use LDC205C and the TED200C with the mount LM14S2 and laser diode FPL1053S. Is that so ? jvigroux
(posted 2012-01-09 11:17:00.0) A response from Julien at Thorlabs: Hello Lalit, this diode will work fine with the LDC205C and the TED200C which are comprised within the LTC100-C and a LM14S2 bslalit
(posted 2012-01-09 05:46:32.0) Hello
Thanks for the reply.
We are planning to use FPL1053S laser diode alongwith LM14S2 and LTC100-C . Are they compatible according to the TEC specifications as you said LM14S2 does not has TEC element ?
Regards
Lalit jvigroux
(posted 2012-01-09 04:12:00.0) A response from Julien at Thorlabs: Thank you for your inquiry. The controllers Laser diode driver and temperature controller) used in the LTC100 are directly compatible wit the LM14S2 and support all hardware features of this mount. Please note that the LM14S2 does not contain any TEC element as those are normally integrated within the butterfly mount such that in order to check the compatibility of the temperature controller with your system, one would need to check the specs of its TEC element. bslalit
(posted 2012-01-09 00:41:01.0) I want to know whether LTC100-c is compatible with LM14S2(Butterfly Laser Diode Mount). Regards Lalit jjurado
(posted 2011-07-11 16:34:00.0) Response from Javier at Thorlabs to richardson.leao: Thank you very much for your interest in our products. We can certainly offer a version of the LTC100-B with the 2A LDC220C controller. I will contact you directly to start the quotation process. richardson.leao
(posted 2011-07-11 00:22:07.0) Can I have this kit with the 2A laser controller instead? If so, what would be the price? Cheers
richardson Javier
(posted 2010-06-11 09:04:41.0) Response from Javier at Thorlabs to dnmessias: We can offer a special configuration of the LTC100-B with an LDC220C controller. We will contact you directly with a quotation. dnmessias
(posted 2010-06-10 19:09:20.0) I would like to use a similar kit with diode laser of hig her power, about 1 W. Is it possible to replace the LDC205C driver by the LDC220C one? In this case, how can I obtain a cotation?
Best regards
Djalmir N Messias jjurado
(posted 2010-06-01 08:50:43.0) Response from Javier at Thorlabs to kobiadi: our distributor for Israel is Rosh Electroptics. You may contact them for sales and general inquiries at info@roshelop.co.il. For technical inquiries about our products, you may contact us directly at techsupport@thorlabs.com. kobiadi
(posted 2010-05-30 03:44:13.0) Dear Sir / Madame,
If you have an Israelian representive I would like to speak to him about the LTC100B and even other products (detector system).
Best regards,
Kobi Jakobsohn |

| LDMXY Adapter Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Flexure | |
| Optic Cell Travel | ±1.0 mm |
| Optic Cell Threading | SM1 (1.035"-40) Through Tapped |
| XY Adjusters | M3 x 0.25 (250 μm/rev) |
| Slip Plate | |
| Slip Plate Travel | ±1.0 mm (Coarse Adjustment) |
| Cage Compatibility | 4-40 Taps (8 Places) for 30 mm and 60 mm Cage Systems |
| General | |
| Material | Aluminum |
| Dimensions | 4.00" x 4.00" x 0.60" (101.6 mm x 101.6 mm x 15.2 mm) |
| Mass | 0.33 kg (0.73 lbs) |
- XY Flexure Translation of SM1 Thread (±1.0 mm Travel)
- Slip Plate with Cage System Taps for Independent Translation (±1.0 mm Travel)
- Compatible with 30 mm and 60 mm Cage Systems
- Mounts Directly to the Front of LDM Series Laser Diode Mounts
The LDMXY Flexure Adapter provides collimation optics with ±1.0 mm of XY translation. The translating optic cell is SM1 threaded for compatibility with our aspheric lens adapters and aspheric lenses. The front slip plate also offers ±1.0 mm of coarse XY translation independently of the SM1-threaded optic cell and features the same eight 4-40 taps for 30 mm and 60 mm cage system compatibility. This isolates the load of attached cage systems to the LDM Series LD Mount rather than the flexure mechanism. Four standard cap screws can be loosened to adjust the slip plate, while four captive screws are used to attach the LDMXY adapter to the laser diode mount. All screws are compatible with 5/64" (2.0 mm) hex balldrivers and hex keys.

Click to Enlarge
The LDMXY can be used to increase the working distance to the lens, as well as provide X and Y translation.

Click to Enlarge
The flexure translates the
SM1-threaded optic cell independently from the cage system slip plate.

The LDM56DJ mounting flange is used to secure a 532 nm DPSS laser to the LDM56(/M) temperature-controlled laser diode mount. To use, mount either the DJ532-10 or the DJ532-40 laser in the LDM56(/M) mount. Using the two 2-56 x 3/8" cap head screws provided with the flange, or with the mount itself, attach the flange to the mount.
Please note: this flange is sold separately from the LDM56(/M) Temperature Controlled Laser Diode Mount.
 Products Home
Products Home
















 Zoom
Zoom
 LD / TEC Controller & Mount Kit
LD / TEC Controller & Mount Kit