Epi-Illumination for DIY Cerna® Systems

- Modular, User-Configurable Epi-Illuminator Modules
- Breadboard Tops for Custom Illumination
- Exchange Fluorescence Filter Sets
Using a Turret or Cube
WFA2001
Single-Cube Epi-Illuminator Module
OPX2400
Breadboard Top with Two-Position Slider
CSE2100
Epi-Illuminator Module with Removable Filter Turret
Application Idea
Cerna® Microscope with
CSE2100 Epi-Illuminator Turret
CSE2000W
Extra Removable Filter Turret
MDFM-MF2
Filter Cube for Single-Cube Epi-Illuminator Modules

Please Wait

Click to Enlarge
Together, these components allow user-built microscopes to be constructed with a high degree of modularity.

Click to Enlarge
As an alternative or as a supplement to an epi-illuminator module, our breadboard tops can be used.

Click to Enlarge
The dovetail aligns the epi-illuminator module with the optical path of the microscope.

Click to Enlarge
The epi-illumination arm of the microscope body has a female D1N dovetail aligned with the 7.74" throat depth.
Features
- Optical Ports Aligned with 7.74" Throat Depth of DIY Cerna® Systems
- Ready-to-Use Epi-Illuminator Modules
- One Filter Cube Slot or Removable Turret for Six Filter Sets
- Compatible with Uncollimated or Collimated Illumination Sources
- CSE2100 and CSE2200 Offer Additional Optical Side Port
- DIY Epi-Illuminator Modules
- One Filter Cube Slot or Removable Turret for Six Filter Sets
- SM1, SM2, 30 mm Cage, and/or 60 mm Cage Compatible (See Selection Guide Below)
- Breadboard Tops
- 1/4"-20 (M6 x 1.0) Tapped Holes
- OPX2400 has Two-Position Slider for Combining or Switching Between Optical Paths
- Fluorescence Filter Cube for WFA200x Epi-Illuminator Modules
- Extra Removable Filter Turret for CSE2xxx Epi-Illuminator Modules
- Collimation Adapters for Liquid Light Guide (LLG) Integration
- Dovetail Adapters for Thorlabs' Lens Tube and Cage Construction Systems
We offer several epi-illuminator modules and accessories for constructing epi-illumination pathways in DIY Cerna systems. These components are used to guide light through the objective and generate intense illumination across the field of view.
Our ready-to-use epi-illuminator modules condition incoming light to provide even illumination across the field of view at the sample plane. The WFA2001 Epi-Illuminator Module ships ready to connect to illumination sources such as Thorlabs' mounted LEDs and high-power Solis® microscopy LEDs, while the CSE2100 and CSE2200 Epi-Illuminator Modules accept collimated illumination sources that are coupled into our Ø1" lens tubes, Ø2" lens tubes via the SM2A56 dovetail adapter, and 30 mm and 60 mm cage systems. Alternatively, our DIY Epi-Illuminator Modules, Breadboard Tops, and Breadboard Top with Two-Position Slider enable completely home-built illumination setups. See the selection guide below for additional details.
We offer the MDFM-MF2 Microscopy Filter Cube for the WFA2001 and WFA2002 Epi-Illuminator Modules. For the CSE2000, CSE2100, and CSE2200 Epi-Illuminator Modules, we have designed the CSE2000W Filter Turret, which holds up to six filter sets directly without the need for separate filter cubes.
Both the filter cubes and filter turret accept Ø25 mm excitation and emission filters and 25 mm x 36 mm dichroic filters, making them compatible with filters from all major manufacturers. We also manufacture 25 mm x 36 mm plate beamsplitters for white-light imaging with epi-illumination and a 25 mm x 36 mm protected silver mirror.
Selection Guide
| Item # | WFA2001a | WFA2002 | CSE2100a | CSE2200a | CSE2000 | CSA3000(/M) | CSA3010(/M) | OPX2400(/M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epi-Illuminator Module Type |
Ready to Use | DIY | Ready to Use | DIY | Breadboard Top | Breadboard Top with Two-Position Slider | ||
| Fluorescence Filter Set Mounting |
One Filter Cube (Not Included) | Turret for Six Filter Sets (Included) | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||
| Compatible Illumination Source |
Uncollimated | User-Constructed Optical Pathb |
Primary Path: Collimated Additional Path: User-Constructed, Uncollimated |
User-Constructed Optical Pathb |
User-Constructed Optical Pathb | |||
| Illumination Source Mounting |
SM1 Threads Ø3 mm LLG |
SM1 Threads 30 mm Cage System |
D3T Dovetail 60 mm Cage System |
60 mm Cage System | 1/4"-20 (M6 x 1.0) Taps | 1/4"-20 (M6 x 1.0) Taps 30 mm Cage System 60 mm Cage System |
1/4"-20 (M6 x 1.0) Taps SM2 Threads 60 mm Cage System |
|
| Additional Optical Port: SM1 Threads 30 mm Cage System |
||||||||
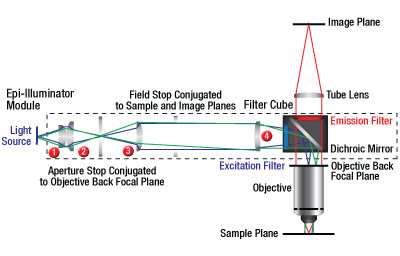
Click to Enlarge
WFA2001 Ready-to-Use Epi-Illuminator Module
The WFA2001 includes a field stop, aperture stop, and optical elements that produce homogeneous illumination across the field of view. It contains one filter cube slot for holding a fluorescence filter set, a beamsplitter with crossed polarizers, or a mirror. It is designed for an uncollimated illumination source.
| WFA2001 Lenses | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 |
AL2018-A |  |
LBF254-040-A |
 |
LBF254-040-A |  |
LBF254-100-A |
| Zemax Black Box | |||
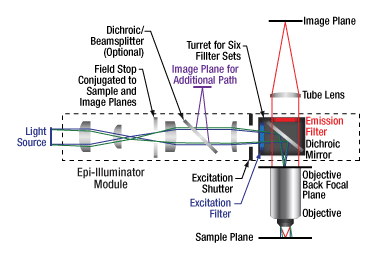
Click for Details
CSE2100 and CSE2200 Ready-to-Use Epi-Illuminator Module
In addition to a field stop and optical elements that provide homogeneous illumination across the field of view, these modules features an additional optical side port. The primary optical path is designed for a collimated illumination source and the additional optical path is designed for a focused illumination source at a distance D1 from the module body (see enlarged diagram). The working distance between the bottom of the dovetail and the back focal plane of the objective (D2 in enlarged diagram) is 50 mm for the CSE2100 and 150 mm for the CSE2200. Both the CSE2100 and CSE2000 contain a removable filter turret, providing room for up to six fluorescence filter sets, beamsplitters with crossed polarizers, or mirrors.
Please note that, unlike the WFA2001, the CSE2100 and CSE2000 use lenses not currently sold separately by Thorlabs.
| CSE2100 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Zemax Black Box |
Cerna® microscopes support several imaging modalities, including epi-fluorescence, brightfield illumination, differential interference contrast (DIC) imaging, and Dodt gradient contrast imaging. Each of these methods requires different accessories and confers different advantages to the microscopist, as described below.
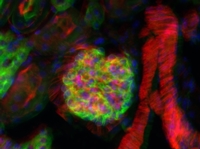
Click to Enlarge
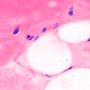
Epi-Fluorescence Image of Mouse Kidney with Multiple Labels
Epi-Fluorescence
Epi-fluorescence makes use of fluorescent labels and intrinsic fluorescence in a specimen to identify sample features. To create an epi-fluorescence image, light that has been passed through an excitation filter is directed through an objective and absorbed by a sample. This excitation causes fluorophores within the sample to emit light of a longer wavelength (i.e., lower energy) than the excitation light. Some of this emitted light is collected by the objective, which helps direct the emission onto a camera for observation. Additional details on this imaging modality are available here.
For performing epi-fluorescence measurements in DIY Cerna systems, we offer a range of widefield viewing and epi-illumination accessories, as well as fluorescence filter sets targeted at common fluorophores.
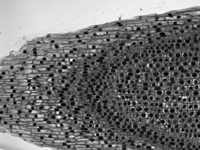
Click for Details
Brightfield Image of Onion Mitosis
Brightfield Illumination
Brightfield illumination is the simplest method of trans-illumination. In this modality, light from an illumination source is collected by a condenser and passed through a sample, which is observed by its effect on the intensity of the transmitted light. Brightfield illumination only requires an illumination source (i.e., an illumination kit) and a condenser to be attached to a DIY Cerna system.
Click to Enlarge
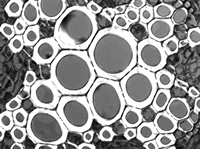
DIC Image of a Buttercup Root
DIC Imaging
In differential interference contrast (DIC) imaging, light transmitted through the sample is manipulated by a number of polarization optics. Light from the illumination source is polarized and then split into two orthogonally polarized beams before it reaches the sample. Small differences in the optical path length experienced by the two beams cause interference when the beams are recombined, providing enhanced contrast for sample features that would be transparent under brightfield illumination. In addition to an illumination source and a condenser, DIC imaging requires several additional optical elements: a DIC polarizer, a condenser prism, an objective prism, and an analyzer.

Click to Enlarge
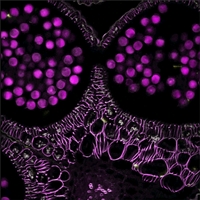
Dodt Contrast Image of a Mouse Retina
Dodt Contrast
Dodt gradient contrast, also known more simply as Dodt contrast, can be understood as an improvement upon oblique illumination. Both methods use a mask to generate an illumination gradient, but in Dodt contrast, the mask occurs much earlier in the optical path. This configuration improves the image contrast to a point where it is comparable to that obtained using DIC.
The Dodt illumination gradient is generated using a specially shaped quarter annulus and diffusers, and reveals thickness changes in a sample over the field of view. Compared to brightfield illumination, Dodt contrast offers improved resolution of sample features, and compared to DIC, it allows thicker samples to be studied. Thorlabs manufactures a pre-configured, pre-aligned illumination module for Dodt contrast that generates the desired gradient; it requires an illumination source and a condenser for operation.
Click to Enlarge
Laser Scanned Image of a Flower Bud
Laser Scanning
Like epi-fluorescence, laser scanning makes use of fluorescent labels and intrinsic fluorescence in a specimen to identify sample features. Unlike epi-fluorescence, laser scanning is able to resolve thin individual planes relatively deep into a thick sample, enabling 3D volumetric images and opening the door to in vivo studies.
Laser scanning techniques (e.g., multiphoton and confocal microscopy) rely upon the coherence of laser beams to provide significantly improved axial resolution. In confocal microscopy, a pinhole eliminates the out-of-focus light that would reduce the axial resolution (as it does in epi-fluorescence), while in multiphoton microscopy, the necessity of two- or three-photon absorption by the fluorophore, a low-probability event, effectively creates optical sections.
Additional details are available at our laser scanning microscopy tutorial.
| Thorlabs Dovetail Referencea | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Shape | Outer Dimension | Angle |
| 95 mm | Linear | 95 mm | 45° |
| D1N | Circular | Ø2.018" | 60° |
| D2Nb | Circular | Ø1.50" | 90° |
| D2NBb | Circular | Ø1.50" | 90° |
| D3N | Circular | Ø45 mm | 70° |
| D5N | Circular | Ø1.58" | 90° |
| D6N | Circular | Ø1.90" | 90° |
| D7N | Circular | Ø2.05" | 90° |
| D1T | Circular | Ø1.50" | 60° |
| D3T | Circular | Ø1.65" | 90° |
| D1Y | Circular | Ø107 mm | 60° |
| D2Y | Circular | Ø2.32" | 50° |
| D3Y | Circular | Ø1.75" | 90° |
| D4Y | Circular | Ø56 mm | 60° |
| D5Y | Circular | Ø46 mm | 60° |
| D6Y | Circular | Ø41.9 mm | 45° |
| D1Z | Circular | Ø54 mm | 60° |
| D2Z | Circular | Ø57 mm | 60° |
| D3Z | Circular | Ø54 mm | 45° |

Click to Enlarge
This photo shows the male D1N dovetail on the trinoculars next to the female D1N dovetail on the epi-illumination arm.

Click to Enlarge
This photo shows the male 95 mm dovetail on the microscope body and the female 95 mm dovetail on the CSA1002 Fixed Arm.
Introduction to Microscope Dovetails
Dovetails are used for mechanical mating and optical port alignment of microscope components. Components are connected by inserting one dovetail into another, then tightening one or more locking setscrews on the female dovetail. Dovetails come in two shapes: linear and circular. Linear dovetails allow the mating components to slide before being locked down, providing flexible positioning options while limiting unneeded degrees of freedom. Circular dovetails align optical ports on different components, maintaining a single optical axis with minimal user intervention.
Thorlabs manufactures many components which use dovetails to mate with our own components or those of other manufacturers. To make it easier to identify dovetail compatibility, we have developed a set of dovetail designations. The naming convention of these designations is used only by Thorlabs and not other microscope manufacturers. The table to the right lists all the dovetails Thorlabs makes, along with their key dimensions.
In the case of Thorlabs’ Cerna® microscopes, different dovetail types are used on different sections of the microscope to ensure that only compatible components can be mated. For example, our WFA2002 Epi-Illuminator Module has a male D1N dovetail that mates with the female D1N dovetail on the microscope body's epi-illumination arm, while the CSS2001 XY Microscopy Stage has a female D1Y dovetail that mates with the male D1Y dovetail on the CSA1051 Mounting Arm.
To learn which dovetail type(s) are on a particular component, consult its mechanical drawing, available by clicking on the red Docs icon (![]() ) below. For adapters with a female dovetail, the drawing also indicates the size of the hex key needed for the locking setscrew(s). It is important to note that mechanical compatibility does not ensure optical compatibility. Information on optical compatibility is available from Thorlabs' web presentations.
) below. For adapters with a female dovetail, the drawing also indicates the size of the hex key needed for the locking setscrew(s). It is important to note that mechanical compatibility does not ensure optical compatibility. Information on optical compatibility is available from Thorlabs' web presentations.
For customers interested in machining their own dovetails, the table to the right gives the outer diameter and angle (as defined by the drawings below) of each Thorlabs dovetail designation. However, the dovetail's height must be determined by the user, and for circular dovetails, the user must also determine the inner diameter and bore diameter. These quantities can vary for dovetails of the same type. One can use the intended mating part to verify compatibility.
In order to reduce wear and simplify connections, dovetails are often machined with chamfers, recesses, and other mechanical features. Some examples of these variations are shown by the drawings below.
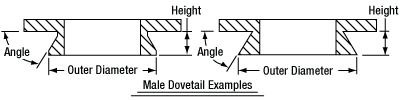
Click to Enlarge
Two examples of how circular male dovetails can be manufactured.
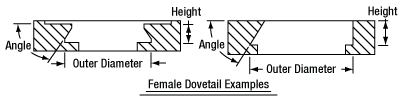
Click to Enlarge
Two examples of how circular female dovetails can be manufactured.
Standard Mechanical Interfaces on DIY Cerna® Components
The table below gives the dovetail, optical component threads, and cage system interfaces that are present on each DIY Cerna component. If a DIY Cerna component does not have one of the standard interfaces in the table, it is not listed here. Please note that mechanical compatibility does not ensure optical compatibility. Information on optical compatibility is available from Thorlabs' web presentations.
| Item # | Microscope Dovetails | Optical Component Threadsa | Cage Systemsb | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95 mm | D1N | D2N | D2NB | D3N | D5N | D1T | D3T | D1Y | D5Y | Internal | External | ||
| 2CM1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM1c (1.035"-40) and SM2d (2.035"-40) | SM1c (1.035"-40) | 60 mmd |
| 2CM2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM1c (1.035"-40) and SM2d (2.035"-40) | SM1c (1.035"-40) | 30 mmc |
| BSA2000e | - | - | - | - | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CEA1350 | Male | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 60 mmd |
| CEA1400 | Male | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 60 mmd |
| CEA1500 | Male | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 60 mmd |
| CEA1600 | Male | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 60 mmd |
| CFB1500 | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CSA1000 | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CSA1001 | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM1c (1.035"-40) | - | 30 mmc |
| CSA1002 | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM2d (2.035"-40) | - | 60 mmd |
| CSA1003 | - | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 60 mmd |
| CSA1051 | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Male | - | - | - | - |
| CSA1200e,f | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 60 mmd |
| CSA1400e | - | - | - | - | - | - | Female | - | - | - | - | - | 60 mmd |
| CSA1500e,g | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CSA2000e | - | - | - | - | Female | - | - | - | - | - | SM2d (2.035"-40) | - | 60 mmd |
| CSA2001 | - | - | - | - | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM2d (2.035"-40) | - |
| CSA2100e | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM2d (2.035"-40) | - | 60 mmd |
| CSA3000(/M) | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CSA3010(/M) | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 30 mmc and 60 mmd |
| Item # | 95 mm | D1N | D2N | D2NB | D3N | D5N | D1T | D3T | D1Y | D5Y | Internal | External | Cage Systems |
| CSC1001 | - | - | - | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CSC1002 | - | - | - | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CSC2001 | - | - | - | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CSD1001 | - | Male & Female | - | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CSD1002 | - | Male & Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | C-Mounth | - |
| CSE2000 | - | Male & Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 60 mmd |
| CSE2100 | - | Male & Female | - | - | - | - | - | Female | - | - | SM1c (1.035"-40) | - | 30 mmc and 60 mmd |
| CSE2200 | - | Male & Female | - | - | - | - | - | Female | - | - | SM1c (1.035"-40) | - | 30 mmc and 60 mmd |
| CSN100e | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | M32 x 0.75 | - | 60 mmd |
| CSN110 | - | - | - | - | - | - | Male | - | - | - | M32 x 0.75 | - | 30 mmc and 60 mmd |
| CSNK10 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | M32 x 0.75 | - | 60 mmd |
| CSNK100e | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | M32 x 0.75 | - | 60 mmd |
| CSN200 | - | - | - | - | - | - | Male | - | - | - | M32 x 0.75 | - | - |
| CSN210 | - | - | - | - | - | - | Male | - | - | - | M32 x 0.75 | - | - |
| CSN1201f | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | M32 x 0.75 | - | - |
| CSN1202f | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | M25 x 0.75 | - | - |
| CSS2001 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Female | - | - | - | - |
| LAURE1 | - | Male | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| LAURE2 | - | Male | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| LCPN1 | - | - | - | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | SM30 (M30.5 x 0.5) | - | 30 mmc and 60 mmd |
| LCPN2 | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM30 (M30.5 x 0.5) | - | 30 mmc and 60 mmd |
| Item # | 95 mm | D1N | D2N | D2NB | D3N | D5N | D1T | D3T | D1Y | D5Y | Internal | External | Cage Systems |
| LCPN3 | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Female | SM30 (M30.5 x 0.5) | - | 60 mmd |
| LCPN4 | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM2d (2.035"-40) | - | 60 mmd |
| LCPN5 | - | - | - | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | SM2d (2.035"-40) | - | 60 mmd |
| LCPN6 | - | - | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM1c (1.035"-40) | - | 30 mmc and 60 mmd |
| LCPY2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Male | SM30 (M30.5 x 0.5) | - | 30 mmc and 60 mmd |
| LCPY3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Female | - | - | 30 mmc and 60 mmd |
| OPX2400(/M) | - | Male & Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM2d (2.035"-40) | - | 60 mmd |
| SM1A70 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM30 (M30.5 x 0.5) | SM1c (1.035"-40) | - |
| SM1A58 | - | - | Male | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM1c (1.035"-40) | SM2d (2.035"-40) | 30 mmc |
| SM2A56 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Male | - | - | - | SM2d (2.035"-40) | - |
| SM2A59 | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM2d (2.035"-40) | - | - |
| TC1X | - | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| WFA0150 | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| WFA1000 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 30 mmc |
| WFA1010 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM1c (1.035"-40) | - | 30 mmc |
| WFA1020 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM1c (1.035"-40) | - | 30 mmc |
| WFA1051 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM1c (1.035"-40) | - | 30 mmc |
| WFA1100 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 30 mmc |
| WFA2001 | - | Male & Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM1c (1.035"-40) | SM1c (1.035"-40) | - |
| WFA2002 | - | Male & Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM1c (1.035"-40) | - | 30 mmc |
| Item # | 95 mm | D1N | D2N | D2NB | D3N | D5N | D1T | D3T | D1Y | D5Y | Internal | External | Cage Systems |
| WFA4100 | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM1c (1.035"-40) | C-Mounth | - |
| WFA4101 | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM1c (1.035"-40) | C-Mounth | - |
| WFA4102 | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM1c (1.035"-40) | C-Mounth | - |
| WFA4111 | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SM2d (2.035"-40) | - |
| WFA4112 | - | - | - | Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | C-Mounth | - |
| Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| XT95P12(/M) | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| ZFM1020 | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| ZFM1030 | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| ZFM2020 | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| ZFM2030 | Female | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Building a Cerna® Microscope
The Cerna microscopy platform's large working volume and system of dovetails make it straightforward to connect and position the components of the microscope. This flexibility enables simple and stable set up of a preconfigured microscope, and provides easy paths for later upgrades and modification. See below for a couple examples of the assembly of some DIY Cerna microscopes.
DIY Cerna Design and Assembly
Walkthrough of a DIY Microscope Configuration
This DIY microscope uses a CSA3000(/M) Breadboard Top, a CSA2001 Dovetail Adapter, our CSA1001 and CSA1002 Fixed Arms, and other body attachments and extensions. These components provide interfaces to our lens tube and cage construction systems, allowing the rig to incorporate two independent trans-illumination modules, a home-built epi-illumination path, and a custom sample viewing optical path.
The simplicity of Thorlabs optomechanical interfaces allows a custom DIY microscope to be quickly assembled and reconfigured for custom imaging applications.
| Posted Comments: | |
Ik Hwan Kwon
(posted 2022-04-01 16:38:55.77) Hello.
I have question for using CSE 2000 control program.
I installed CSE 2000 control program version 4.0.
However, It looks non-connected hardware to PC.
Because, When I started program, It doesn't show any control panel even CSE 2000 connected with PC using USB 2.0 cable.
(it only shows that "File" menu button & Thorlabs "logo mark")
Could you solve this problem? cdolbashian
(posted 2022-04-05 04:22:07.0) Thank you for reaching out to us with this troubleshooting issue. I have reached out to you directly to identify and solve your problem. For future technical support requests, please feel free to contact Techsupport@thorlabs.com. Ed Carlen
(posted 2021-09-26 16:47:28.093) According the optical diagram of the WFA2001, lens 4 is the LBF254-100A with a focal length of 100mm. However, the distance D1 (in optical diagram) is specified to be 110mm from bottom of dovetail to the back focal plane of the objective. Are these specifications correct? cdolbashian
(posted 2021-11-09 03:35:35.0) Thank you for reaching out to us at Thorlabs. based on the drawing in the optical diagram, I see your confusion. The optical path from the back of lens 4 to the back focal plane of the objective is ~174mm, which is notably longer than the focal length of lens 4 (100mm), so it would seem like the light would converge at some intermediate distance between lens 4 and the back focal plane of the objective. However, the light between lens 3 and 4 is still diverging, so that the focal point of the 100mm lens is still at the back focal plane, rather than ~100mm beyond the last lens surface. I have reached out to you to discuss this further! Noah Kolodziejski
(posted 2020-06-19 12:39:20.157) For CSE2200, I would like to move the last lens before the excitation filter to the bottom of the unit to buy extra distance between CSE2200 and the objective. This is so that I might fit a laser autofocus assembly between CSE2200 and the objective lens, and I like having an infinity corrected system in the filter area, allowing me to stack additional spectroscopic hardware above the CSE 2200. Is this violating some fundamental of the device or is it achievable ? YLohia
(posted 2020-07-21 04:29:06.0) Thank you for contacting Thorlabs. We do not recommend doing this. The lenses within the CSE2200 are designed for light delivery, not imaging. It is not a tube lens. The camera usually sits on top with a separate tube lens before it, something like the WFA4100. If you want a filter wheel, you could use the CSE2000 and use the cage rod connections to build your autofocus in, or you could get a LCPN2 to build you own setup on top of the CSE2x00. user
(posted 2020-03-22 13:24:07.763) For CSE2100, is it possible to have AR coated optics for NIR or IR range?
I also want to have the light in/out from the side port on CSE 2100. (So the returning light is not directed into the camera). Instead of using a two-position slider, is it possible to have a thin gold mirror (25mmx36mmx1mm) to replace the dichroic mirror in side the filter cube? YLohia
(posted 2020-04-13 11:09:29.0) Hello, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. We can offer a B-coated version of the CSE2100 as a custom option. I have reached out to you directly to discuss other options. t.isaac
(posted 2018-02-20 15:54:41.667) Are there any plans to make a dovetail adapter with a D3T female port and an external thread such as SM2? I would find this very useful for interchanging parts from the Cerna microscope inputs to other setups. llamb
(posted 2018-03-31 02:18:56.0) Hello, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. While we currently have the SM2A56 adapter with a male D3T dovetail and external SM2 threads, we do not plan to release an adapter with a female D3T port and external SM2 threads soon. I will add this to our internal product forum. parksj003
(posted 2017-03-31 09:35:00.697) The The filter qube is working with a Nikon Eclipse Ti.
Thanks
Seongjun Park tfrisch
(posted 2017-04-18 04:43:12.0) Hello, thank you for this additional information. parksj003
(posted 2017-03-31 09:27:15.397) Hello,
I am looking for a module for 9103 (filter qube mady by Chroma)to work with Thorlabs' cage components. (something like WFA2002). Would you let me know if there is any?
Best,
Seongjun Park tfrisch
(posted 2017-04-18 04:24:20.0) Hello, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. I will reach out to you directly about your application. I will need more details on 9103. |
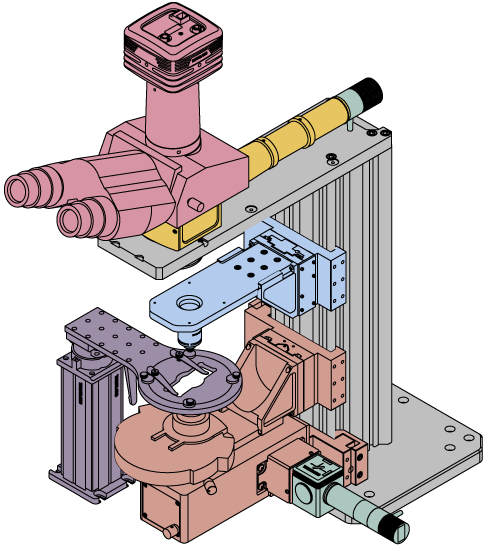
Click on the different parts of the microscope to explore their functions.
Elements of a Microscope
This overview was developed to provide a general understanding of a Cerna® microscope. Click on the different portions of the microscope graphic to the right or use the links below to learn how a Cerna microscope visualizes a sample.
Terminology
Arm: Holds components in the optical path of the microscope.
Bayonet Mount: A form of mechanical attachment with tabs on the male end that fit into L-shaped slots on the female end.
Bellows: A tube with accordion-shaped rubber sides for a flexible, light-tight extension between the microscope body and the objective.
Breadboard: A flat structure with regularly spaced tapped holes for DIY construction.
Dovetail: A form of mechanical attachment for many microscopy components. A linear dovetail allows flexible positioning along one dimension before being locked down, while a circular dovetail secures the component in one position. See the Microscope Dovetails tab or here for details.
Epi-Illumination: Illumination on the same side of the sample as the viewing apparatus. Epi-fluorescence, reflected light, and confocal microscopy are some examples of imaging modalities that utilize epi-illumination.
Filter Cube: A cube that holds filters and other optical elements at the correct orientations for microscopy. For example, filter cubes are essential for fluorescence microscopy and reflected light microscopy.
Köhler Illumination: A method of illumination that utilizes various optical elements to defocus and flatten the intensity of light across the field of view in the sample plane. A condenser and light collimator are necessary for this technique.
Nosepiece: A type of arm used to hold the microscope objective in the optical path of the microscope.
Optical Path: The path light follows through the microscope.
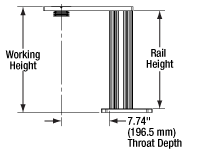
Rail Height: The height of the support rail of the microscope body.
Throat Depth: The distance from the vertical portion of the optical path to the edge of the support rail of the microscope body. The size of the throat depth, along with the working height, determine the working space available for microscopy.
Trans-Illumination: Illumination on the opposite side of the sample as the viewing apparatus. Brightfield, differential interference contrast (DIC), Dodt gradient contrast, and darkfield microscopy are some examples of imaging modalities that utilize trans-illumination.
Working Height: The height of the support rail of the microscope body plus the height of the base. The size of the working height, along with the throat depth, determine the working space available for microscopy.
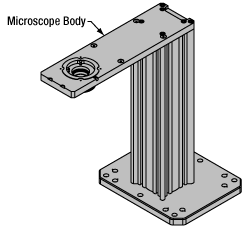 Click to Enlarge
Click to EnlargeCerna Microscope Body
Click to Enlarge
Body Details
Microscope Body
The microscope body provides the foundation of any Cerna microscope. The support rail utilizes 95 mm rails machined to a high angular tolerance to ensure an aligned optical path and perpendicularity with the optical table. The support rail height chosen (350 - 600 mm) determines the vertical range available for experiments and microscopy components. The 7.74" throat depth, or distance from the optical path to the support rail, provides a large working space for experiments. Components attach to the body by way of either a linear dovetail on the support rail, or a circular dovetail on the epi-illumination arm (on certain models). Please see the Microscope Dovetails tab or here for further details.
 Click to Enlarge
Click to EnlargeIllumination with a Cerna microscope can come from above (yellow) or below (orange). Illumination sources (green) attach to either.
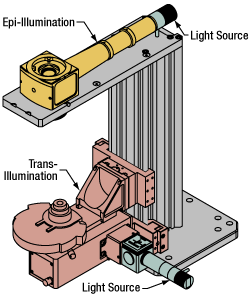
Illumination
Using the Cerna microscope body, a sample can be illuminated in two directions: from above (epi-illumination, see yellow components to the right) or from below (trans-illumination, see orange components to the right).
Epi-illumination illuminates on the same side of the sample as the viewing apparatus; therefore, the light from the illumination source (green) and the light from the sample plane share a portion of the optical path. It is used in fluorescence, confocal, and reflected light microscopy. Epi-illumination modules, which direct and condition light along the optical path, are attached to the epi-illumination arm of the microscope body via a circular D1N dovetail (see the Microscope Dovetails tab or here for details). Multiple epi-illumination modules are available, as well as breadboard tops, which have regularly spaced tapped holes for custom designs.
Trans-illumination illuminates from the opposite side of the sample as the viewing apparatus. Example imaging modalities include brightfield, differential interference contrast (DIC), Dodt gradient contrast, oblique, and darkfield microscopy. Trans-illumination modules, which condition light (on certain models) and direct it along the optical path, are attached to the support rail of the microscope body via a linear dovetail (see Microscope Dovetails tab or here). Please note that certain imaging modalities will require additional optics to alter the properties of the beam; these optics may be easily incorporated in the optical path via lens tubes and cage systems. In addition, Thorlabs offers condensers, which reshape input collimated light to help create optimal Köhler illumination. These attach to a mounting arm, which holds the condenser at the throat depth, or the distance from the optical path to the support rail. The arm attaches to a focusing module, used for aligning the condenser with respect to the sample and trans-illumination module.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Epi-Illumination Modules | Breadboards & Body Attachments |
Brightfield | DIC | Dodt | Condensers | Condenser Mounting | Light Sources |
 Click to Enlarge
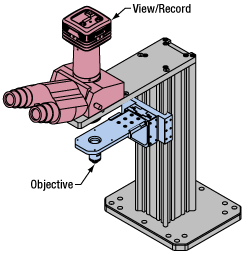
Click to EnlargeLight from the sample plane is collected through an objective (blue) and viewed using trinocs or other optical ports (pink).
Sample Viewing/Recording
Once illuminated, examining a sample with a microscope requires both focusing on the sample plane (see blue components to the right) and visualizing the resulting image (see pink components).
A microscope objective collects and magnifies light from the sample plane for imaging. On the Cerna microscope, the objective is threaded onto a nosepiece, which holds the objective at the throat depth, or the distance from the optical path to the support rail of the microscope body. This nosepiece is secured to a motorized focusing module, used for focusing the objective as well as for moving it out of the way for sample handling. To ensure a light-tight path from the objective, the microscope body comes with a bellows (not pictured).
Various modules are available for sample viewing and data collection. Trinoculars have three points of vision to view the sample directly as well as with a camera. Double camera ports redirect or split the optical path among two viewing channels. Camera tubes increase or decrease the image magnification. For data collection, Thorlabs offers both cameras and photomultiplier tubes (PMTs), the latter being necessary to detect fluorescence signals for confocal microscopy. Breadboard tops provide functionality for custom-designed data collection setups. Modules are attached to the microscope body via a circular dovetail (see the Microscope Dovetails tab or here for details).
 Click to Enlarge
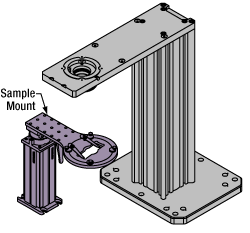
Click to EnlargeThe rigid stand (purple) pictured is one of various sample mounting options available.
Sample/Experiment Mounting
Various sample and equipment mounting options are available to take advantage of the large working space of this microscope system. Large samples and ancillary equipment can be mounted via mounting platforms, which fit around the microscope body and utilize a breadboard design with regularly spaced tapped through holes. Small samples can be mounted on rigid stands (for example, see the purple component to the right), which have holders for different methods of sample preparation and data collection, such as slides, well plates, and petri dishes. For more traditional sample mounting, slides can also be mounted directly onto the microscope body via a manual XY stage. The rigid stands can translate by way of motorized stages (sold separately), while the mounting platforms contain built-in mechanics for motorized or manual translation. Rigid stands can also be mounted on top of the mounting platforms for independent and synchronized movement of multiple instruments, if you are interested in performing experiments simultaneously during microscopy.

the WFA2001 Single-Cube Epi-Illuminator Module
Click for Details
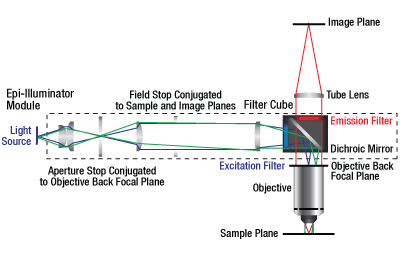
Optical Diagram for WFA2001 (See Optical Diagrams Tab for More Details)
- WFA2001: Pre-Installed Optical Path that Accepts an Uncollimated Illumination Source with a Ø3 mm Core Liquid Light Guide or SM1 Threads
- WFA2002: Build Your Own Optical Path using SM1 and 30 mm Cage Components
- Magnetic Door Cover Holds One Olympus-Compatible Filter Cube
- Stackable Design with Female and Male D1N Dovetails on Top and Bottom, Respectively
- MDFM-MF2 Filter Cube is Sold Separately Below
These epi-illuminator modules hold one filter cube in the epi-illumination pathway of a DIY Cerna system. With a female D1N dovetail on top and a male D1N dovetail on the bottom, they are designed to mate with the epi-illumination arm of a Cerna microscope body, as well as with each other. Additional details on dovetails are available in the Microscope Dovetails tab.
The WFA2001 Epi-Illuminator Module's optical input port has internal SM1 (1.035"-40) threads. For this port, we include two adapters: an adapter that accepts a Ø3 mm core liquid light guide and an SM1T10 adapter that accepts an uncollimated light source with an internally SM1-threaded output, such as a mounted LED. For use with a Ø5 mm core liquid light guide, the AD5LLG adapter is available for purchase separately. This module is designed so that evenness of illumination is optimized at a 110 mm working distance between the bottom of the dovetail and the back focal plane of the objective; see the optical diagram to the right. Its pre-installed optical path consists of collimating optics that are AR coated for 350 - 700 nm, as well as field stop and aperture stop diaphragms (Item # SM1D12D) that can be adjusted from Ø0.8 mm to Ø12.0 mm (Ø0.03" to Ø0.47").
In contrast, the WFA2002 Epi-Illuminator Module does not include the pre-installed optical path of the WFA2001. As shown by the photo below, removing the optical path exposes internal SM1 threads and four 4-40 taps for 30 mm cage systems on the back of the module. These mechanical interfaces enable Thorlabs' extensive selection of SM1 and 30 mm cage components to be used to build custom epi-illumination paths.
Each of these modules includes a magnetically secured cover that can be connected to an MDFM-MF2 Filter Cube (sold separately below), as shown by the animation in the upper right. Extra covers, which the user can attach to the filter cubes to speed up filter cube exchange, are sold as Item # WFA2001C.
Please note that these epi-illuminators do not have the slot required for the WFA3110 DIC Analyzer, so a custom mounting solution will be needed. The CSE2100, CSE2000, and CSE2200 Epi-Illuminator Modules sold below are directly compatible with this DIC analyzer.

Click to Enlarge
The WFA2001 Epi-Illuminator Module has a ready-to-use beam path, with field stop and aperture stop diaphragms, for a mounted LED or another uncollimated source with SM1 threads or a Ø3 mm liquid light guide.
The back of the WFA2002 Epi-Illuminator Module has internal SM1 threads and four 4-40 taps for a 30 mm cage system, which can be used to support home-built epi-illumination setups.

Turret Position Sensor Software
Version 4.0 (October, 2019)
This software package contains the installation files for the GUI interface, driver, SDK, and support documentation. The software is compatible with Windows® 7 (64-bit) and Windows 10 (64-bit) systems.

Click to Enlarge
The CSE2000 Epi-Illuminator Module features 4-40 taps to connect to a 60 mm cage system.
- Included Removable Turret Holds Up to Six Filter Sets without the Need for Filter Cubes
- Stackable Design with Female and Male D1N Dovetails on Top and Bottom, Respectively
- Directly Compatible with WFA3110 DIC Analyzer
- Monitor Filter Turret Position on a PC Using Included Software Package
- Ready-to-Use Epi-Illuminator Modules with Beam Conditioning Optics
- Do-It-Yourself CSE2000 Epi-Illuminator Module without Beam Conditioning Optics
- Side Port for Additional Optical Path Included on CSE2100 and CSE2200
These Epi-Illuminator Modules hold a rotating, removable turret in the epi-illumination pathway of a DIY microscope system. One turret is included with each epi-illuminator module, and additional turrets can be purchased separately below (Item # CSE2000W). Fluorescence filter sets, beamsplitters, mirrors, and/or bandpass filters can be directly loaded into the turret without the need for filter cubes. In all models, turret position may be monitored remotely on a PC (not included) with included software; see the Software box at the top right to download the GUI installation files. In addition, a tab opens and closes a shutter that blocks the optical path directed through the excitation filter.
Unlike the WFA2001 and WFA2002 Epi-Illuminator Modules sold above, the CSE2000, CSE2100, and CSE2200 Epi-Illuminator Modules have a slot for direct compatibility with the WFA3110 DIC Analyzer.
Microscope Compatibility
With a female D1N dovetail on top and a male D1N dovetail on the bottom, these modules are designed to mate with the epi-illumination arm of a Cerna microscope body, Thorlabs' four-channel confocal microscopes, the breadboard tops sold below, other epi-illuminator modules, and other widefield viewing accessories. Additional details on dovetails are available in the Microscope Dovetails tab.
Ready-to-Use Epi-Illuminator Modules
The CSE2100 and CSE2200 include beam conditioning optics optimized for homogeneous illumination at the sample plane. The CSE2100 is designed so that evenness of illumination is optimized at a 50 mm working distance between the bottom of the dovetail and the back focal plane of the objective. The CSE2200 Epi-Illuminator Module is designed to provide a longer working distance of 150 mm, ideal for use with a Thorlabs confocal microscope system or Cerna microscopes that require additional optics between the module and the objective lens. For details, see optical diagram to the lower right.
Both the CSE2100 and CSE2200 Epi-Illuminator Modules features AR-coated optical elements designed for homogeneous illumination over 365 - 700 nm, as well as a field stop diaphragm, creating a ready-to-use optical path for the epi-illumination source. A collimated illumination source, such as our Solis® High-Power LED, can be attached using the female D3T dovetail on the back of the module; the SM2A56 adapter and LLG collimation adapters are sold below. Alternatively, by removing the back piece, a 60 mm cage system can be mounted using the
An additional optical path can also be utilized by inserting a beamsplitter or dichroic (32 mm x 44 mm, 2.0 ± 0.1 mm in thickness) into the module; please contact Tech Support for compatible dichroics or beamsplitters. This side port features internal SM1 (1.035"-40) threading as well as 4-40 taps for our 30 mm cage system.
DIY Epi-Illuminator Module
In contrast to the CSE2100 and CSE2200 (described above), the CSE2000 Epi-Illuminator Module does not include beam conditioning optics. This standalone module features four 4-40 taps for 60 mm cage systems on the back side. This mechanical interface enables Thorlabs' extensive selection of 60 mm cage components to be used to build custom epi-illumination paths. To utilize the CSE2000 with an existing microscope featuring alternate dovetails, contact Tech Support for a custom solution.

Click to Enlarge
The CSE2100's or CSE2200's ready-to-use optical path allows an illumination source to be attached through either a D3T dovetail on a back piece, or 4-40 taps for a 60 mm cage system when the back piece is removed. The D3T dovetail can be converted to SM2 threading using the SM2A56 adapter.

Click for Details
The CSE2100 (shown here) and CSE2200 Epi-Illuminator Modules provide a field stop diaphragm and conditioning optics for the main optical path as well as a side port for an additional optical path.
| Specifications |
|---|


Click for Details
CSA3000 Used to Mount a Custom Epi-Illuminator and Widefield Viewing Apparatus with a sCMOS Camera

Click for Details
CSA3010 Used to Mount a Custom Epi-Illuminator and Widefield Viewing Apparatus with a sCMOS Camera
- Male D1N Dovetail on Bottom for Attachment to DIY Cerna Microscope Bodies
- Available in Two Sizes in Imperial and Metric Versions:
- Imperial: 14.00" x 11.00" or 18.00" x 4.60"
- Metric: 350.0 mm x 275.0 mm or 450.0 mm x 116.8 mm
- 1/4"-20 or M6 x 1.0 Mounting Holes

Click to Enlarge
Each breadboard has a male D1N dovetail on the bottom.
These black-anodized aluminum breadboard tops support user-designed widefield viewing apparatuses, epi-illumination pathways, and laser scanning pathways on top of upright Cerna microscopes. Each contains a Ø1.5" (Ø38.1 mm) through hole that is centered on a male D1N dovetail. This dovetail allows the breadboard to be connected directly to the epi-illumination arm of the microscope body, and it can also be used to stack the breadboard on top of an epi-illumination module. Additional details on the dovetail are available in the Microscope Dovetails tab.
The breadboards are available in two sizes. The larger version [Item # CSA3000(/M)] provides additional work surface, but protrudes past the sides of the epi-illumination arm, which may restrict approach angles around the objective for micromanipulators. The smaller version [Item # CSA3010(/M)] does not restrict approach angles and also has eight 4-40 taps around the Ø1.5" through hole for 30 mm and 60 mm cage systems.
In configurations where the breadboard is mounted directly on top of the epi-illumination arm, four M4 counterbores can be used to provide additional mounting stability.


Click to Enlarge
Here, a white-light illumination path has been connected to the OPX2400 using our 60 mm cage system, and a GFP fluorescence path has been mounted on top of the OPX2400 via our WFA2002 epi-illuminator module.
- Two-Position Slider to Combine or Switch Between DIY Optical Paths
- Slider has Internal SM2 Threads and Holds One 35 mm x 52 mm x 3 mm Optic
- Back Port has Internal SM2 Threads and Four 4-40 Taps for Our 60 mm Cage System
- Imperial and Metric Versions
- OPX2400: 10.16" x 3.94" Breadboard with Double-Density 1/4"-20 Tapped Holes
- OPX2400/M: 258 mm x 100 mm Breadboard with Double-Density M6 x 1.0 Tapped Holes
- Stackable Design with Female and Male D1N Dovetails on Top and Bottom, Respectively

Click to Enlarge
Slider Located Above Objective

Click to Enlarge
Slider Not in Optical Path with Objective
The lid of the slider housing is opened by removing four cap screws with a 3 mm balldriver. The slider and the slider housing are internally SM2-threaded. Two stainless steel tracks and detents provide repeatable positioning.
The OPX2400(/M) Breadboard Top with Two-Position Slider adds a manually operated optic slider to the epi-illumination arm of a Cerna microscope body. By mounting a dichroic, beamsplitter, or mirror into the slider, users may combine or switch between widefield viewing, epi-illumination, and/or laser scanning pathways.
The optic slider has a clear aperture of Ø1.65" (Ø41.9 mm) and uses a leaf spring to retain a rectangular optic (minimum size: 34.9 mm x 51.9 mm x 2.8 mm; maximum size: 35.0 mm x 52.0 mm x 3.2 mm); the large aperture and optic size make this ideal for applications requiring large area scanning. It has internal SM2 (2.035"-40) threads that face the back of the stationary housing, allowing a tube lens to be installed at a fixed distance from the dichroic. The back of the housing also has internal SM2 threads, as well as four 4-40 taps spaced for our 60 mm cage system.
In addition, a breadboard with sixty-eight 1/4"-20 (M6 x 1.0) through-tapped holes in a double-density hole pattern is included to support a home-built optical path. More 1/4"-20 (M6 x 1.0) tapped holes (sixteen on the imperial version and eighteen on the metric version) are located on the sides of the breadboard. Measured from the top of the breadboard, the beam height is 50.0 mm. Thorlabs manufactures Ø12 mm pedestal posts that center many of our 30 mm and 60 mm cage plates at this beam height, as illustrated in this photo, which provide structural support for large or heavy setups.
Thorlabs offers a 750 nm shortpass dichroic (Item # DMSP750B) and a protected silver mirror (Item # PFR14-P02) as stocked items. Beamsplitters and dichroics at additional cutoff wavelengths are available by contacting Tech Support. Once the optic is mounted, a 5/64" (2 mm) hex balldriver can be used to fine tune the optic slider's pitch and yaw adjusters. The slider may be locked in either position by tightening the included locking screw with a 3/32" balldriver. In the photo to the upper right, the locking screw is installed in the forward position.
In laser scanning Cerna systems, we recommend attaching the tube lens using the internal SM2 threads on the slider, since this will maximize the distance available along the throat depth to mount the objective and, if desired, non-descanned detectors.

Installation of Filters into the MDFM-MF2 Cube
- Compatible with WFA2001 and WFA2002 Epi-Illuminator Modules
- OEM Filter Cube from Olympus
- Designed for Use with Thorlabs' and Third-Party Fluorescence Filter Sets
This OEM Filter Cube is manufactured by Olympus. It holds one set of fluorescence filters: an excitation filter (Ø25 mm, up to 5 mm thick), an emission filter (Ø25 mm, up to 3.5 mm thick), and a dichroic mirror (up to 25.2 mm x 36.0 mm x 1.0 mm). Optics can be mounted, aligned, and swapped out easily as illustrated in the video to the right. The filter cube body may be disassembled for optic installation or removal using a Phillips head screwdriver. For detailed assembly instructions, please refer to the assembly manual in the table below.
We also offer additional Thorlabs and OEM Microscope Filter Cubes that are compatible with select Olympus and Nikon Microscopes.
| Item # | Manufacturer Part # |
Microscope Manufacturer |
Compatible Microscopes | Assembly Manual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDFM-MF2 | Olympus U-MF2 | Olympus | AX, BX2, and IX2 Series | MDFM-MF2 Manual |
| Thorlabs | Cerna Epi-Fluorescence Microscopes with WFA2001 or WFA2002 Epi-Illuminator Module |
Please contact Tech Support with questions regarding other cube compatibility, mounting, and filter options.


Click for Details
Remove the Top Plate from the Turret to Install Dichroics or Mirrors

Click to Enlarge
CSE2000W Filter Turret with Top Plate
- Removable Turret Compatible with CSE2000, CSE2100, and CSE2200 Epi-Illuminator Modules
- Easily Install Multiple Filter Sets in a Particular Configuration
- Designed for Use with Thorlabs' and Third-Party Fluorescence Filter Sets
The CSE2000W Turret allows for simple installation of up to six fluorescence filter sets, without the need for filter cubes. This turret directly accepts up to six filter sets without requiring filter cubes: six excitation filters (Ø25.4 mm, <5.1 mm in thickness), six emission filters (Ø25.4 mm, <5.1 mm in thickness), and six rectangular optics (25 mm x 36 mm, 1 ± 0.1 mm in thickness). The emission filters are mounted at a 5° angle to reduce unwanted back reflections. Having multiple filter sets in the same turret, or multiple turrets with particular optic configurations, makes it easy to switch amongst fluorescence filter sets, beamsplitters with crossed polarizers for reflected light imaging, and mirrors. When used with the CSE2000, CSE2100, or CSE2200 epi-illuminator modules (sold above), the turret position can be monitored remotely on a PC with software included with those modules.
The circular optic apertures feature internal SM1 (1.035"-40) threading for simple mounting of Ø1" optical elements; each turret ships with twelve SM1RR retaining rings, one to secure each circular filter. To install the rectangular optics, remove the top plate of the turret by loosening the three M3 screws, then remove the leaf springs to secure each optic. The turret utilizes grip holes on either side of each filter set, both for ease of use and to ensure the optical elements are not touched once installed. Once inserted into an epi-illumination module, simply turn the exposed knurled wheel to switch the filter set in the optical path.

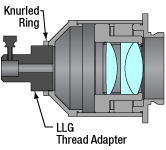
Click to Enlarge
Cutaway View of LLG3A6 and LLG5A6 Collimation Adapters
To provide compatibility with our CSE2100 and CSE2200 epi-illuminator modules, Thorlabs offers collimation adapters to mount onto the end of either a Ø3 mm or Ø5 mm liquid light guide (LLG). To provide even collimation of input light, each adapter features an optic pair of an achromatic doublet and a double convex lens; see the table below for details. The LLG is secured to the back of the collimator with a screw. Each adapter utilizes a male D3T dovetail adapter.
All adapters are calibrated such that the image plane from the LLG output is located at the back aperture of the objective when used with the compatible epi-illuminator module. Each adapter allows fine adjustment to optimize illumination for your microscope or realign the image plane via the knurled ring on the thread adapter (see image to the right).
| Specifications | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item # | LLG3A6 | LLG5A6 | LLG3A7 | LLG5A7 |
| Compatible Epi-Illuminator Module |
CSE2100 | CSE2200 | ||
| Accepted LLG Diameter | 3 mm | 5 mm | 3 mm | 5 mm |
| LLG Retention Screw | Thumbscrew | |||
| Mechanical Connection | Male D3T Dovetail | |||
| Effective Focal Length | 40 mm | 70 mm | ||
| Collimating Optics | Achromatic Doublet & Double Convex Lensa | |||
| AR Coating | 350 nm - 650 nm Ravg < 0.5% at Each Surface |
|||
| Transmission Graph | Click Here for Raw Data |
|||
| Numerical Aperture | 0.3 | |||
| Magnification | Infinite | |||

This adapter allows a collimated illumination source, such as Thorlabs' Solis® LEDs, to attach to the epi-illumination module of a Cerna microscope. We offer the SM2A56 adapter for use with our CSE2100 and CSE2200 epi-illuminator modules. See the table below for adapter attachment compatibility.


Click for Details
Here, the CSA1003 Dovetail Adapter is being used to connect a 60 mm cage system to the bottom of a WFA2002 Epi-Illuminator Module.

Click to Enlarge
Here, the WFA4111 adapter is being used to mount an SM2 lens tube on top of an WFA2002 Epi-Illuminator Module.
- Extend Versatility of Thorlabs' Lens Tube and Cage Construction Systems to DIY Cerna Systems
- LCPN2: Male D1N Dovetail, Internal SM30 Threads, and 30 mm and 60 mm Cage Compatibility
- LCPN3: Male D1N Dovetail, Female D5Y Dovetail, Internal SM30 Threads, and 60 mm Cage Compatibility
- WFA4111: Male D1N Dovetail, Internal M38 x 0.5 Threads, and External SM2 Threads
- SM2A59: Male D1N Dovetail and Internal SM2 Threads
- LCPN4: Male D1N Dovetail, Internal SM2 Threads, and 60 mm Cage Compatibility
- CSA1003: Female D1N Dovetail and 60 mm Cage Compatibility
These dovetail adapters integrate the D1N dovetail on the epi-illumination arm of a Cerna microscope body with Thorlabs' SM30 (M30 x 0.5) lens tubes, SM2 (2.035"-40) lens tubes, and 30 mm and 60 mm cage systems. Additionally, the WFA4111 and SM2A59 adapters feature internal M38 x 0.5 and SM2 threads, respectively, that can directly accept one of our infinity-corrected tube lenses. We also offer the LCPN3 trinocular port adapter, designed to allow Olympus trinoculars that have a male D5Y dovetail to be used with DIY Cerna systems.
The dovetail designations are specific to Thorlabs products; see the Microscope Dovetails tab for details.
 Products Home
Products Home










































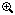 Zoom
Zoom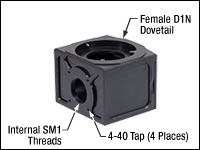








 Epi-Illumination
Epi-Illumination